Abstract
Background
Lactate-dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) is an important isoenzyme converting pyruvate to lactate under hypoxic conditions and might play an important role in the development and progression of malignancies. However, the role of LDH-5 in gastric cancer is still unclear. In this study, we investigated the clinical significance of LDH-5 expression in gastric carcinoma.
Methods
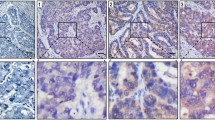
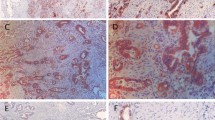
LDH-5 expression in 152 patients with different grade and stage gastric carcinoma was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. In addition, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) as a marker of tumor hypoxia, as well as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) as angiogenesis parameters were also assessed in this study. Correlations between the expression of investigated proteins and various clinicopathological factors including survival were determined.
Results
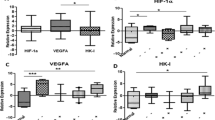
There were 94 cases (61.8%) showing high LDH-5 expression, and 95 patients (62.5%) had high HIF-1α expression. Positive correlation was found between LDH-5 expression and HIF-1α, VEGF, and COX-2. The overexpression of LDH-5 was more prevalent in advanced tumors having positive vessel invasion. Patients with overexpression of LDH-5 showed far lower disease-free (63.5% vs 82.7%) and overall (56.3% vs 78.4%) survival rates compared with patients with low LDH-5 expression. HIF-1α expression was shown to have no significance on survival. In multivariate analysis, high LDH-5 expression kept its independence as a negative prognostic indicator.
Conclusion
The results of the current study show that LDH-5 expression may be a useful prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dicken BJ, Bigam DL, Cass C, et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma: review and considerations for future directions. Ann Surg 2005; 241:27–39.
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1965; 123:309–14.
Holbrook JJ, Liljas A, Steindel SJ, et al. (1975) Lactate dehydrogenase. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes, 3rd edition, vol. XI, part A. New York: Academic Press, pp 191–2
Markert CL. Lactate dehydrogenase isozymes: dissociation and recombination of subunits. Science 1963; 140:1329–30.
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E. Lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes 1 and 5: differential expression by neoplastic and stromal cells in non-small cell lung cancer and other epithelial malignant tumors. Tumour Biol 2003; 24:199–202.
Hockel M, Vaupel P. Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biological, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93:266–76.
Semenza GL. HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 2000; 88:1474–80.
Semenza GL, Nejfelt MK, Chi SM, Antonarakis SE. Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3′ to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88:5680–4.
Semenza G. Signal transduction to hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64:993–8.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 1999; 59:5830–5.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, et al. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia inducible factors for oxygen dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999; 399:271–5.
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94:8104–9.
Semenza GL. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1999; 15:551–78.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma—2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer 1998; 1:10–24
Kolev YV, Uetake H, Iida S, Ishikawa T, Kawano T, Sugihara K. Prognostic significance of VEGF expression in correlation with COX-2, microvessel density, and clinicopathological characteristics in human gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2007; 14:2738–47.
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Kouskoukis C, Gatter KC, Harris AL Koukourakis MI. Hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha are related to vascular endothelial growth factor expression and a poorer prognosis in nodular malignant melanomas of the skin. Melanoma Res 2003; 13:493–501.
Yuce K, Baykal C, Genc C, Al A, Ahyan A. Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum and peritoneal fluid lactate dehydrogenase in epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 2001; 22:228–32.
Brizel DM, Schroeder T, Sher RL, et al. Elevated tumor lactate concentrations predict for an increased risk of metastases in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001; 51:349–53.
Taz F, Aykan F, Alici S, et al. Prognostic factors in pancreatic carcinoma: serum LDH levels predict survival in metastatic disease. Am J Clin Oncol 2001; 24:547–50.
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) overexpression in non-small-cell lung cancer tissues is linked to tumour hypoxia, angiogenic factor production and poor prognosis. Br J Cancer 2003; 89:877–85.
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Turley H, Harris AL, Koukourakis MI. Lactate dehydrogenase 5 (LDH-5) expression in endometrial cancer relates to the activated VEGF/VEGFR2(KDR) pathway and prognosis. Gynecol Oncol 2006; 103:912–18.
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Harris AL. Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in operable colorectal cancer: strong association with survival and activated vascular endothelial growth factor pathway—A report of the Tumour Angiogenesis Research Group. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24:4301–8.
Song YL, Yang GL, Dong YM. Immunohistochemical study of lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in gastric cancer. China Natl J New Gastroenterol 1995; 1:13–7.
Stubbs M, McSheehy PM, Griffiths JR, Bashford CL. Causes and consequences of tumour acidity and implications for treatment. Mol Med Today 2000; 6:15–1.
Urano N, Fujiwara Y, Doki Y, et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in gastric adenocarcinoma. Gastric Cancer 2006; 9:44–9.
Griffiths EA, Pritchard SA, Welch IM, Price PM, West CM. Is the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway important in gastric cancer? Eur J Cancer 2005; 41:2792–805.
Wang W, Davis DA, Haque M, Huang LE, Yarchoan R. Differential gene up-regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in HEK293T cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65:3299–306.
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, et al. Role of HIF-1α in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation, and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 1998; 394:485–90.
Griffiths EA, Pritchard SA, Valentine HR, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in the gastric carcinogenesis sequence and its prognostic role in gastric and gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer 2007; 96:95–103.
Lu H, Forbes RA, Verma A. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277:23111–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolev, Y., Uetake, H., Takagi, Y. et al. Lactate Dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) Expression in Human Gastric Cancer: Association with Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF-1α) Pathway, Angiogenic Factors Production and Poor Prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 2336–2344 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-9955-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-9955-5