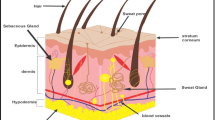
Abstract
Vesicular drug delivery systems have revolutionized the pharmaceutical field, offering a promising path for achieving targeted and sustained drug delivery. The oral, transdermal, and ocular routes of administration offer optimal ease in attaining desired therapeutic outcomes. However, conventional treatment strategies are all plagued with several challenges, such as poor skin permeability, ocular barriers, and gastrointestinal (GIT) degradation leading to vesicular disruption with the release of the encapsulated drug before reaching the targeted site of action. In recent years, bilosomes-stabilized nanovesicles containing bile salts have received considerable attention due to their versatility and adaptability for diverse applications. These bilayered vesicles enhance the solubility of lipophilic drugs and improve formulation stability in the gastrointestinal tract. They exhibit ultra-deformable properties, improving stratum corneum permeability, making them ideal candidates for oral and transdermal drug delivery. In addition, bilosomes find utility in topical drug delivery, making them applicable for ocular administration. Over the past decade, extensive research has highlighted bilosomes’ potential as superior vesicular carriers surpassing liposomes and niosomes. Advances in this field have led to the development of modified bilosomes, such as probilosomes and surface-modified bilosomes, further enhancing their capabilities and therapeutic potential. Thus, the present review provides a comprehensive summary of bilosomes, modified bilosomes, surface modifications with their mechanism of action, formulation components, preparation methods, patents, and a wide array of recent pharmaceutical applications in oral, transdermal, and ocular drug delivery. The enhanced properties of bilosomes offer promising prospects for targeted and effective drug delivery, providing potential solutions for addressing various therapeutic challenges.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miki H, Tomohiro A, Naato O, Yoshihiko A, Minoru T, Nobuyuki E. Liposomes and nanotechnology in drug development: focus on neurological targets. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:951–60.
Buchiraju R, Nama S, Sakala B, Chandu BR, Kommu A, Chebrolu JKB, et al. Vesicular drug delivery system - an over view. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2013;4:462–74.
Jain S, Jain V, Mahajan SC. Lipid based vesicular drug delivery systems. Adv Pharm. 2014;2014:1–12. http://www.hindawi.com/archive/2014/574673/.
Ntimenou V, Fahr A, Antimisiaris SG. Elastic vesicles for transdermal drug delivery of hydrophilic drugs: a comparison of important physicochemical characteristics of different vesicle types. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2012;8:613–23.
Witika BA, Mweetwa LL, Tshiamo KO, Edler K, Matafwali SK, Ntemi PV, et al. Vesicular drug delivery for the treatment of topical disorders: current and future perspectives. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021;73:1427–41.
Masjedi M, Montahaei T. An illustrated review on nonionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes) as an approach in modern drug delivery: fabrication, characterization, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol [Internet]. 2021;61:102234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102234.
Waglewska E, Pucek-kaczmarek A, Bazylinska U. Novel surface-modified bilosomes as functional and biocompatible nanocarriers of hybrid compounds. Nanomaterials. 2020;10:1–14.
Aburahma MH. Bile salts-containing vesicles: promising pharmaceutical carriers for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs and peptide/protein-based therapeutics or vaccines. Drug Deliv. 2016;23:1847–67.
Morilla MJ, Romero EL. Ultradeformable phospholipid vesicles as a drug delivery system : a review. Res Reports Transdermal Drug Deliv. 2015;4:55–69.
Saifi Z, Md R, Mir SR, Amin S. Bilosomes nanocarriers for improved oral bioavailability of acyclovir: a complete characterization through in vitro, ex-vivo and in vivo assessment. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020;57:101634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101634.
Abdellatif MM, Khalil IA, Khalil AF (2017) Sertaconazole nitrate loaded nanovesicular systems for targeting skin fungal infection : in-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.029.
D’Souza AA, Devarajan PV. Asialoglycoprotein receptor mediated hepatocyte targeting - strategies and applications. J Control Release. 2015;203:126–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.022.
Thadanki M, Babu AK. Review on Ethosomes : a novel approach of Liposomes. Int J Pharm Life Sci. 2015;6:4171–6.
Amnuaikit T, Limsuwan T, Khongkow P. Vesicular carriers containing phenylethyl resorcinol for topical delivery system; liposomes, transfersomes and invasomes. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2018;13:472–84.
Conacher M, Alexander J, Brewer JM. Oral immunisation with peptide and protein antigens by formulation in lipid vesicles incorporating bile salts (bilosomes). Vaccine. 2001;19:2965–74.
Niu M, Tan Y, Guan P, Hovgaard L, Lu Y, Qi J, et al. Enhanced oral absorption of insulin-loaded liposomes containing bile salts: a mechanistic study. Int J Pharm. 2014;460:119–30.
Chen Y, Lu Y, Chen J, Lai J, Sun J, Hu F, et al. Enhanced bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug fenofibrate by using liposomes containing a bile salt. Int J Pharm. 2009;376:153–60.
Palekar-Shanbhag P, Lande S, Chandra R, Rane D. Bilosomes: superior vesicular carriers. Curr Drug ther. 2019;15:312–20.
Shukla A, Mishra V, Kesharwani P. Bilosomes in the context of oral immunization: development, challenges and opportunities. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21:888–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.03.013.
Rajput T, Chauhan MK. Bilosome: a bile salt based novel carrier system gaining interest in pharmaceutical research. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2017;7:4–16.
Elnaggar YSR. Multifaceted applications of bile salts in pharmacy: an emphasis on nanomedicine. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:3955–71.
Abdel-moneum R, Abdel-Rashid RS. Bile salt stabilized nanovesicles as a promising drug delivery technology: a general overview and future perspectives. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023;79:104057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.104057.
Haritha P, Lakshmi P. Probilosomes: a novel bile salt containing nanocarrier for enhancing oral bioavailability. Int J Pharm Investig. 2020;10:49–53.
Zafar A, Alruwaili NK, Imam SS, HadalAlotaibi N, Alharbi KS, Afzal M, et al. Bioactive Apigenin loaded oral nano bilosomes: formulation optimization to preclinical assessment. Saudi Pharm J. 2021;29:269–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2021.02.003.
Faustino C, Serafim C, Rijo P, Reis CP. Bile acids and bile acid derivatives: use in drug delivery systems and as therapeutic agents. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13:1133–48.
Ahad A, Raish M, Ahmad A, Al-Jenoobi FI, Al-Mohizea AM. Eprosartan mesylate loaded bilosomes as potential nano-carriers against diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;111:409–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.10.012.
Aziz DE, Abdelbary AA, Elassasy AI. Investigating superiority of novel bilosomes over niosomes in the transdermal delivery of diacerein: in vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo skin deposition study. J Liposome Res. 2019;29:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2018.1430831.
Joseph Naguib M, Moustafa Kamel A, ThabetNegmeldin A, Elshafeey AH, Elsayed I. Molecular docking and statistical optimization of taurocholate-stabilized galactose anchored bilosomes for the enhancement of sofosbuvir absorption and hepatic relative targeting efficiency. Drug Deliv. 2020;27:996–1009. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2020.1787557.
Matloub AA, Salama AH, Aglan HA, AbouSamra MM, ElSouda SSM, Ahmed HH. Exploiting bilosomes for delivering bioactive polysaccharide isolated from Enteromorpha intestinalis for hacking hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44:523–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2017.1402922.
Mohsen AM, Asfour MH, Salama AAA. Improved hepatoprotective activity of silymarin via encapsulation in the novel vesicular nanosystem bilosomes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017;43:2043–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2017.1361968.
Elnaggar YSR, Omran S, Hazzah HA, Abdallah OY. Anionic versus cationic bilosomes as oral nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of the hydrophilic drug risedronate. Int J Pharm. 2019;564:410–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.04.069.
Parashar P, Rana P, Dwivedi M, Saraf SA. Dextrose modified bilosomes for peroral delivery: improved therapeutic potential and stability of silymarin in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic carcinoma in rats. J Liposome Res. 2019;29:251–63.
Islam N, Zahoor AF, Syed HK, Iqbal MS, Khan IU, Abbas G, et al. Improvement of solubility and dissolution of ebastine by fabricating phosphatidylcholine/ bile salt bilosomes. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020;33:2301–6.
Kumar GP, Rajeshwarrao P. Nonionic surfactant vesicular systems for effective drug delivery — an overview. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2011;1:208–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2011.09.002.
Sahoo RK, Biswas N, Guha A, Sahoo N, Kuotsu K. Nonionic surfactant vesicles in ocular delivery: innovative approaches and perspectives. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:1–12.
Jiao J. Polyoxyethylated nonionic surfactants and their applications in topical ocular drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1663–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.002.
Li J, Wang X, Zhang T, Wang C, Huang Z, Luo X, et al. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2015;10:81–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.09.004.
Yang H, Liu Z, Song Y, Hu C. Hyaluronic acid-functionalized bilosomes for targeted delivery of tripterine to inflamed area with enhancive therapy on arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2019;26:820–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2019.1636423.
Singh P, Prabakaran D, Jain S, Mishra V, Jaganathan KS, Vyas SP. Cholera toxin B subunit conjugated bile salt stabilized vesicles (bilosomes) for oral immunization. Int J Pharm. 2004;278:379–90.
D’souza GGM, Zhang H. Liposomes methods and protocols. Biol: Methods Mol; 2023.
Ganesan P, Karthivashan G, Park SY, Kim J, Choi DK. Microfluidization trends in the development of nanodelivery systems and applications in chronic disease treatments. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:6109–21.
Chen Y, Chen J, Cheng Y, Luo L, Zheng P, Tong Y, et al. A lyophilized sterically stabilized liposome-containing docetaxel: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Liposome Res. 2017;27:64–73.
Ertekin Z, Bayindir Z, Yuksel N. Stability studies on piroxicam encapsulated niosomes. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12:192–9.
Jin Y, Wen J, Garg S, Liu D, Zhou Y, Teng L, et al. Development of a novel niosomal system for oral delivery of Ginkgo biloba extract. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:421–30.
Ismail A, Teiama M, Magdy B, Sakran W. Development of a novel bilosomal system for improved oral bioavailability of sertraline hydrochloride : formulation design, in vitro characterization, and ex vivo and in vivo studies. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022;23:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02339-0.
Mosallam S, Sheta NM, Elshafeey AH, Abdelbary AA. Fabrication of highly deformable bilosomes for enhancing the topical delivery of terconazole: in vitro characterization, microbiological evaluation, and in vivo skin deposition study. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;22:1–12.
D’Elia RV, Woods S, Butcher W, McGahon J, Khadke S, Perrie Y, et al. Exploitation of the bilosome platform technology to formulate antibiotics and enhance efficacy of melioidosis treatments. J Control Release. 2019;298:202–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.02.002.
Salem HF, Nafady MM, Ali AA, Khalil NM, Elsisi AA. Evaluation of metformin hydrochloride tailoring bilosomes as an effective transdermal nanocarrier. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1185–201.
Seleci DA, Maurer V, Stahl F, Scheper T, Garnweitner G. Rapid microfluidic preparation of niosomes for targeted drug delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1–12.
Obeid MA, Elburi A, Young LC, Mullen AB, Tate RJ, Ferro VA. Formulation of nonionic surfactant vesicles (NISV) prepared by microfluidics for therapeutic delivery of siRNA into cancer cells. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:2450–8.
Obeid MA, Khadra I, Mullen AB, Tate RJ, Ferro VA. The effects of hydration media on the characteristics of non-ionic surfactant vesicles (NISV) prepared by microfluidics. Int J Pharm. 2017;516:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.015.
Vemuri S, Rhodes CT. Preparation and characterization of liposomes as therapeutic delivery systems: a review. Pharm Acta Helv. 1995;70:95–111.
Castañeda-Reyes ED, Perea-Flores M de J, Davila-Ortiz G, Lee Y, de Mejia EG (2020) Development, characterization and use of liposomes as amphipathic transporters of bioactive compounds for melanoma treatment and reduction of skin inflammation: a review. Int J Nanomedicine 15:7627–50.
Teaima MH, Alsofany JM, El-Nabarawi MA, Nanogel B, Design F, Evaluation I (2022) Clove oil endorsed transdermal flux of dronedarone hydrochloride loaded bilosomal nanogel: factorial design, in vitro evaluation and ex vivo permeation. AAPS PharmSciTech 23. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02337-2
Abdelbary AA, Abd-Elsalam WH, Al-mahallawi AM. Fabrication of novel ultradeformable bilosomes for enhanced ocular delivery of terconazole: in vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo safety assessment. Int J Pharm. 2016;513:688–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.006.
Khalil RM, Abdelbary A, Kocova El-Arini S, Basha M, El-Hashemy HA. Evaluation of bilosomes as nanocarriers for transdermal delivery of tizanidine hydrochloride: in vitro and ex vivo optimization. J Liposome Res. 2019;29:171–82.
Ammar HO, Mohamed MI, Tadros MI, Fouly AA. Transdermal Delivery of Ondansetron Hydrochloride via Bilosomal Systems. In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Characterization Studies. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19:2276–87.
Albash R, Refai H, Abdelbary AA. Tailoring of PEGylated bilosomes for promoting the transdermal delivery of olmesartan medoxomil : in-vitro characterization, ex-vivo permeation and in-vivo assessment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:6555–74.
Janga KY, Tatke A, Balguri SP, Surya P, Ibrahim MM, Maria DN et al (2018) Ion-sensitive in situ hydrogels of natamycin bilosomes for enhanced and prolonged ocular pharmacotherapy : in vitro permeability, cytotoxicity and in vivo evaluation. Artif Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1443117
Bashyal S, Seo JE, Keum T, Noh G, Choi YW, Lee S. Facilitated permeation of insulin across TR146 cells by cholic acid derivatives-modified elastic bilosomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:5173–86.
El Menshawe SF, Aboud HM, Elkomy MH, Kharshoum RM, Abdeltwab AM. A novel nanogel loaded with chitosan decorated bilosomes for transdermal delivery of terbutaline sulfate: artificial neural network optimization, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020;10:471–85.
El-Nabarawi M, Nafady M, Elmenshawe S, Elkarmalawy M, Teaima M. Liver targeting of daclatasvir via tailoring sterically stabilized bilosomes: Fabrication, comparative in vitro/in vivo appraisal and biodistribution studies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:6413–26.
Hu S, Niu M, Hu F, Lu Y, Qi J, Yin Z, et al. Integrity and stability of oral liposomes containing bile salts studied in simulated and ex vivo gastrointestinal media. Int J Pharm. 2013;441:693–700.
Ren Y, Wu W, Zhang X. The feasibility of oral targeted drug delivery: gut immune to particulates? Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:2545–58.
Pridgen EM, Alexis F, Farokhzad OC. Polymeric nanoparticle drug delivery technologies for oral delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12:1459–73.
Dawson PA, Lan T, Rao A. Thematic review series: Bile acids. Bile acid transporters J Lipid Res. 2009;50:2340–57.
Moghimipour E, Ameri A, Handali S. Absorption-enhancing effects of bile salts. Molecules. 2015;20:14451–73.
Chen Y, Jiang Z, Xu J, Zhang J, Sun R, Zhou J et al (2021) Improving the ameliorative effects of berberine and curcumin combination via dextran ‑ coated bilosomes on non ‑ alcohol fatty liver disease in mice. J Nanobiotechnology 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00979-1.
Jepson MA, Clark MA, Hirst BH. M cell targeting by lectins: a strategy for mucosal vaccination and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:511–25.
Aramaki Y, Tomizawa H, Hara T, Yachi K, Kikuchi H, Tsuchiya S. Stability of liposomes in vitro and their uptake by Rat Peyer’s Patches following oral administration. Pharm Res. 1993;10:1228–31.
Khafagy ES, Almutairy BK, Abu Lila AS. Tailoring of novel bile salt stabilized vesicles for enhanced transdermal delivery of simvastatin: a new therapeutic approach against inflammation. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15:1–18.
Imam SS, Alshehri S, Altamimi MA, Raed Khalid Hassan Almalki AH, Bukhari SI, Mahdi WA et al. Formulation of chitosan-coated apigenin bilosomes: in vitro characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity assessment. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14:1–15.
Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Hamblin Michael R. Chitin and chitosan: production and application of versatile biomedical nanomaterials Daniel. Int J Adv Res. 2016;4:411–27.
Cuomo F, Cofelice M, Venditti F, Ceglie A, Miguel M, Lindman B, et al. In-vitro digestion of curcumin loaded chitosan-coated liposomes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;168:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.11.047.
Peppas NA, Sahlin JJ. Hydrogels as mucoadhesive and bioadhesive materials: a review. Biomaterials. 1996;17:1553–61.
Tan G, Yu S, Pan H, Li J, Liu D, Yuan K, et al. Bioadhesive chitosan-loaded liposomes: a more efficient and higher permeable ocular delivery platform for timolol maleate. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;94:355–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.035.
Mohammed MA, Syeda JTM, Wasan KM, Wasan EK. An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2017;9:1–26.
Zhou F, Xu T, Zhao Y, Song H, Zhang L, Wu X, et al. Chitosan-coated liposomes as delivery systems for improving the stability and oral bioavailability of acteoside. Food Hydrocoll. 2018;83:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.040.
Gagliardi A, Voci S, Salvatici MC, Fresta M, Cosco D. Brij-stabilized zein nanoparticles as potential drug carriers. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 2021;201:1–11.
Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:751–60.
Varki A, Cummings R, McEver R, Esko J. C-type lectins [Internet]. Cold Spring Harb. Lab. Press. 2009. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1943/.
Abouhussein DMN, El Nabarawi MA, Shalaby SH, El-Bary AA. Sertraline-cyclodextrin complex orodispersible sublingual tablet: optimization, stability, and pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Innov. 2021;16:53–66.
Zafar A, Alruwaili NK, Imam SS, Yasir M, Alsaidan OA, Alquraini A, et al. Development and optimization of nanolipid-based formulation of diclofenac sodium: in vitro characterization and preclinical evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1–16.
Zafar A, Imam SS, Alruwaili NK, Yasir M, Alsaidan OA, Alshehri S, et al. Formulation and evaluation of topical nano-lipid-based delivery of butenafine: in vitro characterization and antifungal activity. Gels. 2022;8:1–17.
El-Nabarawi MA, Shamma RN, Farouk F, Nasralla SM. Bilosomes as a novel carrier for the cutaneous delivery for dapsone as a potential treatment of acne: preparation, characterization and in vivo skin deposition assay. J Liposome Res. 2020;30:1–11.
Al-Mahallawi AM, Abdelbary AA, Aburahma MH. Investigating the potential of employing bilosomes as a novel vesicular carrier for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam. Int J Pharm. 2015;485:329–40.
Diabetes [Internet]. [cited 2022 Oct 27]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes.
Funakoshi-Tago M, Nakamura K, Tago K, Mashino T, Kasahara T. Anti-inflammatory activity of structurally related flavonoids, Apigenin, Luteolin and Fisetin. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11:1150–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.03.012.
Gambhire VM, Gambhire MS, Ranpise NS. Solid lipid nanoparticles of dronedarone hydrochloride for oral delivery: optimization, in vivo pharmacokinetics and uptake studies. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2019;7:375–88.
Guan P, Lu Y, Qi J, Wu W. Readily restoring freeze-dried probilosomes as potential nanocarriers for enhancing oral delivery of cyclosporine A. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;144:143–51.
Donaldson EF, Harrington PR, O’Rear JJ, Naeger LK. Clinical evidence and bioinformatics characterization of potential hepatitis C virus resistance pathways for sofosbuvir. Hepatology. 2015;61:56–65.
Calvaresi EC, Hergenrother PJ. Glucose conjugation for the specific targeting and treatment of cancer. Chem Sci. 2013;4:2319–33.
Elkomy MH, El Menshawe SF, Kharshoum RM, Abdeltwab AM, Hussein RRS, Hamad DS, et al. Innovative pulmonary targeting of terbutaline sulfate-laded novasomes for non-invasive tackling of asthma: statistical optimization and comparative in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2022;29:2058–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2092236.
Tolman EL, Isaacson DM, Rosenthale ME, McGuire JL, Van Cutsem J, Borgers M, et al. Anticandidal activities of terconazole, a broad-spectrum antimycotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986;29:986–91.
Williamson DE, Elia RVD, Roberts CW, Woods S. Method for the preparation of a pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation and associated products and uses. The Secretary of State for Defence: University of Strathclyde, United States; 2022.
Sanderson David J. Transmucosal delivery device and method of manufacturing same. Nanostrips, INC, Canada: Canada; 2019.
Ferro V. Preparation of non-ionic surfactant vesicles and variants. University of Strathclyde; 2018.
Arunachalam A, Mani S. Stability studies: a review. Asian J Pharm Anal Med Chem. 2013;1:184–95.
Jain S, Indulkar A, Harde H, Agrawal AK. Oral mucosal immunization using glucomannosylated bilosomes. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10:932–47.
Roy S, Kumar V. A Practical Approach on SDS PAGE for Separation of Protein. Int J Sci Res [Internet]. 2014;3:955–60. Available from: http://www.ijsr.net/archive/v3i8/MDIwMTU0MDk=.pdf.
Wilkhu JS, McNeil SE, Anderson DE, Perrie Y. Characterization and optimization of bilosomes for oral vaccine delivery. J Drug Target. 2013;21:291–9.
Ahmed S, Kassem MA, Sayed S. Bilosomes as promising nanovesicular carriers for improved transdermal delivery: construction, in vitro optimization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9783–98.
Toh MR, Chiu GNC. Liposomes as sterile preparations and limitations of sterilisation techniques in liposomal manufacturing. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2013;8:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2013.07.011.
Abdelkader H, Alani AWG, Alany RG. Recent advances in non-ionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes): self-assembly, fabrication, characterization, drug delivery applications and limitations. Drug Deliv. 2014;21:87–100.
Wei XQ, Zhu JF, Wang XB, Ba K. Improving the stability of liposomal curcumin by adjusting the inner aqueous chamber pH of liposomes. ACS Omega. 2020;5:1120–6.
Jain S, Jain V, Mahajan SC. Lipid based vesicular drug delivery systems. Adv Pharm [Internet]. 2014;2014:1–12. Available from: http://www.hindawi.com/archive/2014/574673/.
Acknowledgements
We, the authors, gratefully acknowledge the support of the Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Science and the Manipal Academy of Higher Education throughout the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Preparation of original draft, literature search, conceptualization, writing, and editing: DN.
Guidance, review, editing, conceptualization, and supervision: Dr. VKT and Dr. MR.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, D., Rathnanand, M. & Tippavajhala, V.K. Unlocking the Potential of Bilosomes and Modified Bilosomes: a Comprehensive Journey into Advanced Drug Delivery Trends. AAPS PharmSciTech 24, 238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-023-02696-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-023-02696-4