Abstract
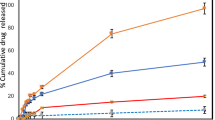
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) represents 20% of cases of non-melanoma skin cancer, and the most common treatment is the removal of the tumor, which can leave large scars. 5-Fluorouracil (5FU) is a drug used in the treatment of SCC, but it is highly hydrophilic, resulting in poor skin penetration in topical treatment. Some strategies can be used to increase the cutaneous penetration of the drug, such as the combination of liposomes containing penetration enhancers, for instance, surfactants, associated with the use of microneedling. Thus, the present work addresses the development of liposomes with penetration enhancers, such as sorbtitan monolaurate, span 20, for topical application of 5-FU and associated or not with the use of microneedling for skin delivery. Liposomes were developed using the lipid film hydration, resulting in particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, and 5-FU encapsulation efficiency of 88.08 nm, 0.169, −12.3 mV, and 50.20%, respectively. The presence of span 20 in liposomes potentiated the in vitro release of 5-FU. MTT assay was employed for cytotoxicity evaluation and the IC50 values were 0.62, 30.52, and 24.65 μM for liposomes with and without span 20 and 5-FU solution, respectively after 72-h treatment. Flow cytometry and confocal microscopy analysis evidenced high cell uptake for the formulations. In skin penetration studies, a higher concentration of 5-FU was observed in the epidermis + dermis, corresponding to 1997.71, 1842.20, and 2585.49 ng/cm2 in the passive penetration and 3214.07, 2342.84, and 5018.05 ng/cm2 after pretreatment with microneedles, for solution, liposome without and with span 20, respectively. Therefore, herein, we developed a nanoformulation for 5-FU delivery, with suitable physicochemical characteristics, potent skin cancer cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake. Span 20–based liposomes increased the skin penetration of 5-FU in association of microneedling. Altogether, the results shown herein evidenced the potential of the liposome containing span 20 for topical delivery of 5-FU.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alomrani A, Badran M, Harisa GI, Alshehry M, Alhariri M, Alshamsan A, Alkholief M. The use of chitosan-coated flexible liposomes as a remarkable carrier to enhance the antitumor efficacy of 5-fluorouracil against colorectal cancer. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2019;27(5):603–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2019.02.008.
Amasya G, Aksu B, Badilli U, Onay-Besikci A, Tarimci N. QbD guided early pharmaceutical development study: production of lipid nanoparticles by high pressure homogenization for skin cancer treatment. Int J Pharm. 2019;563(March):110–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.03.056.
Amasya G, Gumustas M, Badilli U, Ozkan SA, Tarimci N. Development of a HILIC method for the determination of 5-fluorouracil from nano drug delivery systems and rat skin extracts. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018;154:285–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.03.021.
Badran MM, Kuntsche J, Fahr A. Skin penetration enhancement by a microneedle device (Dermaroller®) in vitro: dependency on needle size and applied formulation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009;36(4–5):511–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2008.12.008.
Bahramizadeh M, Bahramizadeh M, Kiafar B, Jafarian AH, Nikpoor AR, Hatamipour M, Esmaily H, et al. Development, characterization and evaluation of topical methotrexate-entrapped deformable liposome on imiquimod-induced psoriasis in a mouse model. Int J Pharm. 2019;569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118623.
Bruch GE, Fernandes LF, Bassi BLT, Marco TR, Alves IO, Pereira FF, Massensini AR. Liposomes for drug delivery in stroke. Brain Res Bull. 2019;152(June):246–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.07.015.
Calienni MN, Temprana CF, Prieto MJ, Paolino D, Fresta M, Tekinay AB, del Valle Alonso S, Montanari J. Nano-formulation for topical treatment of precancerous lesions: skin penetration, in vitro, and in vivo toxicological evaluation. Drug Delivery and Translational Research. 2018;8(3):496–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-017-0469-1.
Carita AC, Eloy JO, Chorilli M, Lee RJ, Leonardi GR. Recent advances and perspectives in liposomes for cutaneous drug delivery. Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(5):606–35. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666171009120154.
Chacko IA, Ghate VM, Dsouza L, Lewis SA. Lipid vesicles: a versatile drug delivery platform for dermal and transdermal applications. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2020;195(July):111262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111262.
Coviello T, Trotta AM, Marianecci C, Carafa M, Di Marzio L, Rinaldi F, Di Meo C, Alhaique F, Matricardi P. Gel-embedded niosomes: preparation, characterization and release studies of a new system for topical drug delivery. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2015;125:291–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.10.060.
Cristiano MC, Froiio F, Mancuso A, Iannone M, Fresta M, Fiorito S, Celia C, Paolino D. In vitro and in vivo trans-epidermal water loss evaluation following topical drug delivery systems application for pharmaceutical analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020;186:113295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113295.
Dar MJ, Khalid S, Mcelroy CA, Satoskar AR, Majid G. Topical treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis with novel amphotericin B- miltefosine co-incorporated second generation ultra-deformable liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2020;573(October 2019):118900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118900.
Eaton P, Quaresma P, Soares C, Neves C, de Almeida MP, Pereira E, West P. A direct comparison of experimental methods to measure dimensions of synthetic nanoparticles. Ultramicroscopy. 2017;182:179–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultramic.2017.07.001.
Eloy JO, Petrilli R, Topan JF, Antonio HMR, Barcellos JPA, Chesca DL, Serafini LN, Tiezzi DG, Lee RJ, Marchetti JM. Co-loaded paclitaxel/rapamycin liposomes: development, characterization and in vitro and in vivo evaluation for breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2016;141:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.01.032.
Eloy JO, Claro M, de Souza R, Petrilli JP, Barcellos A, Lee RJ, Marchetti JM. Liposomes as carriers of hydrophilic small molecule drugs: strategies to enhance encapsulation and delivery. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2014;123:345–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.09.029.
Eyerich S, Eyerich K, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Biedermann T. Cutaneous barriers and skin immunity: differentiating a connected network. Trends Immunol. 2018;39(4):315–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2018.02.004.
Farooqui RK, Kaurav M, Kumar M, Sudheesh MS, Pandey RS (2022) Permeation enhancer nanovesicles mediated topical delovery of curcumin for the treatment of hyperpigmentation. J Liposome Res 2022, https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2021.2024567
Guan Y, Wang G, Fails D, Nagarajan P, Ge Y (2019) Unraveling cancer lineage drivers in squamous cell carcinomas. Pharmacol Ther, 107448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107448
Handali S, Moghimipour E, Kouchak M, Ramezani Z, Amini M, Angali KA, Saremy S, Dorkoosh FA, Rezaei M. New folate receptor targeted nano liposomes for delivery of 5-fluorouracil to cancer cells: strong implication for enhanced potency and safety. Life Sci. 2019;227(March):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.030.
Hussain A, Samad A, Ramzan M, Ahsan MN, Rehman ZU, Ahmad FJ. Elastic liposome-based gel for topical delivery of 5-fluorouracil: in vitro and in vivo investigation. Drug Delivery. 2016;23(4):1115–29. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.976891.
Jaimes-Lizcano YA, Lawson LB, Papadopoulos KD. Oil-frozen W1/O/W2 double emulsions for dermal biomacromolecular delivery containing ethanol as chemical penetration enhancer. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100:1398–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.
Jain A, Jain SK. In vitro release kinetics model fitting of liposomes: an insight. Chem Phys Lipids. 2016;201:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2016.10.005.
Junyaprasert VB, Singhsa P, Suksiriworapong J, Chantasart D. Physicochemical properties and skin permeation of span 60/tween 60 niosomes of ellagic acid. Int J Pharm. 2012;423(2):303–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.11.032.
Kraft JC, Freeling JP, Wang Z, Ho RJY. Emerging research and clinical development trends of liposome and lipid nanoparticle drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci. 2014;103(1):29–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23773.
Krishnan V, Mitragotri S. Nanoparticles for topical drug delivery: potential for skin cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;153:87–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.05.011.
Lakkadwala S, Singh J. Dual functionalized 5-fluorouracil liposomes as highly efficient nanomedicine for glioblastoma treatment as assessed in an in vitro brain tumor model. J Pharm Sci. 2018;107(11):2902–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.07.020.
Larrucea E, Arellano A, Santoyo S, Ygartua P. Combined effect of oleic acid and propylene glycol on the percutaneous penetration of tenoxicam and its retention in the skin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2001;52(2):113–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(01)00158-8.
Lei L, Liu X, Shen YY, Liu JY, Tang MF, Wang ZM, Guo SR, Cheng L. Zero-order release of 5-fluorouracil from PCL-based films featuring trilayered structures for stent application. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;78(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.01.003.
Li D, Hu D, Xu H, Patra HK, Liu X, Zhou Z, Tang J, Slater N, Shen Y. Progress and perspective of microneedle system for anti-cancer drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2020;264(May 2020):120410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120410.
López-Castellano A, Cortell-Ivars C, López-Carballo G, Herráez-Domínguez M. The influence of Span®20 on stratum corneum lipids in langmuir monolayers: comparison with Azone®. Int J Pharm. 2000;203(1–2):245–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00463-4.
López A, Llinares F, Cortell C, Herráez M. Comparative enhancer effects of Span®20 with Tween®20 and Azone® on the in vitro percutaneous penetration of compounds with different lipophilicities. Int J Pharm. 2000;202(1–2):133–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00427-0.
Losquadro WD. Anatomy of the skin and the pathogenesis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America. 2017;25(3):283–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2017.03.001.
Moghimipour E, Rezaei M, Ramezani Z, Kouchak M, Amini M, Angali KA, Dorkoosh FA, Handali S. Transferrin targeted liposomal 5-fluorouracil induced apoptosis via mitochondria signaling pathway in cancer cells. Life Sci. 2018;194(October 2017):104–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.026.
Naguib YW, Kumar A, Cui Z. The effect of microneedles on the skin permeability and antitumor activity of topical 5-fluorouracil. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2014;4(1):94–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2013.12.013.
Oliveira RRL De, Albuquerque DAC, Cruz TGS (2012) Measurement of the nanoscale roughness by atomic force microscopy: basic principles and applications. www.intechopen.com.
Permana AD, Paredes AJ, Volpe-Zanutto F, Anjani QK, Utomo E, Donnelly RF. Dissolving microneedle-mediated dermal delivery of itraconazole nanocrystals for improved treatment of cutaneous candidiasis. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;154(July):50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.06.025.
Petrilli R, Eloy JO, Saggioro FP, Chesca DL, Claro M, de Souza MVS, Dias LLP, daSilva R, Lee J, Lopez RFV. Skin cancer treatment effectiveness is improved by iontophoresis of EGFR-targeted liposomes containing 5-FU compared with subcutaneous injection. J Control Release. 2018;283:151–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.038.
Petropoulos GP, Pandazaras CN, Davim JP (2010) Surface texture characterization and evaluation related to machining. Surface Integrity in Machining, 37–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84882-874-2_2.
Pleguezuelos-Villa M, Mir-Palomo S, Díez-Sales O, Buso MAOV, Sauri AR, Nácher A. A novel ultradeformable liposomes of naringin for anti-inflammatory therapy. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2018;162:265–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.11.068.
Rata DM, Niculina A, Ionut L, Popa M, Mihai C-t, Solcan C, Ochiuz L, Vochita G. Topical Formulations Containing Aptamer-Functionalized Nanocapsules Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil - An Innovative Concept for the Skin Cancer Therapy. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;119(11):111591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111591.
Sabri AH, Cater Z, Gurnani P, Ogilvie J, Segal J, Scurr DJ, Marlow M. Intradermal delivery of imiquimod using polymeric microneedles for basal cell carcinoma. Int J Pharm. 2020;589(May):119808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119808.
Tang H, Mitragotri S, Blankschtein D, Langer R. Theoretical description of transdermal transport of hydrophilic permeants: application to low-frequency sonophoresis (Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2001) 90, (545-568)). J Pharm Sci. 2001;98(10):3878. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21906.
Thomas AM, Kapanen AI, Hare JI, Ramsay E, Edwards K, Karlsson G, Bally MB. Development of a liposomal nanoparticle formulation of 5-fluorouracil for parenteral administration: formulation design, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. J Control Release. 2011;150(2):212–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.11.018.
Tseng CL, Chen JC, Yu Chun W, Fang HW, Lin FH, Tang TP. Development of lattice-inserted 5-fluorouracil-hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a chemotherapeutic delivery system. J Biomater Appl. 2015;30(4):388–97. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328215588307.
Verma DD, Verma S, Blume G, Fahr A. Liposomes increase skin penetration of entrapped and non-entrapped hydrophilic substances into human skin: a skin penetration and confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2003;55(3):271–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(03)00021-3.
Waldman A, Schmults C. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2018.08.001.
Walters KA, Bialik W, Brain KR. The effects of surfactants on penetration across the skin. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1993;15(6):260–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2494.1993.tb00572.x.
Williams AC, Barry BW. Penetration enhancers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(Suppl):128–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.032.
Yaman Ü, Aslan M, Ozturk S, Ulubayram K, Eroğlu İ (2020) Surface modified nanoliposome formulations provide sustained release for 5-FU and increase cytotoxicity on A431 cell line. Pharm Dev Technol 7450. https://doi.org/10.1080/10837450.2020.1803910.
Yamashita F, Koyama Y, Kitano M, Takakura Y, Hashida M. Analysis of in vivo skin penetration enhancement by oleic acid based on a two-layer diffusion model with polar and nonpolar routes in the stratum corneum. Int J Pharm. 1995;117(2):173–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(94)00327-2.
Zaki RM, Ibrahim MA, Alshora DH, El Sayeh A, Abou El Ela. 2022 Formulation and evaluation of transdermal gel containing tacrolimus-loaded spanlastics: in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies. Polymers 14 (8). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081528.
Zhang N, Yi-Xin Cai, Yong-Yong Wang, Yi-Tao Tian, Xiao-Li Wang, and Benjamin Badami. 2019 Skin cancer diagnosis based on optimized convolutional neural network. Artif Intell Med, 101756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101756
Zhou W, Liu W, Zou L, Liu W, Liu C, Liang R, Chen J. Storage stability and skin permeation of vitamin C liposomes improved by pectin coating. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2014;117:330–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.02.036.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Central Analítica-UFC (funded by Finep-CT-INFRA, CAPES-Pró-Equipamentos, and MCTI-CNPq-SisNano2.0) for confocal microscopy measurements. The authors would like to thank Maria Karolina de Araújo Barroso (Department of Pharmacy - Federal University of Ceará) for technical assistance in cell studies.
Funding
This work was supported by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) (grants # 409352/2018-7; #409362/ 2018-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Luiziana C.C. Fernandes Crisótomo: data acquistion, interpretation, and manuscript writing; Genuína Stephanie G. Carvalho: data acquisition; Luzia Kalyne A. M. Leal: analysis and interpretation; Tamara Gonçalves de Araújo: analysis and interpretation; Karina Alexandre B. Nogueira: data acquisition and interpretation; Durcilene Alves da Silva: data acquisition; Fabio de Oliveira Silva Ribeiro: data acquisition; Raquel Petrilli: data analysis and interpretation, revision and approval of the final version; Josimar O. Eloy: funding, data analysis and interpretation, revision and approval of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crisóstomo, L.C.C.F., Carvalho, G.S.G., Leal, L.K.A.M. et al. Sorbitan Monolaurate–Containing Liposomes Enhance Skin Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and in Association with Microneedling Increase the Skin Penetration of 5-Fluorouracil. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 212 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02356-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02356-z