Abstract
Objective
This study was designed to investigate the expression patterns of CEACAM1 and its relationship with angiogenesis in nonneoplastic and neoplastic gastric lesions.
Methods
CEACAM1 and TGF-β expression was detected by immunohistochemical staining and dual-labeling immunohistochemical staining in neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions. MVD-CD31 and MVD-CD105 were counted in CEACAM1-positive areas by dual-labeling immunohistochemistry.
Results
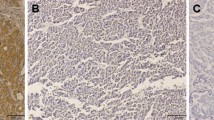
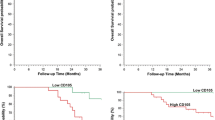
There was no expression of CEACAM1 in normal gastric mucosa. In IM and GIN, CEACAM1 was mainly expressed with membranous pattern. CEACAM1 was expressed with membranous pattern in well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, with cytoplasmic pattern in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, and with cytoplasmic and membranous pattern mixed together in intermediately adenocarcinoma. The expression patterns of CEACAM1 showed a significant difference (P < 0.05) in nonneoplastic and neoplastic lesions. Coexpression of CEACAM1 and TGF-β was elevated and significantly different from nonneoplastic to neoplastic lesions (P < 0.05). Moreover, CEACAM1 and TGF-β coexpression were related to carcinoma progression (r = 0.35; P < 0.05). MVD-CD31 and MVD-CD105 showed significant differences from nonneoplastic to neoplastic lesions (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
CEACAM1 has different expression patterns in nonneoplastic and neoplastic lesions. The coexpression of CEACAM1 and TGF-β increased from nonneoplastic to neoplastic lesions and may be related with tumor progression via promoting tumorous angiogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singer BB, Scheffrahn I, Obrink B. The tumor growth inhibiting cell adhesion molecule CEACAM1 (C-CAM) is differently expressed in proliferating and quiescent epithelial cells and regulates cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1236–44.
Nakajima A, Iijima H, Neurath MF, Nagaishi T, Nieuwenhuis EE, Raychowdhury R, Glickman J, et al. Activation-induced expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-cell adhesion molecule 1 regulates mouse T lymphocyte function. J Immunol. 2002;168:1028-35.
Chen D, Iijima H, Nagaishi T, Nakajima A, Russell S, Raychowdhury R, Morales V, et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cellular adhesion molecule 1 isoforms alternatively inhibit and costimulate human T cell function. J Immunol. 2004;172:3535–43.
Ergun S, Kilic N, Ziegeler G, Hansen A, Nollau P, Gotze J, et al. CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 1: a potent angiogenic factor and a major effector of vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol Cell. 2000;5:311–20.
Wagener C, Ergun S. Angiogenic properties of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1. Exp Cell Res. 2000;261:19–24.
Kilic N, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Wurmbach JH, Loges S, et al. Pro-angiogenic signaling by the endothelial presence of CEACAM1. J Bio Chem. 2005;280(3):2361–9.
Oliveira-Ferrer L, Tilki D, Ziegeler G, Hauschild J, Loges S, et al. Dual role of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in angiogenesis and invasion of human urinary bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8932–8.
Kammerer R, Riesenberg R, Weiler C, Lohrmann J, Achleypen J, Zimmermann W. The tumour suppressor gene CEACAM1 is completely but reversibly downregulated in renal cell carcinoma. J Pathol. 2004;204:258–67.
Laack E, Nikbakht H, Petera A, Kugler C, Jasiewicz Y, et al. Expression of CEACAM1 in adenocarcinoma of the lung: a factor of independent prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4279–84.
Kang W-Y, Chen W-T, Wu M-T. The expression of CD66a and possible roles in colorectal adenoma and adenocarcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007;22:869–74.
Muller MM, Singer BB, Klaile E, et al. Transmembrane CEACAM1 affects integrin-dependent signaling and regulates extracellular matrix protein-specific morphology and migration of endothelial cells. Blood. 2005; 105: 3925–3934.
Tilki D, Irmak S, Oliveira-Ferrer L, et al. CEA-related cell adhesion molecule-1 is involved in angiogenic switch in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:4965–74,
Gray-Owen SD, Blumberg RS. CEACAM1: contact-dependent control of immunity. Immunology. 2006;6:433–46.
Riethdorf L, Lisboa BW, Henkel U, Naumann M, Wagener C, Löning T. Differential expression of CD66a (BGP), a Cell adhesion molecule of the carcinoembryonic antigen family, in benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions of the human mammary gland. J Histochem Cytochem. 1997;45:957–64.
Volpert O, Luo W, Liu TJ, Vicky T, et al. Inhibition of prostate tumor angiogenesis by the tumor suppressor CEACAM1. J Bio Chem. 2002; 277(38): 35696–35702.
Moh MC, Shen S. The roles of cell adhesion molecules in tumor suppression and cell migration. Cell Adh Migr. 2009;3:334–6.
Song JH, Cao Z, Yoon JH, et al. Genetic alterations and expression pattern of CEACAM1 in colorectal adenomas and cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011; 17:67–74.
Nouvion AL, Oubaha M, Leblanc S, et al. CEACAM1: a key regulator of vascular permeability. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 24):4221–30.
Fonsatti E, Sigalotti L, Arslan P, Altomonte M, Maio M. Emerging role of endoglin (CD105) as a marker of angiogenesis with clinical potential in human malignancies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3(6):427–32.
Li CG, Wilson PB, Bernabeu C, Raab U, Wang JM, Kumar S. Immunodetection and characterisation of soluble CD105-TGFbeta complexes. J Immunol Method. 1998;218:85–93.
Seon BK. Expression of endoglin (CD105) in tumor blood vessels. Int J Cancer 2002;99:310–1.
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S. CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J. 2003;17:984–92.
Li C, Gardy R, Seon BK, et al. Both high intratumoral microvessel density determined using CD105 antibody and elevated plasma levels of CD105 in colorectal cancer patients correlate with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:1424–31.
Yagasaki H, Kawata N, Takimoto Y, Nemoto N. Histopathological analysis of angiogenic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2003;10:220–7.
Kumar S, Ghellal A, Li C, Byrne G, Haboubi N, Wang JM, Bundred N. Breast carcinoma: vascular density determined using CD105 antibody correlates with tumor prognosis. Cancer Res. 1999;59:856–61.
Tanaka F, Otake Y, Yanagihara K, et al. Evaluation of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: comparison between anti-CD34 antibody and anti-CD105 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3410–5.
Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA. WHO classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. IARC Press: Lyon; 2000.
Kleinerman DI, Troncoso P, Lin SH, Pisters LL, Sherwood ER, Brooks T, et al. Consistent expression of an epithelial cell adhesion molecule (c-cam) during human prostate development and loss of expression in prostate cancer: implication as a tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1215–20.
Shinozuka K, Uzawa K, Fushimi K, Yamano Y, Shiiba M, Bukawa H, et al. Downregulation of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Oncology. 2009;76:387-97.
Riethdorf L, Lisboa BW, Henkel U, Naumann M, Wagener C, Löning T. Differential expression of CEACAM1 (bgp), a cell adhesion molecule of the carcinoembryonic antigen family, in benign, premalignant and malignant lesions of the human mammary gland. J Histochem Cytochem. 1997;45:957–63.
Yamato Y, Koike T, Yoshiya K, Fukui M, Kitahara A, Toyabe S. Factors influencing long-term survival and surgical indications for pulmonary metastasectomy for metastases from colorectal cancer. Thoracic Cancer. 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1759-7714.2011.00044.x.
Ebrahimnejad A, Streichert T, Nollau P, Horst AK, Wagener C, Bamberger AM, et al. CEACAM1 enhances invasion and migration of melanocytic and melanoma cells. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:1781–7.
Liu W, Wei W, Winer D, Bamberger AM, Bamberger C, Wagener C, et al. Ceacam1 impedes thyroid cancer growth but promotes invasiveness: a putative mechanism for early metastases. Oncogene. 2007;26:2747–58.
Zhou CJ, Liu B, Zhu KX, et al. The different expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) and possible roles in gastric carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract. 2009;205(7):483–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, JQ., Yu, WH., Wang, HJ. et al. Different Expression Patterns of CEACAM1 and its Impacts on Angiogenesis in Gastric Nonneoplastic and Neoplastic Lesions. Ann Surg Oncol 19 (Suppl 3), 365–374 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1811-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1811-3