Abstract
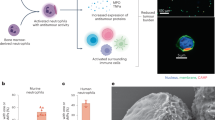
The role of neutrophils in tumor metastasis has recently attracted widespread interest. Neutrophils are the most abundant immune cells in human peripheral blood, and large numbers can spontaneously migrate to metastatic sites, where they form an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Polysialic acid (PSA) can target peripheral blood neutrophils (PBNs) mediated by l-selectin, and abemaciclib (ABE) and mitoxantrone (MIT) can treat immunosuppressive microenvironments. Here, we aimed to inhibit lung metastasis of breast cancer and improve chemoimmunotherapy by designing a PSA-modified ABE and MIT co-delivery system (AM-polyion complex (PIC)) to target PBNs in mice with metastatic tumors. We found that through electrostatic interactions between the strong negative charge of PSA and the positive charge of the drug can form stable nanocomplexes and that spontaneous migration of neutrophils can mediate the aggregation of these complexes in the lungs, induce antimetastatic immune responses, enhance the effectiveness of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), and inhibit regulatory T cell (Treg) proliferation in vivo and in vitro. Pharmacodynamic results suggested that neutrophil-mediated AM-PIC chemoimmunotherapy inhibited tumor metastasis in mice with lung metastasis of 4T1 breast cancer. Overall, PSA-modified nanocomplexes offer promising neutrophil-mediated, targeted drug delivery systems to treat lung metastasis of breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
Gupta GP, Massagué J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127(4):679–95.
Medeiros B, Allan AL. Molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis to the lung: clinical and experimental perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2272.
Stein U, Schlag PM. Clinical, biological, and molecular aspects of metastasis in colorectal cancer. Target Ther Cancer. 2007;61-80.
Kimbung S, Loman N, Hedenfalk I, editors. Clinical and molecular complexity of breast cancer metastases. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015; Elsevier.
Dan Z, Cao H, He X, Zhang Z, Zou L, Zeng L, Xu Y, Yin Q, Xu M, Zhong D, Yu H, Shen Q, Zhang P, Li Y. A pH-responsive host-guest nanosystem loading succinobucol suppresses lung metastasis of breast cancer. Theranostics. 2016;6(3):435–45.
Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, Tumati V, Ahn C, Hughes RS, et al. Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):e173501-e.
Dewhirst MW, Secomb TW. Transport of drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(12):738–50.
Minchinton AI, Tannock IF. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(8):583–92.
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh N, Peters AM, Chilvers ER. Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol. 2010;31(8):318–24.
Borregaard N. Neutrophils, from marrow to microbes. Immunity. 2010;33(5):657–70.
Mestas J, Hughes CC. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol. 2004;172(5):2731–8.
Wculek SK, Malanchi I. Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells. Nature. 2015;528(7582):413–7.
Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, Santoni A, Bonecchi R, Mantovani A. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(9):485–503.
Hedrick CC, Malanchi I. Neutrophils in cancer: heterogeneous and multifaceted. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;22:1–15.
Swierczak A, Mouchemore KA, Hamilton JA, Anderson RL. Neutrophils: important contributors to tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015;34(4):735–51.
Zhu K, Li P, Mo Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Ge J, Huang W, Liu Y, Tang Y, Gong Z, Liao Q, Li X, Li G, Xiong W, Zeng Z, Yu J. Neutrophils: accomplices in metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020;492:11–20.
Mollinedo F. Neutrophil degranulation, plasticity, and cancer metastasis. Trends Immunol. 2019;40(3):228–42.
Li J, Wang Q, Cheng Z. Research progress in mechanisms of tumor-associated neutrophils promoting tumor metastasis. Chin J Clin Oncol. 2019;524-7.
Demkow U. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in cancer invasion, evasion and metastasis. Cancers. 2021;13(17):4495.
Chen MB, Hajal C, Benjamin DC, Yu C, Azizgolshani H, Hynes RO, Kamm RD. Inflamed neutrophils sequestered at entrapped tumor cells via chemotactic confinement promote tumor cell extravasation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115(27):7022–7.
Spiegel A, Brooks MW, Houshyar S, Reinhardt F, Ardolino M, Fessler E, Chen MB, Krall JA, DeCock J, Zervantonakis IK, Iannello A, Iwamoto Y, Cortez-Retamozo V, Kamm RD, Pittet MJ, Raulet DH, Weinberg RA. Neutrophils suppress intraluminal NK cell–mediated tumor cell clearance and enhance extravasation of disseminated carcinoma cells. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(6):630–49.
Powell DR, Huttenlocher A. Neutrophils in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016;37(1):41–52.
Liang W, Ferrara N. The complex role of neutrophils in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4(2):83–91.
Xue J, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Xue L, Shen S, Wen Y, Wei Z, Wang L, Kong L, Sun H, Ping Q, Mo R, Zhang C. Neutrophil-mediated anticancer drug delivery for suppression of postoperative malignant glioma recurrence. Nat Nanotechnol. 2017;12(7):692–700.
Johnston S, Martin M, Di Leo A, Im S-A, Awada A, Forrester T, et al. MONARCH 3 final PFS: a randomized study of abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2019;5(1):1–8.
Schaer DA, Beckmann RP, Dempsey JA, Huber L, Forest A, Amaladas N, Li Y, Wang YC, Rasmussen ER, Chin D, Capen A, Carpenito C, Staschke KA, Chung LA, Litchfield LM, Merzoug FF, Gong X, Iversen PW, Buchanan S, et al. The CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib induces a T cell inflamed tumor microenvironment and enhances the efficacy of PD-L1 checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep. 2018;22(11):2978–94.
McCartney A, Moretti E, Sanna G, Pestrin M, Risi E, Malorni L, Biganzoli L, di Leo A. The role of abemaciclib in treatment of advanced breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018;10:1758835918776925.
Dickler MN, Tolaney SM, Rugo HS, Cortés J, Diéras V, Patt D, Wildiers H, Hudis CA, O'Shaughnessy J, Zamora E, Yardley DA, Frenzel M, Koustenis A, Baselga J. MONARCH 1, a phase II study of abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor, as a single agent, in patients with refractory HR+/HER2− metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(17):5218–24.
Garg AD, More S, Rufo N, Mece O, Sassano ML, Agostinis P, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Trial watch: immunogenic cell death induction by anticancer chemotherapeutics. Oncoimmunology. 2017;6(12):e1386829.
Mei K-C, Liao Y-P, Jiang J, Chiang M, Khazaieli M, Liu X, Wang X, Liu Q, Chang CH, Zhang X, Li J, Ji Y, Melano B, Telesca D, Xia T, Meng H, Nel AE. Liposomal delivery of mitoxantrone and a cholesteryl indoximod prodrug provides effective chemo-immunotherapy in multiple solid tumors. ACS Nano. 2020;14(10):13343–66.
Wang L, Fuster M, Sriramarao P, Esko JD. Endothelial heparan sulfate deficiency impairs L-selectin-and chemokine-mediated neutrophil trafficking during inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(9):902–10.
Finger EB, Purl KD, Alon R, Lawrence MB, von Andrian UH, Springer TA. Adhesion through L-selectin requires a threshold hydrodynamic shear. Nature. 1996;379(6562):266–9.
Hu L, Luo X, Zhou S, Zhu J, Xiao M, Li C, Zheng H, Qiu Q, Lai C, Liu X, Deng Y, Song Y. Neutrophil-mediated delivery of dexamethasone palmitate-loaded liposomes decorated with a sialic acid conjugate for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Pharm Res. 2019;36(7):97.
Zhang T, She Z, Huang Z, Li J, Luo X, Deng Y. Application of sialic acid/polysialic acid in the drug delivery systems. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2014;9(2):75–81.
Luo X, Liu M, Hu L, Qiu Q, Liu X, Li C, Lu M, Liu Y, Zhang T, Zhou S, McClements DJ, Jia X, Deng Y, Song Y. Targeted delivery of pixantrone to neutrophils by poly (sialic acid)-p-octadecylamine conjugate modified liposomes with improved antitumor activity. Int J Pharm. 2018;547(1-2):315–29.
Kou Y, Feng R, Chen J, Duan L, Wang S, Hu Y, Zhang N, Wang T, Deng Y, Song Y. Development of a nattokinase–polysialic acid complex for advanced tumor treatment. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;145:105241.
Qiu Q, Li C, Yan X, Zhang H, Luo X, Gao X, Liu X, Song Y, Deng Y. Photodynamic/photothermal therapy enhances neutrophil-mediated ibrutinib tumor delivery for potent tumor immunotherapy: more than one plus one? Biomaterials. 2021;269:120652.
Kalchenko V, Shivtiel S, Malina V, Lapid K, Haramati S, Lapidot T, Brill A, Harmelin A. Use of lipophilic near-infrared dye in whole-body optical imaging of hematopoietic cell homing. J Biomed Opt. 2006;11(5):050507.
Chu D, Zhao Q, Yu J, Zhang F, Zhang H, Wang Z. Nanoparticle targeting of neutrophils for improved cancer immunotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(9):1088–93.
von Andrian UH, Chambers JD, Berg EL, Michie SA, Brown DA, Karolak D, et al. L-selectin mediates neutrophil rolling in inflamed venules through sialyl LewisX-dependent and-independent recognition pathways. 1993.
Dzhagalov I, St. John A, He Y-W. The antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 is essential for the survival of neutrophils but not macrophages. Blood. 2007;109(4):1620–6.
Lang T, Dong X, Zheng Z, Liu Y, Wang G, Yin Q, Li Y. Tumor microenvironment-responsive docetaxel-loaded micelle combats metastatic breast cancer. Sci Bull. 2019;64(2):91–100.
Yin S, Cheryan VT, Xu L, Rishi AK, Reddy KB. Myc mediates cancer stem-like cells and EMT changes in triple negative breast cancers cells. PloS one. 2017;12(8):e0183578.
Nair R, Roden D, Teo W, McFarland A, Junankar S, Ye S, et al. c-Myc and Her2 cooperate to drive a stem-like phenotype with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(30):3992–4002.
Senbanjo LT, Chellaiah MA. CD44: a multifunctional cell surface adhesion receptor is a regulator of progression and metastasis of cancer cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:18.
Li C, Qiu Q, Gao X, Yan X, Fan C, Luo X, Liu X, Wang S, Lai X, Song Y, Deng Y. Sialic acid conjugate-modified liposomal platform modulates immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in multiple ways for improved immune checkpoint blockade therapy. J Control Release. 2021;337:393–406.
Shen J, Xiao Z, Zhao Q, Li M, Wu X, Zhang L, Hu W, Cho CH. Anti-cancer therapy with TNF α and IFN γ: a comprehensive review. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(4):e12441.
Engblom C, Pfirschke C, Zilionis R, Martins JDS, Bos SA, Courties G, et al. Osteoblasts remotely supply lung tumors with cancer-promoting SiglecFhigh neutrophils. Science. 2017;358(6367):eaal5081.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 81973271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chuizhong Fan: conceptualization, analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, and writing
Cong Li: conceptualization, analysis, and investigation
Shuang Lu: data curation, analysis, methodology, and validation
Xiaoxue Lai: analysis and methodology
Shuo Wang: analysis and methodology
Xinrong Liu: supervision
Yanzhi Song: supervision
Yihui Deng: supervision, resources, and review
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 708 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Li, C., Lu, S. et al. Polysialic Acid Self-assembled Nanocomplexes for Neutrophil-Based Immunotherapy to Suppress Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02243-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02243-7