Abstract
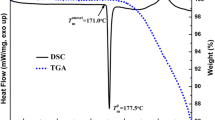
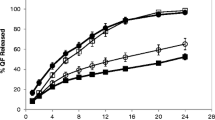
The objective of this study is to investigate the dose-response relationship between various concentrations of permeation enhancers (PEs) and their ability to enhance drug release from a polymer matrix, utilizing an innovative parameter known as release enhancement efficiency (K). Additionally, the molecular mechanism underlying dynamic enhancement was also examined. Isopropyl myristate (IPM) was used as model enhancer and zolmitriptan (ZOL) was used as model drug to investigate dose-effect relationship in pressure sensitive adhesives (PSA). The release behavior of the PEs was determined by LC-MS/MS and verified by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The enhancing effect of the PE on ZOL release was evaluated through in vitro release experiments and further validated by pharmacokinetics study. And the molecular mechanism was characterized with thermal analysis (DSC), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and molecular dynamics simulation. K was 0.156, 0.286 and 0.279 at 3%, 6% and 9% IPM concentrations, indicating that the enhancement efficiency reached the maximum when the 6% IPM was applied. According to the mechanism research results, the fluidity of PSA increased linearly with the increase of IPM concentrations, but the interaction between IPM and ZOL reached its strongest point at 6%. In summary, the increase of K value (from 0 to 6% IPM content) was caused by the synergy of increased mobility of PSA and interaction (dipole-dipole and hydrogen-bond) among three components, and when the above two actions were in antagonistic, K no longer increased (6–9% IPM content).
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PEs:
-
Permeation enhancers
- K :
-
Release enhancement efficiency
- IPM:
-
Isopropyl myristate
- ZOL:
-
Zolmitriptan
- PSA:
-
Pressure sensitive adhesive
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamic
References
Chen W, Li H, Shi D, Liu Z, Yuan W. Microneedles as a delivery system for gene therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:137.
Wu HW, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang L, Yuan W, Zheng JW, Su LX, Fan XD. Topical application of 0.5% timolol maleate hydrogel for the treatment of superficial infantile hemangioma. Front. Oncol. 2017;7:137.
Alfrd MGA, Tagumirwa MC. Asiatic acid-pectin hydrogel matrix patch transdermal delivery system influences parasitaemia suppression and inflammation reduction in P berghei murine malaria infected Sprague-Dawley rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2016;9:1172–80.
Phatale V, Vaiphei KK, Jha S, Patil D, Agrawal M, Alexander A. Overcoming skin barriers through advanced transdermal drug delivery approaches. J Control Release. 2022;351:361–80.
Kováčik A, Kopečná M, Vávrová K. Permeation enhancers in transdermal drug delivery: benefits and limitations. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020;17:145–55.
Maurya A, Rangappa S, Bae J, Dhawan T, Ajjarapu SS, Murthy SN. Evaluation of soluble fentanyl microneedles for loco-regional anti-nociceptive activity. Int J Pharm. 2019;564:485–91.
Haque T, Talukder MMU. Chemical enhancer: a simplistic way to modulate barrier function of the stratum corneum. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018;8:169–79.
Ibrahim SA, Li SK. Effects of chemical enhancers on human epidermal membrane: structure-enhancement relationship based on maximum enhancement (E(max)). J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:926–44.
Wang Z, Xue Y, Zhu Z, Hu Y, Zeng Q, Wu Y, Wang Y, Shen C, Jiang C, Liu L, Zhu H, Liu Q. Quantitative structure-activity relationship of enhancers of Licochalcone A and Glabridin release and permeation enhancement from carbomer hydrogel. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:262.
Ruan S, Wang Z, Xiang S, et al. Mechanisms of white mustard seed (Sinapis alba L.) volatile oils as transdermal penetration enhancers. Fitoterapia. 2019;138:104195.
Patel NA, Patel NJ, Patel RP. Design and evaluation of transdermal drug delivery system for curcumin as an anti-inflammatory drug. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009;35:234–42.
Liu C, Guan Y, Tian Q, Shi X, Fang L. Transdermal enhancement strategy of ketoprofen and teriflunomide: the effect of enhanced drug-drug intermolecular interaction by permeation enhancer on drug release of compound transdermal patch. Int J Pharm. 2019;572:118800.
Xu W, Liu C, Zhang Y, Quan P, Yang D, Fang L. An investigation on the effect of drug physicochemical properties on the enhancement strength of enhancer: the role of drug-skin-enhancer interactions. Int J Pharm. 2021;607:120945.
Kaushik D, Batheja P, Kilfoyle B, Rai V, Michniak-Kohn B. Percutaneous permeation modifiers: enhancement versus retardation. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008;5:517–29.
Ibrahim SA, Li SK. Efficiency of fatty acids as chemical penetration enhancers: mechanisms and structure enhancement relationship. Pharm Res. 2010;27:115–25.
Romero EL, Morilla MJ. Highly deformable and highly fluid vesicles as potential drug delivery systems: theoretical and practical considerations. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:3171–86.
Shen M, Liu C, Wan X, Farah N, Fang L. Development of a daphnetin transdermal patch using chemical enhancer strategy: insights of the enhancement effect of Transcutol P and the assessment of pharmacodynamics. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44:1642–9.
Song W, Quan P, Li S, Liu C, Lv S, Zhao Y, Fang L. Probing the role of chemical enhancers in facilitating drug release from patches: mechanistic insights based on FT-IR spectroscopy, molecular modeling and thermal analysis. J Control Release. 2016;227:13–22.
Budd PM, Mckeown NB, Fritsch D. Free volume and intrinsic microporosity in polymers. J. Mater Chem. 2005;15(20):1977–86.
Li N, Quan P, Wan X, Liu C, Liu X, Fang L. Mechanistic insights of the enhancement effect of sorbitan monooleate on olanzapine transdermal patch both in release and percutaneous absorption processes. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;107:138–47.
Wang W, Liu C, Luo Z, Wan X, Fang L. Investigation of molecular mobility of pressure-sensitive-adhesive in oxybutynin patch in vitro and in vivo: effect of sorbitan monooleate on drug release and patch mechanical property. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;122:116–24.
Arun G, Shweta P, Upendra KJ. Formulation and evaluation of ternary solid dispersion of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012;4:360–5.
Sarode AL, Sandhu H, Shah N, Malick W, Zia H. Hot melt extrusion (HME) for amorphous solid dispersions: predictive tools for processing and impact of drug-polymer interactions on supersaturation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;48:371–84.
Xiang TX, Anderson BD. Effects of molecular interactions on miscibility and mobility of ibuprofen in amorphous solid dispersions with various polymers. J Pharm Sci. 2019;108:178–86.
Liu C, Fang L. Drug in adhesive patch of zolmitriptan: formulation and in vitro/in vivo correlation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015;16:1245-1253.
Luo Z, Liu C, Quan P, Zhang Y, Fang L. Effect of chemical penetration enhancer-adhesive interaction on drug release from transdermal patch: mechanism study based on FT-IR spectroscopy, 13C NMR spectroscopy, and molecular simulation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;22:198.
Shteinikov VY, Barygin OI, Gmiro VE, Tikhonov DB. Multiple modes of action of hydrophobic amines and their guanidine analogues on ASIC1a. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;844:183–94.
Evlanenkov KK, Komarova MS, Dron MY, Nikolaev MV, Zhukovskaya ON, Gurova NA, Tikhonov DB. Derivatives of 2-aminobenzimidazole potentiate ASIC open state with slow kinetics of activation and desensitization. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1018551.
Al Sulaiman D, Chang JYH, Bennett NR, et al. Hydrogel-coated microneedle arrays for minimally invasive sampling and sensing of specific circulating nucleic acids from skin interstitial fluid. ACS Nano. 2019;13:9620–8.
Bhujbal SS, Hadawale SS, Kulkarni PA, Bidkar JS, Thatte VA, Providencia CA, Yeola RR. A novel herbal formulation in the management of diabetes. Int J Pharm Investig. 2011;1:222–6.
Srinivasu MK, Rao BM, Sridhar G, Kumar PR, Chandrasekhar KB, Islam A. A validated chiral LC method for the determination of zolmitriptan and its potential impurities. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005;37:453–60.
Chen J, Jiang XG, Jiang WM, Mei N, Gao XL, Zhang QZ. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of zolmitriptan in human plasma using fluorescence detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2004;35:639–45.
Zhang ZJ, Osmałek T, Michniak-Kohn B. Deformable liposomal hydrogel for dermal and transdermal delivery of Meloxicam. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9319–35.
Dai X, Gu Y, Guo J, Huang L, Cheng G, Peng D, Hao H. Clinical breakpoint of apramycin to swine Salmonella and its effect on Ileum Flora. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1424.
Yang D, Liu C, Quan P, Fang L. A systematic approach to determination of permeation enhancer action efficacy and sites: molecular mechanism investigated by quantitative structure-activity relationship. J Control Release. 2020;322:1–12.
Lv C, Wang Z, Wang P, Tang X. Photodegradable polyesters for triggered release. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:16387–99.
Youssouf L, Bhaw-Luximon A, Diotel N, Catan A, Giraud P, Gimié F, Koshel D, Casale S, Bénard S, Meneyrol V, Lallemand L, Meilhac O, Lefebvre D'Hellencourt C, Jhurry D, Couprie J. Enhanced effects of curcumin encapsulated in polycaprolactone-grafted oligocarrageenan nanomicelles, a novel nanoparticle drug delivery system. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;217:35–45.
Barth JH, Field HP, Yasmin E, Balen AH. Defining hyperandrogenism in polycystic ovary syndrome: measurement of testosterone and androstenedione by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and analysis by receiver operator characteristic plots. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010;162:611–5.
Dei Cas M, Zulueta A, Mingione A, Caretti A, Ghidoni R, Signorelli P, Paroni R. An innovative lipidomic workflow to investigate the lipid profile in a cystic fibrosis cell line. Cells. 2020;9:1197.
Chen J, Jiang XG, Jiang WM, Mei N, Gao XL, Zhang QZ. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of zolmitriptan in human plasma using fluorescence detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2004;35:639–45.
Ma Y, Zhu J, He H, Yuan P, Shen W, Liu D. Infrared investigation of organo-montmorillonites prepared from different surfactants. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2010;76(2):122–9.
Plazzer MB, Henry DJ, Yiapanis G, Yarovsky I. Comparative study of commonly used molecular dynamics force fields for modeling organic monolayers on water. J Phys Chem B. 2011;115:3964–71.
Kowsari MH, Alavi S, Ashrafizaadeh M, Najafi B. Molecular dynamics simulation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. I. Dynamics and diffusion coefficient. J Chem Phys. 2008;129(22):224508.
Siepmann J, Siepmann F. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2008;364(2):328–43.
Guy RH, Hadgraft J. Rate control in transdermal drug delivery? Int. J. Pharm. 1992;82:R1–6.
Drogoń A, Skotnicki M, Skotnicka A, Pyda M. Physical ageing of amorphous indapamide characterised by differential scanning calorimetry. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(9):800.
Jeong YI, Kim DH, Chung CW, Yoo JJ, Choi KH, Kim CH, Ha SH, Kang DH. Doxorubicin-incorporated polymeric micelles composed of dextran-b-poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1415–27.
Wang Y, Snee RD, Keyvan G, Muzzio FJ. Statistical comparison of dissolution profiles. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42:796–807.
Zhang H, Du X, Tang Y, Lu X, Zhou L, Zheng C, Lin H, Tao S. Introducing trifluoromethyl to strengthen hydrogen bond for high efficiency organic solar cells. Front Chem. 2020 Mar;24(8):190.
Li C, Stracha A. Cohesive energy density and solubility parameter evolution during the curing of thermoset. Polymer. 2018;135:162–70.
Lu Y, Shu Y, Liu N, Lu X, Xu M. Molecular dynamics simulations on ε-CL-20-based PBXs with added GAP and its derivative polymers. RSC Adv. 2018;8:4955–62.
Bae JH, Won JC, Lim WB, Kim BJ, Lee JH, Min JG, Seo MJ, Mo YH, Huh PH. Tacky-free polyurethanes pressure-sensitive adhesives by molecular-weight and HDI trimer design. Materials (Basel). 2021;14:2164.
Wolff HM, Irsan DK. Investigations on the viscoelastic performance of pressure sensitive adhesives in drug-in-adhesive type transdermal films. Pharm Res. 2014;31:2186–202.
Yasunori M, Takemasa K, Kenji S. Diffusion of drugs in acrylic-type pressure-sensitive adhesive matrix. II. Influence of interaction. J. Control. Release. 1992;18:113–21.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau, The Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research Jointly Funded by Municipality and University (Hospital) (Fund No. 2023A03J0345).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiuheng Ruan: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. Sida Liao: Writing original draft, Formal analysis, Validation. Jinye Tang: Project administration. Liang Fang: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1300 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, J., Liao, S., Tang, J. et al. Evaluation of Dose-Response Relationship of Permeation Enhancer Isopropyl Myristate Release on Drug Release: Release Enhancement Efficiency and Molecular Mechanism. AAPS PharmSciTech 25, 1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-023-02713-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-023-02713-6