Abstract
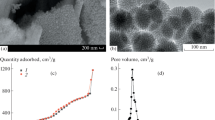
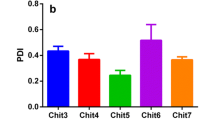
The postprandial glycemic regulation is essential for diabetic patients to reduce the risk of long-term microvascular and macrovascular complications. Herein, we designed a glucose-responsive oral insulin delivery system based on polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) for controlling the increasing postprandial glucose concentrations. Briefly, alginate-g-3-aminophenylboronic acid (ALG-g-APBA) and chitosan-g-3-fluoro-4-carboxyphenylboronic acid (CS-g-FPBA) were wrapped on mesoporous silica (MSN) to form the negative charged ALG-g-APBA@MSN and the positive charged CS-g-FPBA@MSN nanoparticles, with an optimum insulin loading capacity of 124 mg/g and 295 mg/g, respectively. ALG-g-APBA@MSN was further cross-linked with CS-g-FPBA@MSN to form PECs through electrostatic interaction and borate esters. The dense polyelectrolyte network wrapped on MSN was capable of preventing insulin from diffusion and regulating its release. The in vitro insulin release of PECs demonstrated an obvious glucose response profile in different glucose concentrations (0 mg/mL, 2 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL) and presented a switch “on” and “off” release regulation at hyperglycemic or normal state. The CCK-8 assay showed that none of the MSN, ALG-g-APBA@MSN, CS-g-FPBA@MSN, and PECs possessed cytotoxicity to Caco-2 cells. For in vivo tests, the oral PECs exhibited a significant hypoglycemic effect and maintained in the euglycemic levels up to approximately 12 h on diabetic rats. Overall, the PECs directly triggered by postprandial glucose in the intestine have a good potential to be applied in intelligent insulin delivery by the oral route.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti G, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association. 1998;15:539–53.
Amer DA. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020 (vol 43, pg S98, 2020). Diabetes Care. 2020;43:1979.
Sonmez M, Ficai D, Ficai A, Alexandrescu L, Georgescu M, Trusca R, et al. Applications of mesoporous silica in biosensing and controlled release of insulin. Int J Pharm. 2018;549:179–200.
Agrawal AK, Gupta PN, Khanna A, Sharma RK, Chandrabanshi HK, Gupta N, et al. Development and characterization of in situ gel system for nasal insulin delivery. Die Pharmazie - An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2010;65(3):188–93.
Zhou X, Wu H, Long R, Wang S, Huang H. Xia Y, et al. Journal of Nanobiotechnology: Oral delivery of insulin with intelligent glucose-responsive switch for blood glucose regulation; 2020.
Singh S, Kushwah V, Agrawal AK, Jain S. Insulin- and quercetin-loaded liquid crystalline nanoparticles: implications on oral bioavailability, antidiabetic and antioxidant efficacy. Nanomedicine. 2018;13(5):521–37.
Agrawal AK, Kumar K, Swarnakar NK, Kushwah V, Jain S. “Liquid crystalline nanoparticles”: rationally designed vehicle to improve stability and therapeutic efficacy of insulin following oral administration. Mol Pharm. 2017;14(6):1874–82.
Agrawal AK, Harde H, Thanki K, Jain S. Improved stability and antidiabetic potential of insulin containing folic acid functionalized polymer stabilized multilayered liposomes following oral administration. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1):350–60.
Chen TT, Li SY, Zhu WT, Liang Z, Zeng QB. Self-assembly pH-sensitive chitosan/alginate coated polyelectrolyte complexes for oral delivery of insulin. J Microencapsul. 2019;36:96–107.
Wong CY, Al-Salami H. Dass CR. AAPS PharmSciTech: Lyophilisation improves bioactivity and stability of insulin-loaded polymeric-oligonucleotide nanoparticles for diabetes treatment; 2020.
Urimi D, Agrawal AK, Kushwah V, Jain S. Polyglutamic acid functionalization of chitosan nanoparticles enhances the therapeutic efficacy of insulin following oral administration. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;20(3):131.
Lang XQ, Wang T, Sun MJ, Chen XG, Liu Y. Advances and applications of chitosan-based nanomaterials as oral delivery carriers: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;154:433–45.
Yan C, Gu J, Lv Y, Shi W, Huang Z, Liao Y. 5-cholanic acid/glycol chitosan self-assembled nanoparticles (5-CHA/GC-NPs) for enhancing the absorption of FDs and insulin by rat intestinal membranes. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;20:30.
Agrawal AK, Urimi D, Harde H, Kushwah V, Jain S. Folate appended chitosan nanoparticles augment the stability, bioavailability and efficacy of insulin in diabetic rats following oral administration. RSC Adv. 2015;5(127):105179–93.
Abeer MM, Meka AK, Pujara N, Kumeria T, Strounina E, Nunes R, et al. Rationally designed dendritic silica nanoparticles for oral delivery of Exenatide. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(8).
George M, Abraham TE. Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: alginate and chitosan - a review. J Control Release. 2006;114:1–14.
Hua SB, Ma HZ, Li X, Yang HX, Wang A. pH-sensitive sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads prepared by combined Ca2+ crosslinking and freeze-thawing cycles for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Int J Biol Macromol. 2010;46:517–23.
Abeer MM, Rewatkar P, Qu Z, Talekar M, Kleitz F, Schmid R, et al. Silica nanoparticles: a promising platform for enhanced oral delivery of macromolecules. J Control Release. 2020;326:544–55.
Li LL, Liu TL, Fu CH, Tan LF, Meng XW, Liu HY. Biodistribution, excretion, and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles after oral administration depend on their shape. Nanomed-Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2015;11(8):1915–24.
Lamson NG, Berger A, Fein KC, Whitehead KA. Anionic nanoparticles enable the oral delivery of proteins by enhancing intestinal permeability. Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2020;4(1):84–96.
Qu Z, Wong KY, Moniruzzaman M, Begun J, Santos HA, Hasnain SZ, et al. One-Pot synthesis of pH-responsive Eudragit-mesoporous silica nanocomposites enable colonic delivery of glucocorticoids for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Advanced therapeutics. 2021;4(2):2000165.
Raza A, Alavi SE, Sime FB, Han FY, Roberts JA, Popat A, et al. Microfluidic assembly of pomegranate-like hierarchical microspheres for efflux regulation in oral drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:277–90.
Hou L, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Hu Y, Shi J, Liu Q, et al. Self-regulated carboxyphenylboronic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles with "touch switch" releasing property for insulin delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:21927–38.
Shen D, Yu H, Wang L, Khan A, Haq F, Chen X, et al. Recent progress in design and preparation of glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems. J Control Release. 2020;321:236–58.
Volpatti LR, Matranga MA, Cortinas AB, Delcassian D, Daniel KB, Langer R, et al. Glucose-responsive nanoparticles for rapid and extended self-regulated insulin Delivery. ACS Nano. 2020;14(1):488–97.
Yin R, Wang K, Du S, Chen L, Nie J, Zhang W. Design of genipin-crosslinked microgels from concanavalin A and glucosyloxyethyl acrylated chitosan for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;103(1):369–76.
Shi D, Ran M, Zhang L, Huang H, Li X, Chen M, et al. Fabrication of biobased polyelectrolyte capsules and their application for glucose-triggered insulin Delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:13688–97.
Yetisen AK, Jiang N, Fallahi A, Montelongo Y, Ruiz-Esparza GU, Tamayol A, et al. Glucose-sensitive hydrogel optical fibers functionalized with phenylboronic acid. Adv Mater. 2017;29:11.
Brooks WLA, Deng CC, Sumerlin BS. Structure–reactivity relationships in boronic acid–diol complexation. ACS Omega. 2018;3:17863–70.
Springsteen G, Wang B. A detailed examination of boronic acid–diol complexation. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:5291–300.
Matsumoto A, Ikeda S, Harada A, Kataoka K. Glucose-responsive polymer bearing a novel phenylborate derivative as a glucose-sensing moiety operating at physiological pH conditions. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:1410–6.
Matsumoto A, Ishii T, Nishida J, Matsumoto H, Kataoka K, Miyahara Y. A synthetic approach toward a self-regulated insulin delivery system. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition. 2012;51:2124–8.
Shen DK, Yang JP, Li XM, Zhou L, Zhang RY, Li W, et al. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica Nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014;14(2):923–32.
Juere E, Caillard R, Marko D, Del Favero G, Kleitz F. Smart protein-based formulation of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles: toward oral delivery of insulin. Chem Eur J. 2020;26(23):5195–9.
Belbekhouche S, Charaabi S, Picton L, Le Cerf D, Carbonnier B. Glucose-sensitive polyelectrolyte microcapsules based on (alginate/chitosan) pair. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;184:144–53.
Mansour O, El Joukhar I, Belbekhouche S. H2O2-sensitive delivery microparticles based on the boronic acid chemistry: (phenylboronic-alginate derivative/dextran) system. React Funct Polym. 2019;145:104377.
Zhang D, Yu GH, Long Z, Yang GH, Wang B. Controllable layer-by-layer assembly of PVA and phenylboronic acid-derivatized chitosan. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;140:228–32.
Han CY, Huang HT, Dong Y, Sui XY, Jian BY, Zhu WQ. A comparative study of the use of mesoporous carbon and mesoporous silica as drug carriers for oral delivery of the water-insoluble drug carvedilol. Molecules. 2019;24(9).
Gu Z, Aimetti AA, Wang Q, Dang TT, Zhang YL, Veiseh O, et al. Injectable nano-network for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. ACS Nano. 2013;7(5):4194–201.
Zhao LL, Jin WL, Cruz JG, Marasini N, Khalil ZG, Capon RJ, et al. Development of polyelectrolyte complexes for the delivery of peptide-based subunit vaccines against group A streptococcus. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(5).
Hou L, Zheng YZ, Wang YC, Hu YR, Shi JJ, Liu Q, et al. Self-regulated carboxyphenylboronic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles with "touch switch" releasing property for insulin delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(26):21927–38.
Ji N, Hong Y, Gu ZB, Cheng L, Li ZF, Li CM. Chitosan coating of zein-carboxymethylated short-chain amylose nanocomposites improves oral bioavailability of insulin in vitro and in vivo. J Control Release. 2019;313:1–13.
Tian MP, Song RX, Wang T, Sun MJ, Liu Y, Chen XG. Inducing sustained release and improving oral bioavailability of curcumin via chitosan derivatives-coated liposomes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120:702–10.
Li SY, Chen ZR, Wang J, Yan LB, Chen TT, Zeng QB. Fabrication and characterization of a novel semi-interpenetrating network hydrogel based on sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and poly(methacrylic acid) for oral insulin delivery. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(1):3–14.
Chen XY, Wu W, Guo ZZ, Xin JY, Li JS. Controlled insulin release from glucose-sensitive self-assembled multilayer films based on 21-arm star polymer. Biomaterials. 2011;32(6):1759–66.
Jiao JQ, Fu JY, Wei YC, Zhao Z, Duan AJ, Xu CM, et al. Al-modified dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres-supported NiMo catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene: efficient accessibility of active sites and suitable metal-support interaction. J Catal. 2017;356:269–82.
Pettignano A, Grijalvo S, Haring M, Eritja R, Tanchoux N, Quignard F, et al. Boronic acid-modified alginate enables direct formation of injectable, self-healing and multistimuli-responsive hydrogels. Chem Commun. 2017;53(23):3350–3.
Shi DJ, Ran MS, Huang H, Zhang L, Li XJ, Chen MQ, et al. Preparation of glucose responsive polyelectrolyte capsules with shell crosslinking via the layer-by-layer technique and sustained release of insulin. Polym Chem. 2016;7(44):6779–88.
Smoum R, Rubinstein A, Srebnik M. Chitosan-pentaglycine-phenylboronic acid conjugate: a potential colon-specific platform for calcitonin. Bioconjug Chem. 2006;17(4):1000–7.
Li J, Wang PG, Zhang N, Yang Y, Zheng JB. Enhanced detection of saccharide using redox capacitor as an electrochemical indicator via a redox-cycling and its molecular logic behavior. Electrochim Acta. 2015;166:253–60.
Castangia I, Manca ML, Caddeo C, Maxia A, Murgia S, Pons R, et al. Faceted phospholipid vesicles tailored for the delivery of Santolina insularis essential oil to the skin. Colloid Surface B. 2015;132:185–93.
Tsuboi T, McMahon HT, Rutter GA. Mechanisms of dense core vesicle recapture following "kiss and run" ("cavicapture") exocytosis in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(45):47115–24.
Yu JC, Zhang YQ, Wang JQ, Wen D, Kahkoska AR, Buse JB, et al. Glucose-responsive oral insulin delivery for postprandial glycemic regulation. Nano Res. 2019;12(7):1539–45.
Leng D, Li Y, Zhu J, Liang RZ, Zhang CF, Zhou Y, et al. The antibiofilm activity and mechanism of nanosilver- and nanozinc-incorporated mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:3921–36.
Li L, Jiang GH, Yu WJ, Liu DP, Chen H, Liu YK, et al. Preparation of chitosan-based multifunctional nanocarriers overcoming multiple barriers for oral delivery of insulin. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2017;70:278–86.
Shan W, Zhu X, Liu M, Li L, Zhong JJ, Sun W, et al. Overcoming the diffusion barrier of mucus and absorption barrier of epithelium by self-assembled nanoparticles for oral delivery of insulin. ACS Nano. 2015;9(3):2345–56.
Ihlo CA, Lauritzen T, Sturis J, Skyggebjerg O, Christiansen JS, Laursen T. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of different modes of insulin pump delivery. A randomized, controlled study comparing subcutaneous and intravenous administration of insulin aspart. Diabet Med. 2011;28(2):230–6.
Wang JQ, Yu J, Zhang YQ, Zhang XD, Kahkoska AR, Chen GJ, et al. Charge-switchable polymeric complex for glucose-responsive insulin delivery in mice and pigs. Science Advances. 2019;5(7).
Alibolandi M, Alabdollah F, Sadeghi F, Mohammadi M, Abnous K, Ramezani M, et al. Dextran-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) polymersome for oral delivery of insulin: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2016;227:58–70.
Sheng JY, Han LM, Qm J, Ru G, Li RX, Wu LH, et al. N-Trimethyl chitosan chloride-coated PLGA nanoparticles overcoming multiple barriers to oral insulin absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(28):15430–41.
Bravo-Osuna I, Millotti G, Vauthier C, Ponchel G. In vitro evaluation of calcium binding capacity of chitosan and thiolated chitosan poly(isobutyl cyanoacrylate) core-shell nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2007;338(1-2):284–90.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant [number 81373365] and Guangdong Science and Technology Project under Grant [number 2015A010105014].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, T., Yan, L., Wang, X. et al. Glucose-Responsive Polyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for Oral Insulin Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 22, 226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02088-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02088-6