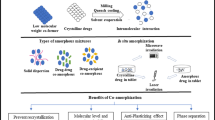
Abstract
Over the past few decades, co-amorphous solids have been used as a promising approach for delivering poorly water-soluble drugs. Co-amorphous solids, comprising pharmacologically relevant drug substances or excipients, improve physical stability, solubility, dissolution, and bioavailability compared with single amorphous ingredients. In this review, we have summarized recent advances in physical stability and in vitro and in vivo performances of co-amorphous solids. We have highlighted the role of molar ratio, molecular interaction, and mobility that affects the physical stability of co-amorphous solids. This review delves deep as to how co-amorphous solids affect the physicochemical properties in vitro and in vivo. We also described the challenges to the formulation of co-amorphous solids. A better understanding of the mechanisms of the physical stability, in vitro and in vivo performance of co-amorphous solids, and proper selection of the co-former is likely to expedite the development of robust co-amorphous-based pharmaceutical formulations and can address the challenges associated with the delivery of poorly soluble drugs.

Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society)

Copyright © 2021 Elsevier)

Copyright © 2018 American Chemical Society)

(Adapted from Ref. 51 with the permission of the American Chemical Society)

(Copyright © 2019 Elsevier)

(Copyright © 2020 Elsevier)

(Copyright © 2022 American Chemical Society))
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalepu S, Nekkanti V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015;5:442–53.
Shi Q, Li F, Yeh S, Wang Y, Xin J. Physical stability of amorphous pharmaceutical solids: nucleation, crystal growth, phase separation and effects of the polymers. Int J Pharm. 2020;590:119925.
Shi Q, Li F, Yeh S, Moinuddin SM, Xin J, Xu J, Chen H, Ling B. Recent advances in enhancement of dissolution and supersaturation of poorly water-soluble drug in amorphous pharmaceutical solids: a review. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;23:16.
Shi Q, Zhang C, Su Y, Zhang J, Zhou D, Cai T. Acceleration of crystal growth of amorphous griseofulvin by low-concentration poly(ethylene oxide): aspects of crystallization kinetics and molecular mobility. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:2262–72.
Yarlagadda DL, Sai Krishna Anand V, Nair AR, Navya Sree KS, Dengale SJ, Bhat K. Considerations for the selection of co-formers in the preparation of co-amorphous formulations. Int J Pharm. 2021;602:120649.
Liu J, Grohganz H, Lobmann K, Rades T, Hempel NJ. Co-amorphous drug formulations in numbers: recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations with focus on co-formability, molar ratio, preparation methods, physical stability, in vitro and in vivo performance, and new formulation strategies. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:389.
Shi Q, Moinuddin SM, Cai T. Advances in coamorphous drug delivery systems. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019;9:19–35.
Haneef J, Chadha R. Drug-drug multicomponent solid forms: cocrystal, coamorphous and eutectic of three poorly soluble antihypertensive drugs using mechanochemical approach. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18:2279–90.
Bahetibieke S, Moinuddin SM, Baiyisaiti A, Liu X, Zhang J, Liu G, Shi Q, Peng A, Tao J, Di C, Cai T, Qi R. Co-amorphous formation of simvastatin-ezetimibe: enhanced physical stability, bioavailability and cholesterol-lowering effects in LDLr-/-Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1258.
Dengale SJ, Grohganz H, Rades T, Lobmann K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;100:116–25.
Chmiel K, Knapik-Kowalczuk J, Jurkiewicz K, Sawicki W, Jachowicz R, Paluch M. A new method to identify physically stable concentration of amorphous solid dispersions (I): case of flutamide + kollidon VA64. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:3370–80.
Knapik-Kowalczuk J, Tu W, Chmiel K, Rams-Baron M, Paluch M. Co-stabilization of amorphous pharmaceuticals-the case of nifedipine and nimodipine. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:2455–65.
Ueda H, Kadota K, Imono M, Ito T, Kunita A, Tozuka Y. Co-amorphous formation induced by combination of tranilast and diphenhydramine hydrochloride. J Pharm Sci. 2017;106:123–8.
Grzybowska K, Capaccioli S, Paluch M. Recent developments in the experimental investigations of relaxations in pharmaceuticals by dielectric techniques at ambient and elevated pressure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;100:158–82.
Wang Y, Wang Y, Cheng J, Chen H, Xu J, Liu Z, Shi Q, Zhang C. Recent advances in the application of characterization techniques for studying physical stability of amorphous pharmaceutical solids. Curr Comput-Aided Drug Des. 2021;11:1440.
Knapik J, Wojnarowska Z, Grzybowska K, Jurkiewicz K, Tajber L, Paluch M. Molecular dynamics and physical stability of coamorphous ezetimib and indapamide Mixtures. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:3610–9.
Fung MH, DeVault M, Kuwata KT, Suryanarayanan R. Drug-excipient interactions: effect on molecular mobility and physical stability of ketoconazole-organic acid coamorphous systems. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:1052–61.
Zhang J, Shi Q, Qu T, Zhou D, Cai T. Crystallization kinetics and molecular dynamics of binary coamorphous systems of nimesulide and profen analogs. Int J Pharm. 2021;610:121235.
Chieng N, Teo X, Cheah MH, Choo ML, Chung J, Hew TK, Keng PS. Molecular dynamics and physical stability of pharmaceutical co-amorphous systems: correlation between structural relaxation times measured by Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts with the width of the glass transition temperature (DeltaTg) and the onset of crystallization. J Pharm Sci. 2019;108:3848–58.
Madejczyk O, Kaminska E, Tarnacka M, Dulski M, Jurkiewicz K, Kaminski K, Paluch M. Studying the crystallization of various polymorphic forms of nifedipine from binary mixtures with the use of different experimental techniques. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:2116–25.
Kissi EO, Kasten G, Lobmann K, Rades T, Grohganz H. The role of glass transition temperatures in coamorphous drug-amino acid formulations. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:4247–56.
Moinuddin SM, Ruan S, Huang Y, Gao Q, Shi Q, Cai B, Cai T. Facile formation of co-amorphous atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide mixtures via cryogenic-milling: enhanced physical stability, dissolution and pharmacokinetic profile. Int J Pharm. 2017;532:393–400.
Wu W, Ueda H, Lobmann K, Rades T, Grohganz H. Organic acids as co-formers for Co-amorphous systems - influence of variation in molar ratio on the physicochemical properties of the co-amorphous systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;131:25–32.
Beyer A, Grohganz H, Lobmann K, Rades T, Leopold CS. Influence of the cooling rate and the blend ratio on the physical stability of co-amorphous naproxen/indomethacin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;109:140–8.
Liu J, Rades T, Grohganz H. Determination of the optimal molar ratio in amino acid-based coamorphous systems. Mol Pharm. 2020;17:1335–42.
Knapik-Kowalczuk J, Kramarczyk D, Jurkiewicz K, Chmiel K, Paluch M. Ternary eutectic ezetimibe-simvastatin-fenofibrate system and the physical stability of its amorphous form. Mol Pharm. 2021;18:3588–600.
Pacult J, Rams-Baron M, Chmiel K, Jurkiewicz K, Antosik A, Szafraniec J, Kurek M, Jachowicz R, Paluch M. How can we improve the physical stability of co-amorphous system containing flutamide and bicalutamide? The case of ternary amorphous solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019;136:104947.
Budiman A, Higashi K, Ueda K, Moribe K. Effect of drug-coformer interactions on drug dissolution from a coamorphous in mesoporous silica. Int J Pharm. 2021;600:120492.
Newman A, Zografi G. What are the important factors that influence API crystallization in miscible amorphous API-excipient mixtures during long-term storage in the glassy state? Mol Pharm. 2022;19:378–91.
Li B, Hu Y, Guo Y, Xu R, Fang X, Xiao X, Jiang C, Lu S. Coamorphous system of florfenicol-oxymatrine for improving the solubility and dissolution rate of florfenicol: preparation, characterization and molecular dynamics simulation. J Pharm Sci. 2021;110:2544–54.
Pang W, Lv J, Du S, Wang J, Wang J, Zeng Y. Preparation of curcumin-piperazine coamorphous phase and fluorescence spectroscopic and density functional theory simulation studies on the interaction with bovine serum albumin. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:3013–24.
Moinuddin SM, Shi Q, Tao J, Guo M, Zhang J, Xue Q, Ruan S, Cai T. Enhanced physical stability and synchronized release of febuxostat and indomethacin in coamorphous solids. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020;21:41.
Alleso M, Chieng N, Rehder S, Rantanen J, Rades T, Aaltonen J. Enhanced dissolution rate and synchronized release of drugs in binary systems through formulation: amorphous naproxen-cimetidine mixtures prepared by mechanical activation. J Control Release. 2009;136:45–53.
Lobmann K, Laitinen R, Grohganz H, Gordon KC, Strachan C, Rades T. Coamorphous drug systems: enhanced physical stability and dissolution rate of indomethacin and naproxen. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:1919–28.
Kasten G, Nouri K, Grohganz H, Rades T, Löbmann K. Performance comparison between crystalline and co-amorphous salts of indomethacin-lysine. Int J Pharm. 2017;533:138–44.
Kasten G, Lobo L, Dengale S, Grohganz H, Rades T, Löbmann K. In vitro and in vivo comparison between crystalline and co-amorphous salts of naproxen-arginine. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;132:192–9.
Wu W, Hiroshi U, Korbinian L, Thomas R, Holger G. Organic acids as co-formers for co-amorphous systems – influence of variation in molar ratio on the physicochemical properties of the co-amorphous systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;131:25–32.
Ojarinta R, Lerminiaux L, Laitinen R. Spray drying of poorly soluble drugs from aqueous arginine solution. Int J Pharm. 2017;532:289–98.
Kasten G, Lobmann K, Grohganz H, Rades T. Co-former selection for co-amorphous drug-amino acid formulations. Int J Pharm. 2019;557:366–73.
Mishra J, Löbmann K, Grohganz H, Rades T. Influence of preparation technique on co-amorphization of carvedilol with acidic amino acids. Int J Pharm. 2018;552:407–13.
Jensen KT, Larsen FH, Cornett C, Lobmann K, Grohganz H, Rades T. Formation mechanism of coamorphous drug-amino acid mixtures. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:2484–92.
Pajula K, Wittoek L, Lehto VP, Ketolainen J, Korhonen O. Phase separation in coamorphous systems: in silico prediction and the experimental challenge of detection. Mol Pharm. 2014;11:2271–9.
Kilpelainen T, Pajula K, Ervasti T, Uurasjarvi E, Koistinen A, Korhonen O. Raman imaging of amorphous-amorphous phase separation in small molecule co-amorphous systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;155:49–54.
Pajula K, Hyyrylainen J, Koistinen A, Leskinen JTT, Korhonen O. Detection of amorphous-amorphous phase separation in small molecular co-amorphous mixtures with SEM-EDS. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;150:43–9.
Taylor LS, Zhang GGZ. Physical chemistry of supersaturated solutions and implications for oral absorption. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;101:122–42.
Jensen KT, Blaabjerg LI, Lenz E, Bohr A, Grohganz H, Kleinebudde P, Rades T, Lobmann K. Preparation and characterization of spray-dried co-amorphous drug-amino acid salts. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016;68:615–24.
Hu Y, Guo Y, Li B, Xu R, Fang X, Cao Y, Liu Z, Jiang C, Lu S. Influence of the pK a value of cinnamic acid and P-hydroxycinnamic acid on the solubility of a lurasidone hydrochloride-based coamorphous system. ACS Omega. 2021;6:3106–19.
Chen X, Li D, Zhang H, Duan Y, Huang Y. Sinomenine-phenolic acid coamorphous drug systems: solubilization, sustained release, and improved physical stability. Int J Pharm. 2021;598:120389.
Pokharkar VB, Mandpe LP, Padamwar MN, Ambile AA, Mahadik KR, Paradkar A. Development, characterization and stabilization of amorphous form of a low Tg drug. Powder Tech. 2006;167:20–5.
Qian S, Li Z, Heng W, Liang S, Ma D, Gao Y, Zhang J, Wei Y. Charge-assisted intermolecular hydrogen bond formed in coamorphous system is important to relieve the pH-dependent solubility behavior of lurasidone hydrochloride. Rsc Adv. 2016;6:106396–412.
Heng W, Su M, Cheng H, Shen P, Liang S, Zhang L, Wei Y, Gao Y, Zhang J, Qian S. Incorporation of complexation into a coamorphous system dramatically enhances dissolution and eliminates gelation of amorphous lurasidone hydrochloride. Mol Pharm. 2020;17:84–97.
Fung MH, Berzins K, Suryanarayanan R. Physical stability and dissolution behavior of ketoconazole-organic acid coamorphous systems. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:1862–9.
Hu Y, Jiang C, Li B, Zhou L, Xu R, Guo Y, Cao Y, Cao G, Lu S. A Novel lurasidone hydrochloride–shikimic acid co-amorphous system formed by hydrogen-bonding interaction with the retained pH-dependent solubility behavior. CrystEngComm. 2020;22:5841–53.
Wang S, Heng W, Wang X, He X, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Zhang J, Gao Y, Qian S. Coamorphization combined with complexation enhances dissolution of lurasidone hydrochloride and puerarin with synchronized release. Int J Pharm. 2020;588:119793.
Hatanaka Y, Uchiyama H, Kadota K, Tozuka Y. Improved solubility and permeability of both nifedipine and ketoconazole based on coamorphous formation with simultaneous dissolution behavior. J Drug Deliv Sci Tech. 2021;65:102715.
Qian S, Heng W, Wei Y, Zhang J, Gao Y. Coamorphous lurasidone hydrochloride–saccharin with charge-assisted hydrogen bonding interaction shows improved physical stability and enhanced dissolution with pH-independent solubility behavior. Cryst Growth Des. 2015;15:2920–8.
Skieneh JM, Sathisaran I, Dalvi SV, Rohani S. Co-amorphous form of curcumin-folic acid dihydrate with increased dissolution rate. Cryst Growth Des. 2017;17:6273–80.
Ojarinta R, Heikkinen AT, Sievanen E, Laitinen R. Dissolution behavior of co-amorphous amino acid-indomethacin mixtures: the ability of amino acids to stabilize the supersaturated state of indomethacin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;112:85–95.
Paluch KJ, McCabe T, Muller-Bunz H, Corrigan OI, Healy AM, Tajber L. Formation and physicochemical properties of crystalline and amorphous salts with different stoichiometries formed between ciprofloxacin and succinic acid. Mol Pharm. 2013;10:3640–54.
Ruponen M, Rusanen H, Laitinen R. Dissolution and permeability properties of co-amorphous formulations of hydrochlorothiazide. J Pharm Sci. 2020;109:2252–61.
Ojarinta R, Saarinen J, Strachan CJ, Korhonen O, Laitinen R. Preparation and characterization of multicomponent tablets containing co-amorphous salts: combining multimodal non-linear optical imaging with established analytical methods. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;132:112–26.
Trasi NS, Taylor LS. Thermodynamics of highly supersaturated aqueous solutions of poorly water-soluble drugs-impact of a second drug on the solution phase behavior and implications for combination products. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104:2583–93.
Trasi NS, Taylor LS. Dissolution performance of binary amorphous drug combinations: impact of a second drug on the maximum achievable supersaturation. Int J Pharm. 2015;496:282–90.
Alhalaweh A, Bergstrom CAS, Taylor LS. Compromised in vitro dissolution and membrane transport of multidrug amorphous formulations. J Control Release. 2016;229:172–82.
Li YW, Zhang HM, Cui BJ, Hao CY, Zhu HY, Guan J, Wang D, Jin Y, Feng B, Cai JH, Qi XR, Shi NQ. “Felodipine-indomethacin” co-amorphous supersaturating drug delivery systems: “spring-parachute” process, stability, in vivo bioavailability, and underlying molecular mechanisms. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;166:111–25.
Yu D, Kan Z, Shan F, Zang J, Zhou J. Triple strategies to improve oral bioavailability by fabricating coamorphous forms of ursolic acid with piperine: enhancing water-solubility, permeability, and inhibiting cytochrome P450 isozymes. Mol Pharm. 2020;17:4443–62.
Shi X, Zhou X, Shen S, Chen Q, Song S, Gu C, Wang C. Improved in vitro and in vivo properties of telmisartan in the co-amorphous system with hydrochlorothiazide: a potential drug-drug interaction mechanism prediction. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;161:105773.
Wei Y, Zhou S, Hao T, Zhang J, Gao Y, Qian S. Further enhanced dissolution and oral bioavailability of docetaxel by coamorphization with a natural P-gp inhibitor myricetin. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019;129:21–30.
Wang R, Han J, Jiang A, Huang R, Fu T, Wang L, Zheng Q, Li W, Li J. Involvement of metabolism-permeability in enhancing the oral bioavailability of curcumin in excipient-free solid dispersions co-formed with piperine. Int J Pharm. 2019;561:9–18.
Bohr A, Nascimento TL, Harmankaya N, Weisser JJ, Wang Y, Grohganz H, Rades T, Lobmann K. Efflux inhibitor bicalutamide increases oral bioavailability of the poorly soluble efflux substrate docetaxel in co-amorphous anti-cancer combination therapy. Molecules. 2019;24:266.
Nair A, Varma R, Gourishetti K, Bhat K, Dengale S. Influence of preparation methods on physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of co-amorphous formulations: the case of co-amorphous atorvastatin: Naringin. J Pharm Innov. 2019;15:365–79.
Suresh K, Mannava MKC, Nangia A. A novel curcumin-artemisinin coamorphous solid: physical properties and pharmacokinetic profile. RSC Adv. 2014;4:58357–61.
Dengale SJ, Hussen SS, Krishna BS, Musmade PB, Gautham Shenoy G, Bhat K. Fabrication, solid state characterization and bioavailability assessment of stable binary amorphous phases of ritonavir with quercetin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;89:329–38.
Teja A, Musmade PB, Khade AB, Dengale SJ. Simultaneous improvement of solubility and permeability by fabricating binary glassy materials of Talinolol with Naringin: Solid state characterization, in-vivo in-situ evaluation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015;78:234–44.
Lodagekar A, Chavan RB, Mannava MKC, Yadav B, Chella N, Nangia AK, Shastri NR. Coamorphous valsartan nifedipine system: preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019;139:105048.
Zhang Y, Gao Y, Du X, Guan R, He Z, Liu H. Combining co-amorphous-based spray drying with inert carriers to achieve improved bioavailability and excellent downstream manufacturability. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:1063.
Maher EM, Ali AM, Salem HF, Abdelrahman AA. In vitro/in vivo evaluation of an optimized fast dissolving oral film containing olanzapine co-amorphous dispersion with selected carboxylic acids. Drug Deliv. 2016;23:3088–100.
Shi X, Song S, Ding Z, Fan B, Huang W, Xu T. Improving the solubility, dissolution, and bioavailability of ibrutinib by preparing it in a coamorphous state with saccharin. J Pharm Sci. 2019;108:3020–8.
Park H, Jin Seo H, Hong SH, Ha ES, Lee S, Kim JS, Baek IH, Kim MS, Hwang SJ. Characterization and therapeutic efficacy evaluation of glimepiride and L-arginine co-amorphous formulation prepared by supercritical antisolvent process: influence of molar ratio and preparation methods. Int J Pharm. 2020;581:119232.
Mannava MKC, Suresh K, Kumar Bommaka M, Bhavani Konga D, Nangia A. Curcumin-artemisinin coamorphous solid: xenograft model preclinical study. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10:7.
Sai Krishna Anand V, Sakhare SD, Navya Sree KS, Nair AR, Raghava Varma K, Gourishetti K, Dengale SJ. The relevance of co-amorphous formulations to develop supersaturated dosage forms: in-vitro, and ex-vivo investigation of ritonavir-lopinavir co-amorphous materials. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;123:124–34.
Liu J, Grohganz H, Rades T. Influence of polymer addition on the amorphization, dissolution and physical stability of co-amorphous systems. Int J Pharm. 2020;588:119768.
Veith H, Wiechert F, Luebbert C, Sadowski G. Combining crystalline and polymeric excipients in API solid dispersions - opportunity or risk? Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;158:323–35.
Liu J, Hwu E, Bannow J, Grohganz H, Rades T. Impact of molecular surface diffusion on the physical stability of co-amorphous systems. Mol Pharm. 2022;19(4):1183–90.
Funding
The authors are grateful for financial support of this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81803452), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20211114), Natural Science Foundation in Colleges of Jiangsu Province (No. 21KJB350016), and the National Subject Cultivation Project of Jiangsu Vocational College of Medicine (No. 20204304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qin Shi: conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition; Yanan Wang: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; Sakib M. Moinuddin: conceptualization, writing—review and editing; Xiaodong Feng: writing—review and editing; Fakhrul Ahsan: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Q., Wang, Y., Moinuddin, S.M. et al. Co-amorphous Drug Delivery Systems: a Review of Physical Stability, In Vitro and In Vivo Performance. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 259 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02421-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02421-7