Abstract
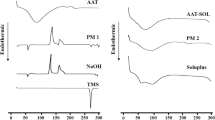
Telmisartan (TLM) is a potent antihypertensive drug with pH-dependent aqueous solubility. This work aimed to enhance the solubility and dissolution rate of TLM by the co-amorphous drug amino acid (AA) approach by combining TLM, with different types and ratios of AAs. The co-amorphous TLM-AA blends were prepared by freeze-drying and investigated for solid-state characteristics like the dissolution rate enhancement of TLM. Among the prepared co-amorphous formulations, TLM-arginine (ARG) exhibited the greatest enhancement in solubility with increasing the molar ratio of ARG. The TLM-ARG at 1:2 ratio showed about a 57-fold increase in solubility of TLM and the highest dissolution percentage in phosphate buffer (pH7.5) (100% in 20 minutes) compared to both crystalline TLM (20% in 60 min) and physical mixture. Powder XRD, DSC, FTIR analysis and SEM demonstrated the formation of amorphous form within the co-amorphous formulations. Only TLM:ARG (1:0.5) were stable at (40°C, 75% RH) for a minimum of 90 days. In conclusion, ARG was able to stabilize the amorphous form of TLM and enhances its aqueous solubility and dissolution. The 1:2 w/w ratio of TLM-ARG co-amorphous showed the best solubility and dissolution rate while the 1:0.5 w/w ratio showed the best stability.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wienen W, Entzeroth M, Meel JC, Stangier J, Busch U, Ebner T, et al. A review on telmisartan: a novel, long-acting angiotensin II-receptor antagonist. Cardiovasc Ther. 2000;18(2):127–54.
Wienen W, Entzeroth M, van Meel JCA, Stangier J, Busch U, Ebner T, et al. A review on telmisartan: a novel, long-acting angiotensin II-receptor antagonist. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews 2000;18(2):127-154.
Arora P, Kaur A, Haneef J, Chadha R. solubility improvement of telmisartan by cocrystallization with citric acid. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2017;8(9):3768–75.
Chadha R, Bhandari S, Haneef J, Khullar S, Mandal S. Cocrystals of telmisartan: characterization, structure elucidation, in vivo and toxicity studies. CrystEngComm. 2014;16(36):8375–89.
Haneef J, Chadha R. Drug-drug multicomponent solid forms: cocrystal, coamorphous and eutectic of three poorly soluble antihypertensive drugs using mechanochemical approach. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017:1–12.
Alatas F, Ratih H, Soewandhi SN. Enhancement of solubility and dissolution rate of telmisartan by telmisartan-oxalic acid cocrystal formation. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;7:423–6.
Reddy VV, Aswini M, Harini P, Prathyusha B, Sreevani MS. Design and characterization of microcrystals for enhanced dissolution rate of telmisartan. International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Research. 2013;4(1):263–8.
Choi J-S. Enhanced stability and solubility of pH-dependent drug, telmisartan achieved by solid dispersion. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2017;37:194–203.
Tran PHL, Tran HTT, Lee B-J. Modulation of microenvironmental pH and crystallinity of ionizable telmisartan using alkalizers in solid dispersions for controlled release. J Control Release. 2008;129(1):59–65.
Dukeck R, Sieger P, Karmwar P. Investigation and correlation of physical stability, dissolution behaviour and interaction parameter of amorphous solid dispersions of telmisartan: a drug development perspective. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;49(4):723–31.
Phulzalke S, Kate B, Bagade M. Solubility enhancement of telmisartan using mixed hydrotropy approach. Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015;5(50):38–40.
Jaiswal P, Aggarwal G, Harikumar SL, Singh K. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system and solid-self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of telmisartan. International journal of pharmaceutical investigation. 2014;4(4):195–206.
Ahmad J, Kohli K, Mir SR, Amin S. Formulation of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for telmisartan with improved dissolution and oral bioavailability. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2011;32(7):958–68.
Swamy N, Shiny E. Formulation and evaluation of telmisartan liquisolid tablets. Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2013;3(3):49–57.
Chella N, Narra N, Rama RT. Preparation and characterization of liquisolid compacts for improved dissolution of telmisartan. J Drug Deliv. 2014;2014:1–10.
Zhang Y, Jiang T, Zhang Q, Wang S. Inclusion of telmisartan in mesocellular foam nanoparticles: drug loading and release property. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2010;76(1):17–23.
Sharma C, Desai MA, Patel SR. Ultrasound-assisted anti-solvent crystallization of telmisartan using dimethyl sulfoxide as organic solvent. Cryst Res Technol. 2018;53(3):1–9.
Lepek P, Sawicki W, Wlodarski K, Wojnarowska Z, Paluch M, Guzik L. Effect of amorphization method on telmisartan solubility and the tableting process. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;83(1):114–21.
Sangwai M, Vavia P. Amorphous ternary cyclodextrin nanocomposites of telmisartan for oral drug delivery: improved solubility and reduced pharmacokinetic variability. Int J Pharm. 2013;453(2):423–32.
Rao M, Bajaj A, Khole I, Munjapara G, Trotta F. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of telmisartan. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2013;77(1-4):135–45.
Borba PAA, Pinotti M, Andrade GRS, da Costa Jr NB, Junior LRO, Fernandes D, et al. The effect of mechanical grinding on the formation, crystalline changes and dissolution behaviour of the inclusion complex of telmisartan and β-cyclodextrins. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;133:373–83.
Isaac J, Ganguly S, Ghosh A. Co-milling of telmisartan with poly (vinyl alcohol)–an alkalinizer free green approach to ensure its bioavailability. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;101:43–52.
Ali AMA, Ali AA, Maghrabi IA. Clozapine-carboxylic acid plasticized co-amorphous dispersions: preparation, characterization and solution stability evaluation. Acta Pharma. 2015;65(2):133–46.
Thakuria R, Sarma B. Drug-drug and drug-nutraceutical cocrystal/salt as alternative medicine for combination therapy: a crystal engineering Approach. Crystals. 2018;8(2):101–40.
Blagden N, de Matas M, Gavan PT, York P. Crystal engineering of active pharmaceutical ingredients to improve solubility and dissolution rates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59(7):617–30.
Yadav A, Shete A, Dabke A, Kulkarni P, Sakhare S. Co-crystals: a novel approach to modify physicochemical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009;71(4):359–70.
Al-Remawi M, Ali AMA, Khames A, Hamaidi M. Meloxicam-paracetamol binary solid dispersion systems with enhanced solubility and dissolution rate: preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation. J Pharm Innov. 2017;12(3):206–15.
Mesallati H, Conroy D, Hudson S, Tajber L. Preparation and characterization of amorphous ciprofloxacin-amino acid salts. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;121:73–89.
Liu M, Hong C, Yao Y, Shen H, Ji G, Li G, et al. Development of a pharmaceutical cocrystal with solution crystallization technology: preparation, characterization, and evaluation of myricetin-proline cocrystals. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;107:151–9.
Pradhan S, Hedberg J, Blomberg E, Wold S, Odnevall Wallinder I. Effect of sonication on particle dispersion, administered dose and metal release of non-functionalized, non-inert metal nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2016;18(9):285-.
Elshanawane AA, Abdelaziz LM, Kamal MM, Hafez HM. Quantitative determination of telmisartan, ramipril, amlodipine besylate, and atorvastatin calcium by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2014;37(2):195–206.
Real D, Orzan L, Leonardi D, Salomon CJ. Improving the dissolution of triclabendazole from stable crystalline solid dispersions formulated for oral delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;21(1):16.
Rambo MKD, Ferreira MMC. Determination of cellulose crystallinity of banana residues using near infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J Braz Chem Soc. 2015;26:1491–9.
Torrado G, Fraile S, Torrado S, Torrado S. Process-induced crystallite size and dissolution changes elucidated by a variety of analytical methods. Int J Pharm. 1998;166(1):55–63.
Diaz DA, Colgan ST, Langer CS, Bandi NT, Likar MD, Van Alstine L. Dissolution similarity requirements: how similar or dissimilar are the global regulatory expectations? AAPS J. 2016;18(1):15–22.
Sterren VB, Aiassa V, Garnero C, Linck YG, Chattah AK, Monti GA, et al. Preparation of chloramphenicol/amino acid combinations exhibiting enhanced dissolution rates and reduced drug-induced oxidative stress. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18(8):2910–8.
Khanfar M, Al-Taani B, Alsmadi M, Zayed A. Enhancement of the dissolution and bioavailability from freeze-dried powder of a hypocholesterolemic drug in the presence of Soluplus. Powder Technol. 2018;329:25–32.
Amend J, Helgeson H. Solubilities of the common L-α-amino acids as a function of temperature and solution pH. Pure Appl Chem. 1997;69(5):935–42.
Liu W, Guo Y, Chen J, Yu X. Measurement and correlation of the solubility of telmisartan (form A) in nine different solvents from 277.85 to 338.35 K. J Solut Chem. 2016;45(6):932–46.
Censi R, Di Martino P. Polymorph impact on the bioavailability and stability of poorly soluble drugs. Molecules. 2015;20(10):18759–76.
Huang Y, Zhang Q, Wang J-R, Lin K-L, Mei X. Amino acids as co-amorphous excipients for tackling the poor aqueous solubility of valsartan. Pharm Dev Technol. 2017;22(1):69–76.
Rangsimawong W, Wattanasri P, Tonglairoum P, Akkaramongkolporn P, Rojanarata T, Ngawhirunpat T, et al. Development of microemulsions and microemulgels for enhancing transdermal delivery of Kaempferia parviflora extract. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(5):2058–67.
Childs SL, Chyall LJ, Dunlap JT, Smolenskaya VN, Stahly BC, Stahly GP. Crystal engineering approach to forming cocrystals of amine hydrochlorides with organic acids. Molecular complexes of fluoxetine hydrochloride with benzoic, succinic, and fumaric acids. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(41):13335–42.
Affandi RMM, Meor M, Tripathy M, Majeed ABA. Arginine complexes with simvastatin: apparent solubility, in vitro dissolution and solid state characterization. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(1):77–86.
Marasini N, Tran TH, Poudel BK, Cho HJ, Choi YK, Chi S-C, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of pH-modulated solid dispersion for telmisartan by spray-drying technique. Int J Pharm. 2013;441(1-2):424–32.
Tilborg A, Springuel G, Norberg B, Wouters J, Leyssens T. On the influence of using a zwitterionic coformer for cocrystallization: structural focus on naproxen–proline cocrystals. CrystEngComm. 2013;15(17):3341–50.
He H, Huang Y, Zhang Q, Wang J-R, Mei X. Zwitterionic cocrystals of flavonoids and proline: solid-state characterization, pharmaceutical properties, and pharmacokinetic performance. Cryst Growth Des. 2016;16(4):2348–56.
Qi X, Zhang J, Wang W, Cao D. Solubility and stability of indomethacin in arginine-assisted solubilization system. Pharm Dev Technol. 2013;18(4):852–5.
Jensen KT, Löbmann K, Rades T, Grohganz H. Improving co-amorphous drug formulations by the addition of the highly water soluble amino acid, proline. Pharmaceutics. 2014;6(3):416–35.
Real D, Hoffmann S, Leonardi D, Salomon C, Goycoolea F. Chitosan-based nanodelivery systems applied to the development of novel triclabendazole formulations. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0207625.
Shimpi MR, Childs SL, Boström D, Velaga SP. New cocrystals of ezetimibe with L-proline and imidazole. CrystEngComm. 2014;16(38):8984–93.
Newman A, Reutzel-Edens SM, Zografi G. Coamorphous active pharmaceutical ingredient–small molecule mixtures: considerations in the choice of coformers for enhancing dissolution and oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci. 2018;107(1):5–17.
Tang L, Khan SU, Muhammad NA. Evaluation and selection of bio-relevant dissolution media for a poorly water-soluble new chemical entity. Pharm Dev Technol. 2001;6(4):531–40.
Patel H, Patel H, Gohel M, Tiwari S. Dissolution rate improvement of telmisartan through modified MCC pellets using 3 2 full factorial design. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2016;24(5):579–87.
Affandi M, Tripathy M, Majeed ABA. Arginine complexes with simvastatin: apparent solubility, in vitro dissolution and solid state characterization. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(1):77–86.
Bakheit AH, Abd-Elgalil AA, Mustafa B, Haque A, Wani TA. Telmisartan. Profiles of drug substances, excipients and related methodology. 40: Elsevier; 2015. p. 371-429.
Zou X, Sha A, Ding B, Tan Y, Huang X. Evaluation and analysis of variance of storage stability of asphalt binder modified by nanotitanium dioxide. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2017;2017:6319697.
Guidence for industry: dissolution testing of immediate release solid oral dosage forms. The US Food and Drug Administration Guidance. 1997;(SUPAC–IR), Rockville, MD.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support, grant number (101/ 2018) provided by Jordan University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanfar, M., Al-Remawi, M., Al-Akayleh, F. et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Co-amorphous Formulations of Telmisartan—Amino Acids as a Potential Method for Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech 22, 112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-01952-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-01952-9