Abstract
Background
RACK1 has been shown to be able to interact with some key cellular proteins involved in tumor development and progression. Our study showed that the expressions of RACK1 and CD147 are correlated with each other. The purpose of this study is to clarify the relationship between expression of RACK1 and CD147 in 180 patients with operable stage T1 human pulmonary adenocarcinoma and their clinicopathological features and prognostic significance.
Methods
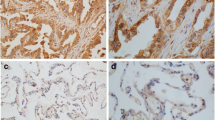
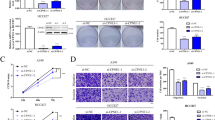
DNA transfection and RNA interference of RACK1 were conducted to produce pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell lines with differential RACK1 expression. Western blot and RT-PCR were used to quantify RACK1 and CD147 expression in protein and mRNA levels in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell lines. Immunohistochemistry, double-labeling immunofluorescence, confocal laser scanning microscopy, and Western blot were used to correlate the clinicopathological significance of RACK1 and CD147 expression in cases of stage T1 pulmonary adenocarcinoma.
Results
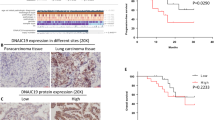
We detected high levels of RACK1 and CD147 mRNA as well as protein expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma in vitro. In pulmonary adenocarcinoma, the expression of RACK1 and CD147 were correlated both in vitro and in vivo. Our clinicopathological analysis demonstrated that RACK1 or CD147 expression correlated with higher incidence of lymph node metastasis and lower differentiation than tumors that were negative for expression of either RACK1 or CD147. The expression of RACK1 and CD147 was not associated with the patient age or gender. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that the co-overexpression of RACK1 and CD147 was an independent prognostic factor for stage T1 pulmonary adenocarcinoma (P = 0.012).
Conclusions
Tumor invasiveness is associated with expression of RACK1 and CD147 in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. The co-expression of RACK1 and CD147 could be an important prognostic biomarker for stage T1 pulmonary adenocarcinoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mochly-Rosen D, Khaner H, Lopez J. Identification of intracellular receptor proteins for activated protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:3997–4000.
Zhang W, Zong CS, Hermanto U, Lopez-Bergami P, Ronai Z, Wang LH. RACK1 recruits STAT3 specifically to insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors for activation, which is important for regulating anchorage-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:413–24.
Li S, Esterberg R, Lachance V, Ren D, Radde-Gallwitz K, Chi F, et al. Rack1 is required for Vangl2 membrane localization and planar cell polarity signaling while attenuating canonical Wnt activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:2264–9.
Wang F, Yamauchi M, Muramatsu M, Osawa T, Tsuchida R, Shibuya M. RACK1 regulates VEGF/Flt1-mediated cell migration via activation of a PI3 K/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:9097–106.
Wu Y, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zhang L, Wang D, Ren F, et al. RACK1 promotes Bax oligomerization and dissociates the interaction of Bax and Bcl-XL. Cell Signal. 2010;22:1495–501.
Kiely PA, Baillie GS, Barrett R, Buckley DA, Adams DR, Houslay MD, et al. Phosphorylation of RACK1 on tyrosine 52 by c-Abl is required for insulin-like growth factor I-mediated regulation of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:20263–74.
Wang Z, Zhang B, Jiang L, Zeng X, Chen Y, Feng X, et al. RACK1, an excellent predictor for poor clinical outcome in oral squamous carcinoma, similar to Ki67. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:490–6.
He X, Wang J, Messing EM, Wu G. Regulation of receptor for activated C kinase 1 protein by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor in IGF-I-induced renal carcinoma cell invasiveness. Oncogene. 2011;30:535–47.
Al-Reefy S, Mokbel K. The role of RACK1 as an independent prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:911.
Gabison EE, Hoang-Xuan T, Mauviel A, Menashi S. EMMPRIN/CD147, an MMP modulator in cancer, development and tissue repair. Biochimie. 2005;87:361–8.
Cao XX, Xu JD, Xu JW, Liu XL, Cheng YY, Wang WJ, et al. RACK1 promotes breast carcinoma proliferation and invasion/metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:375–86.
Dai SD, Wang Y, Zhang JY, Zhang D, Zhang PX, Jiang GY, et al. Upregulation of δ-catenin is associated with poor prognosis and enhances transcriptional activity through Kaiso in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:95–103.
Yaka R, Thornton C, Vagts AJ, Phamluong K, Bonci A, Ron D. NMDA receptor function is regulated by the inhibitory scaffolding protein, RACK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:5710–5.
Mourton T, Hellberg CB, Burden-Gulley SM, Hinman J, Rhee A, Brady-Kalnay SM. The PTPmu protein-tyrosine phosphatase binds and recruits the scaffolding protein RACK1 to cell-cell contacts. J Biol Chem. 2001;27:14896–901.
Yarwood SJ, Steele MR, Scotland G, Houslay MD, Bolger GB. The RACK1 signaling scaffold protein selectively interacts with the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D5 isoform. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:14909–17.
Saito A, Fujii G, Sato Y, Gotoh M, Sakamoto M, Toda G, et al. Detection of genes expressed in primary colon cancers by in situ hybridisation: overexpression of RACK 1. Mol Pathol. 2002;55:34–9.
Mamidipudi V, Cartwright CA. A novel pro-apoptotic function of RACK1: suppression of Src activity in the intrinsic and Akt pathways. Oncogene. 2009;28:4421–33.
Nagashio R, Sato Y, Matsumoto T, Kageyama T, Satoh Y, Shinichiro R, et al. Expression of RACK1 is a novel biomarker in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer. 2010;69:54–9.
Guo H, Li R, Zucker S, Toole BP. EMMPRIN (CD147), an inducer of matrix metalloproteinase synthesis, also binds interstitial collagenase to the tumor cell surface. Cancer Res. 2000;60:888–91.
Ishibashi Y, Matsumoto T, Niwa M, Suzuki Y, Omura N, Hanyu N, et al. CD147 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 protein expression as significant prognostic factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2004;101:1994–2000.
Reimers N, Zafrakas K, Assmann V, Egen C, Riethdorf L, Riethdorf S, et al. Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteases inducer on micrometastatic and primary mammary carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3422–8.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A, Kristensen GB, Reich R. EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20:161–9.
Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Murai Y, Cui ZG, Nomoto K, Miwa S, et al. Upregulated EMMPRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: a good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2006;95:1371–8.
Sienel W, Polzer B, Elshawi K, Lindner M, Morresi-Hauf A, Vay C, et al. Cellular localization of EMMPRIN predicts prognosis of patients with operable lung adenocarcinoma independent from MMP-2 and MMP-9. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:1130–8.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30971114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, X., Li, M., Nie, B. et al. Overexpressions of RACK1 and CD147 Associated with Poor Prognosis in Stage T1 Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 20, 1044–1052 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2377-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2377-4