Abstract
Background
Excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1) is one of the key enzymes in DNA repair. This study was designed to investigate the correlation between ERCC1 expression and chemosensitivity to cisplatin (CDDP) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
Eighty-seven HCC samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for ERCC1 and chemosensitivity was assessed by the succinate dehydrogenase inhibition (SDI) test for four anti-cancer agents, including CDDP. The ERCC1 expression was examined in HCC cell lines. ERCC1 siRNA was transfected to PLC/RPF/5 to investigate the correlation of ERCC1 expression and CDDP sensitivity.
Results
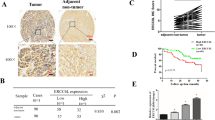
ERCC1 expression was observed in 33% of nuclei in immunohistochemical examination. Patients were divided into two groups as follows: ERCC1 high expression group (n = 43): more than 33% of the nuclei were stained; ERCC1 low expression group (n = 44): 33% or fewer of the nuclei were stained. Tumor size of low expression group was larger than that in the high expression group (p = 0.02). The succinic dehydrogenase (SD) activity only for CDDP was significantly higher in the high expression group than that in the low expression group (p = 0.02). An increased expression of ERCC1 was shown by immunohistochemical and Western blot analyses in PLC/RPF/5. ERCC1 expression was inhibited by ERCC1 siRNA transfection and the LC50 value (nM) of CDDP was reduced from 25.7 to 12.5 (p = 0.01).
Conclusions
Increased ERCC1 expression is associated with CDDP resistance in HCC specimens and cell lines. Therefore, immunohistochemical analysis for resected HCC tissues may be a useful predictor for the effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy, using CDDP.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila MA, Berasain C, Sangro B, Prieto J. New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:3866–84.
Yamashita Y, Taketomi A, Itoh S, Harimoto N, Morita K, Fukuhra T, Ueda S, Sanefuji K, Sugimachi K, Tajima T, Maehara Y. Phase I/II study of the lipiodolization using DDP-H (CDDP powder; IA-call®) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 3. [Epub ahead of print].
Kawaoka T, Aikata H, Takaki S, Katamura Y, Hiramatsu A, Waki K, Takahashi S, Hieda M, Toyota N, Ito K, Chayama K. Transarterial infusion chemotherapy using cisplatin-lipiodol suspension with or without embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2009;32:687–94.
Ando E, Tanaka M, Yamashita F, Kuromatsu R, Yutani S, Fukumori K, Sumie S, Yano Y, Okuda K, Sata M. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: analysis of 48 cases. Cancer. 2002;95(3):588–95.
Okuda K, Tanaka M, Shibata J, Ando E, Ogata T, Kinoshita H, Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Tanikawa K. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with continuous low dose administration of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil for multiple recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical treatment. Oncol Rep. 1999;6(3):587–91.
Hamabe ST, Yamasaki T, Saeki I, Harima Y, Okita K, Terai S, Sakaida I. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: is the addition of subcutaneous interferon-alpha-2b beneficial? Hepatol Res. 2009;39(3):223–30.
Park JY, Ahn SH, Yoon YJ, Kim JK, Lee HW, Lee do Y, Chon CY, Moon YM, Han KH. Repetitive short-course hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with high-dose 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2007;110(1):129–37.
De Laat WL, Appeldoorn E, Jaspers NG, Hoeijmakers JH. DNA structural elements required for ERCC1-XPF endonuclease activity. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:7835–42.
Shirota Y, Stoehlmacher J, Brabender J, Xiong YP, Uetake H, Danenberg KD, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei DD, Danenberg PV, Lenz HJ. ERCC1 and thymidylate synthase mRNA levels predict survival for colorectal cancer patients receiving combination oxaliplatin and fluorouracil chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:4298–304.
Lord RV, Brabender J, Gandara D, Alberola V, Camps C, Domine M, Cardenal F, Sanchez JM, Gumerlock PH, Taron M, Sanchez JJ, Danenberg KD, et al. Low ERCC1 expression correlates with prolonged survival after cisplatin plus gemcitabine chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:2286–91.
Zhou W, Gurubhagavatula S, Liu G, Park S, Neuberg DS, Wain JC, Lynch TJ, Su L, Christiani DC. Excision repair cross-complementation group 1 polymorphism predicts overall survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4939–43.
Simon GR, Sharma S, Cantor A, Smith P, Bepler G. ERCC1 expression is a predictor of survival in resected patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Chest. 2005;127:978–83.
Selvakumaran M, Pisarcik DA, Bao R, Yeung AT, Hamilton TC. Enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity by disturbing the nucleotide excision repair pathway in ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003;63(6):1311–6.
Gossage L, Madhusudan S. Current status of excision repair cross-complementing group 1 (ERCC1) in cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33(6):565–77.
Liver Cancer Study Group. The general rules for the clinical and pathological study of primary liver cancer. 4th ed. Tokyo: Kanehara Publications; 2000.
Wachters FM, Wong LS, Timens W, Kampinga HH, Groen HJ. ERCC1, hRad51, and BRCA1 protein expression in relation to tumour response and survival of stage III/IV NSCLC patients treated with chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2005;50:211–9.
Takenaka, T, Yoshino I, Kouso H, Ohba T, Yohena T, Osoegawa A, Shoji F, Maehara Y. Combined evaluation of Rad51 and ERCC1 expressions for sensitivity to platinum agents in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:895–900.
Takeuchi H, Baba H, Inutsuka S, Takahashi I, Kusumoto H, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K. Antitumor chemosensitivity differs between clinical sarcoma and adenocarcinoma tissues. Anticancer Res. 1994;14:169–71.
Oki E, Baba H, Tokunaga E, Nakamura T, Ueda N, Futatsugi M, Mashino K, Yamamoto M, Ikebe M, Kakeji Y, Maehara Y. AKT phosphorylation associates with LOH of PTEN and leads to chemoresistance for gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;117:376–80.
Itoh S, Taketomi A, Tanaka S, Harimoto N, Yamashita Y, Aishim S, Maeda T, Shirabe K, Shimada M, Maehara Y. Role of growth factor receptor-bound protein 7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(7):667–73.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–3.
Sijbers AM, de Laat WL, Ariza RR, Biggerstaff M, Wei YF, Moggs JG, Carter KC, Shell BK, Evans E, de Jong MC, Rademakers S, de Rooij J, et al. Xeroderma pigmentosum group F caused by a defect in a structure-specific DNA repair endonuclease. Cell. 1996;86:811–22.
Britten RA, Liu D, Tessier A, Hutchison MJ, Murray D. ERCC1 expression as a molecular marker of cisplatin resistance in human cervical tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:453–7.
Kwon HC, Roh MS, Oh SY, Kim SH, Kim MC, Kim JS, Kim HJ. Prognostic value of expression of ERCC1, thymidylate synthase, and glutathione S-transferase P1 for 5-fluorouracil/oxaliplatin chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007:18(3):504–9.
Kondo T, Kubota T, Tanimura H, Yamaue H, Akiyama S, Tanigawa N, Kitajima M, Takagi H. Cumulative results of chemosensitivity tests for antitumor agents in Japan. Japan Research Society for Appropriate Cancer Chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:2389–92.
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, Brambilla E, André F, Haddad V, Taranchon E, Filipits M, Pirker R, Popper HH, Stahel R, Sabatier L, Pignon JP, Tursz T, Le Chevalier T, Soria JC. DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(10):983–91.
Fautrel A, Andrieux L, Musso O, Boudjema K, Guillouzo A, Langouët S. Overexpression of the two nucleotide excision repair genes ERCC1 and XPC in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2005;43(2):288–93.
Andrieux LO, Fautrel A, Bessard A, Guillouzo AL, Baffet G, Sophie L. GATA-1 is essential in EGF-mediated induction of nucleotide excision repair activity and ERCC1 expression through ERK2 in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2114–23.
Tanaka S, Shimada M, Shirabe K, Maehara S, Harimoto N, Tsujita E, Sugimachi K, Maehara Y. A novel intrahepatic arterial chemotherapy after radical resection for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52(63):862–5.
Niguma T, Mimura T, Tsutui N. Adjuvant arterial infusion chemotherapy after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal thrombosis: a pilot study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2005;12:249–53.
Abe T, Goda K, Futami K, Furuichi Y. Detection of siRNA administered to cells and animals by using a fluorescence intensity distribution analysis polarization system. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37 Suppl 7:e56.
Gondi CS, Rao JS. Concepts in in vivo siRNA delivery for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2009;220(2):285–91.
Tam KH, Yang ZF, Lau CK, Lau CT, Pang RWC, Ronnie TP. Inhibition of mTOR enhances chemosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letter. 2009;273:201–9.
Wakamatsu T, Nakahashi Y, Hachimine D, Seki T, Okazaki K. The combination of glycyrrhizin and lamivudine can reverse the cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated proteins. Int J Oncol. 2007;31:1465–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, S., Shirabe, K., Morita, K. et al. Evaluation of ERCC1 Expression for Cisplatin Sensitivity in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18, 1204–1211 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1414-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1414-4