Abstract
Background
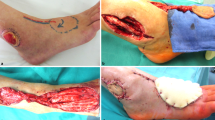
Reconstruction of foot defects following oncologic resection is a crucial element in the treatment of soft tissue malignancy of the foot.
Objective
The present study aimed to comprehensively evaluate outcomes of oncologic foot reconstruction using free perforator flaps.
Methods
Outcomes of patients with soft tissue malignancy of the foot who underwent reconstruction using a free perforator flap following ablative surgery were reviewed, and perioperative and delayed complications (secondary debulking operation and flap instability) were documented. The Foot Function Index (FFI) questionnaire was surveyed to assess functional status.
Results
Overall, 72 patients were analyzed, with a median follow-up period of 28 months. Malignant melanoma was a predominant etiology. Three kinds of perforator flaps were used, with the thoracodorsal artery perforator flap being the most common. Flaps with skin dimensions matching the defect size were inset and the thickness of the flaps was controlled with primary defatting. Flap re-exploration was conducted in 11 (15.2%) cases and total flap loss occurred in 3 (4.2%) cases. Delayed complications developed in an additional 12 cases, therefore 23 (31.9%) cases required a return to the operating room. The average FFI score was 8.86 at postoperative month 36, on average (range 11–128 months). All respondents reported being independently ambulatory and had minimal difficulty in their daily lives. Reconstruction of defects on weight-bearing regions showed a significantly higher FFI score than that on nonweight-bearing regions (mean 11.96 vs. 4.79, p = 0.029), although the scores remained very low for both instances.
Conclusions
Oncologic foot defects can be reliably reconstructed using well-contoured free perforator flaps with minimal functional morbidity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bos GD, Esther RJ, Woll TS. Foot tumors: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10(4):259–70.
Chou LB, Ho YY, Malawer MM. Tumors of the foot and ankle: experience with 153 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(9):836–41.
Ruggieri P, Angelini A, Jorge FD, Maraldi M, Giannini S. Review of foot tumors seen in a university tumor institute. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53(3):282–5.
Tseng JF, Tanabe KK, Gadd MA, et al. Surgical management of primary cutaneous melanomas of the hands and feet. Ann Surg. 1997;225(5):544–50; discussion 550-543.
Tajsic N, Winkel R, Hoffmann R, Husum H. Sural perforator flap for reconstructive surgery in the lower leg and the foot: a clinical study of 86 patients with post-traumatic osteomyelitis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62(12):1701–08.
Nenad T, Reiner W, Michael S, Reinhard H, Hans H. Saphenous perforator flap for reconstructive surgery in the lower leg and the foot: a clinical study of 50 patients with posttraumatic osteomyelitis. J Trauma. 2010;68(5):1200–07.
Hong JP. Reconstruction of the diabetic foot using the anterolateral thigh perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(5):1599–608.
Jeon BJ, Lee KT, Lim SY, et al. Plantar reconstruction with free thoracodorsal artery perforator flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(3):406–13.
Madeley NJ, Wing KJ, Topliss C, Penner MJ, Glazebrook MA, Younger AS. Responsiveness and validity of the SF-36, Ankle Osteoarthritis Scale, AOFAS Ankle Hindfoot Score, and Foot Function Index in end stage ankle arthritis. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(1):57–63.
Pinsker E, Inrig T, Daniels TR, Warmington K, Beaton DE. Reliability and validity of 6 measures of pain, function, and disability for ankle arthroplasty and arthrodesis. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36(6):617–25.
Agel J, Beskin JL, Brage M, et al. Reliability of the Foot Function Index: a report of the AOFAS Outcomes Committee. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(11):962–7.
van Doeselaar DJ, Heesterbeek PJ, Louwerens JW, Swierstra BA. Foot function after fusion of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Foot Ankle Int. 2010;31(8):670–5.
Dux K, Smith N, Rottier FJ. Outcome after metatarsal osteotomy for hallux valgus: a study of postoperative foot function using revised foot function index short form. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;52(4):422–5.
Hwang JH, Mun GH. An evolution of communication in postoperative free flap monitoring: using a smartphone and mobile messenger application. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130(1):125–9.
Evans GR, Friedman J, Shenaq J, Mosser S. Plantar flap reconstruction for acral lentiginous melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 1997;4(7):575–8.
Langstein HN, Chang DW, Miller MJ, et al. Limb salvage for soft-tissue malignancies of the foot: an evaluation of free-tissue transfer. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(1):152–159.
Maker AV, Iteld L. Closure of melanoma defects on the sole of the foot using glaborous skin: the end of the flap? Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(12):4081–2.
Yiacoumettis A, Mallouris A. Reconstructive options for defects after melanoma excision in the foot and ankle region. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50(4):498–503.
Liu JF, Zhao LR, Lu LJ, et al. Limb salvage surgery following resection of a melanoma: Foot and ankle reconstruction using cutaneous flaps. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(5):1966–72.
Roblin P, Healy CM. Heel reconstruction with a medial plantar V-Y flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(3):927–32.
Mahmoud WH. Foot and ankle reconstruction using the distally based sural artery flap versus the medial plantar flap: a comparative study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017. Doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2017.01.019.
Jung JY, Roh HJ, Lee SH, Nam K, Chung KY. Comparison of secondary intention healing and full-thickness skin graft after excision of acral lentiginous melanoma on foot. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37(9):1245–51.
Oh SJ, Moon M, Cha J, Koh SH, Chung CH. Weight-bearing plantar reconstruction using versatile medial plantar sensate flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(2):248–54.
Lu S, Chai Y, Wang C, Wen G. Complex heel reconstruction with a sural fasciomyocutaneous perforator flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2014;30(2):83–90.
Sureda N, Phan A, Poulalhon N, Balme B, Dalle S, Thomas L. Conservative surgical management of subungual (matrix derived) melanoma: report of seven cases and literature review. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165(4):852–58.
Moehrle M, Metzger S, Schippert W, Garbe C, Rassner G, Breuninger H. “Functional” surgery in subungual melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29(4):366–74.
Lee KT, Kim EJ, Lee DY, Kim JH, Jang KT, Mun GH. Surgical excision margin for primary acral melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2016;114(8):933–39.
Oh TS, Lee HS, Hong JP. Diabetic foot reconstruction using free flaps increases 5-year-survival rate. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(2):243–50.
Lin C-H, Mardini S, Wei F-C, Lin Y-T, Chen C-T. Free flap reconstruction of foot and ankle defects in pediatric patients: long-term outcome in 91 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(7):2478–87.
Hollenbeck ST, Woo S, Komatsu I, Erdmann D, Zenn MR, Levin LS. Longitudinal outcomes and application of the subunit principle to 165 foot and ankle free tissue transfers. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(3):924–34.
May JW Jr, Rohrich RJ. Foot reconstruction using free microvascular muscle flaps with skin grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 1986;13(4):681–89.
Kuran I, Turgut G, Bas L, Ozkan T, Bayri O, Gulgonen A. Comparison between sensitive and nonsensitive free flaps in reconstruction of the heel and plantar area. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105(2):574–80.
Santanelli F, Tenna S, Pace A, Scuderi N. Free flap reconstruction of the sole of the foot with or without sensory nerve coaptation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2314–22; discussion 2323-2314.
Morrison WA, Crabb DM, O’Brien BM, Jenkins A. The instep of the foot as a fasciocutaneous island and as a free flap for heel defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983;72(1):56–65.
Shaw WW, Hidalgo DA. Anatomic basis of plantar flap design: clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;78(5):637–49.
Narushima M, Iida T, Kaji N, et al. Superficial circumflex iliac artery pure skin perforator-based superthin flap for hand and finger reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(6):827–34.
Hsu WM, Chao WN, Yang C, et al. Evolution of the free groin flap: the superficial circumflex iliac artery perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(5):1491–8.
Disclosure
None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KT., Park, SJ. & Mun, GH. Reconstruction Outcomes of Oncologic Foot Defect Using Well-Contoured Free Perforator Flaps. Ann Surg Oncol 24, 2404–2412 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-5876-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-5876-5