Abstract
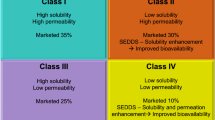
The most common route of the drug administration is oral route despite the fact that most drugs have low oral aqueous solubility and bioavailability especially for BCS class II and class IV drugs. Many methods have been developed in recent years to overcome the poor solubility and oral bioavailability which includes self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) as one of the approaches. Not only for hydrophobic drugs, but also for hydrophilic compounds with low permeability, bioavailability can be enhanced by self nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems. Recently, a lot of focus and attention has been put in the conversion of liquid SEDDS (L-SEDDS) to solid SEDDS (S-SEDDS) to overcome the limitations of liquid formulations related to their physical and chemical stability, portability, accurate dosing, and limited choices of dosage forms. This article aims to review the formulation components used in SEDDS, various approaches used in the conversion of L-SEDDS to S-SEDDS, their applications, merits, and demerits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma S, Bajaj H, Bhardwaj P, Sharma AD, Singh R. Development and characterization of self emulsifying drug delivery system of a poorly water soluble drug using natural oil. Acta Pol Pharm Drug Res. 2012;69(4):713–7.
Chowdary KA, Babu VP, Baratam SR. Formulation and in vitro characterisation of self emulsifying drug delivery system of Diclofenac. IJRASET. 2017;5(II):663–72.
Silva LAD, Almeida SL, Alonso ECP, Priscila BR, Martins FT, Freitas LAP, et al. Preparation of a solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system by hot-melt extrusion. Int J Pharm. 2018;541(1-2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.02.020.
Cheng G, Hu R, Ye L, Wang B, Gui Y, Gao S, et al. Preparation and in vitro / in vivo evaluation of puerarin solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system by spherical crystallization technique. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(6):1336–46. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-015-0469-8.
Kommuru TR, Gurley B, Khan MA, Reddy IK. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of coenzyme Q10: formulation development and bioavailability assessment. Int J Pharm. 2001;212:233–46.
Madagul JK, Parakh DR, Kumar RS, Abhang RR. Formulation and evaluation of solid self micro-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SMEDDS) of chlorthalidone by spray drying technology. Dry Technol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2016.1201833.
Chintalapudi R, Murthy TEGK, Lakshmi KR, Manohar GG. Formulation, optimization, and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems of nevirapine. Int J Pharm Investig. 2015;5(4):205–13.
Gupta S, Kesarla R, Omri A. Formulation strategies to improve the bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs with special emphasis on self-emulsifying systems. ISRN Pharm. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/848043.
Gurav NP, Dandagi PM, Gadad AP. Solubility enhancement of satranidazole using self emulsified drug delivery systems. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2016;50(3). https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.50.2.2050(3).
Müllertz A, Ogbonna A, Ren S. New perspectives on lipid and surfactant based drug delivery systems for oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010;62:1622–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01107.x.
Dokania S, Joshi AK. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS)—challenges and road ahead. Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):675–90. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.896058.
Pouton CW. Lipid formulations for oral administration of the drugs: non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and “self-microemulsifying” drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;11(Suppl. 2):S93–8.
Pouton CW. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: Physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:278–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2006.04.016.
Pouton CW, Porter CJH. Formulation of lipid-based delivery systems for oral administration : materials , methods and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:625–37.
Myers RA, Stella VJ. Systemic bioavailability of penclomedine (NSC-338720) from oil-in-water emulsions administered intraduodenally to rats. Int J Pharm. 1992;78(1–3):217–26.
Carrigan PJ, Bates TR. Biopharmaceutics of the drugs administered in lipid-containing dosage forms I: GI absorption of griseofulvin from an oil-in-water emulsion in the rat. J Pharm Sci. 1973;62(9):1476–9.
Rahman MA, Hussain A, Hussain MS, Mirza MA, Iqbal Z. Role of excipients in successful development of self-emulsifying/ microemulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS/SMEDDS). Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013;39(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2012.660949.
Truong DH, Tran TH, Ramasamy T, Choi JY, Lee HH, Moon C, et al. Development of solid self-emulsifying formulation for improving the oral bioavailability of erlotinib. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016;17(2):466–73. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-015-0370-5.
Porter CJH, Pouton CW, Cuine JF, Charman WN. Enhancing intestinal drug solubilisation using lipid-based delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:673–91.
Strickley RG. Solubilizing excipients in oral and injectable formulations. Pharm Res. 2004;21(2):201–30.
Gursoy RN, Benita S. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004;58(3):173–82.
Khan BA, Bakhsh S, Khan H, Mahmood T, Rasul A. Basics of self micro emulsifying drug delivery system. J Pharm Alternat Med. 2012;1(M):13–20.
Small DM. A classification of biologic lipids based upon their interaction in aqueous systems. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1968;45:108–19.
Azeem A, Rizwan M, Ahmad FJ, Iqbal Z, Khar RK, Aqil M, et al. Nano emulsion components screening and selection: a technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9178-x.
Yetukuri K, Satisha P, Srinivasan S, Thakur RS, Uma Shankar MS. Solid-self emulsifying drug delivery system : formulation techniques and dosage forms. 2011;10(3):87–93.
Saurabh SS, Issarani R, Nagori BP. Formulation and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery system of etoricoxib. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2017;10(7):367–72.
Sinha VR, Ghai D. Formulation design and development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems containing a hydrophobic selective β1-adrenoreceptor blocker. Int J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;6(3):154–67.
Tang B, Cheng G, Gu JC, Xu CH. Development of solid self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: preparation techniques and dosage forms. Drug Discov Today. 2008;13(13/14):606–12.
Khan AW, Kotta S, Ansari SH, Sharma RK, Ali J. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of the poorly water-soluble grapefruit flavonoid Naringenin: design, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2015;22(4):552–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2013.878003.
Zvonar A. Lipid-based systems as a promising approach for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Pharma. 2013;63:427–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/acph-2013-0040.
Soliman KAB, Ibrahim HK, Ghorab MM. Formulation of risperidone as self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system in form of effervescent tablets. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2012;33(8):1127–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2011.599235.
Nokhodchi A, Maghsoodi M. Preparation of spherical crystal agglomerates of naproxen containing disintegrant for direct tablet making by spherical crystallization technique. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(1):54–9. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-007-9019-3.
Sun C, Gui Y, Hu R, Chen J, Wang B, Guo Y, et al. Preparation and pharmacokinetics evaluation of solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system ( S-SMEDDS ) of osthole. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(5):2301–10. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1067-3.
Maghsoodi M, Nokhodchi A. Agglomeration of celecoxib by quasi emulsion solvent diffusion method: effect of stabilizer. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016;6(4):607–16. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2016.075.
Dobry DE, Settell DM, Baumann JM, Ray RJ, Graham LJ, Beyerinck RA. A model-based methodology for spray-drying process development. J Pharm Innov. 2009;4(3):133–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-009-9064-4.
Balakrishnan P, Lee BJ, Oh DH, Kim JO, Hong MJ, Jee JP, et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability of dexibuprofen by a novel solid Self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72(3):539–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.03.001.
Rajesh SY, Singh SK, Pandey NK, Sharma P, Bawa P, Kumar B, et al. Impact of various solid carriers and spray drying on pre/post compression properties of solid SNEDDS loaded with glimepiride: in vitro-ex vivo evaluation and cytotoxicity assessment. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2018.1431656.
Kim DW, Kang JH, Oh DH, Yong CS, Choi HG. Development of novel flurbiprofen-loaded solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system using gelatin as solid carrier. J Microencapsul. 2012;29(4):323–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2011.651497.
Chen Y, Chen C, Zheng J, Chen Z, Shi Q, Liu H. Development of a solid supersaturatable self-emulsifying drug delivery system of docetaxel with improved dissolution and bioavailability. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(2):278–86.
Bushra R, Ahmed A, Shahadat M. Mechanism of adsorption on nanomaterials. Nanomater Chromatogr. 2017;2: 90-111 p. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812792-6/00004-2.
Cirri M, Roghi A, Valleri M, Mura P. Development and characterization of fast- dissolving tablet formulations of glyburide based on solid self-microemulsifying systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.04.008.
Patel H, Patel P, Patel M, Mehta D, Misan C. Development and characterization of liquid and solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of Tacrolimus. Asian J Pharm. 2012;43:385–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-013-0083-2.
Javed M, Mallikarjun C, Gan W. Enhancement of solubility and therapeutic potential of poorly soluble lovastatin by SMEDDS formulation adsorbed on directly compressed spray dried magnesium aluminometasilicate liquid loadable tablets : a study in diet induced hyperlipidemic. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2015;10(1):40–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.08.003.
Gumaste SG, Freire BOS, Serajuddin ATM. Development of solid SEDDS, VI: effect of precoating of Neusilin® US2 with PVP on drug release from adsorbed self-emulsifying lipid-based formulations. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.02.022.
Tan DK, Maniruzzaman M, Nokhodchi A. Advanced pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion coupled with fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing for personalised drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10:203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040203.
Tiwari RV, Patil H, Repka MA. Contribution of hot-melt extrusion technology to advance drug delivery in the 21st century. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(3):451–64. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2016.1126246.
Takabe H, Warnken ZN, Zhang Y, Davis DA, Smyth HDC, Kuhn JG, et al. A repurposed drug for brain cancer: Enhanced atovaquone amorphous solid dispersion by combining a spontaneously emulsifying component with a polymer carrier. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10:60. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020060.
Bhandari V, Avachat A. Formulation and characterization of self emulsifing pellets of carvedilol. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2015;51(3):663–72. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-82502015000300018.
Zhiyuan W. Solid self-emulsifying nitrendipine pellets: preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 383:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010;2009.08.014.
Abbaspour M, Jalayer N, Makhmalzadeh BS. Development and evaluation of a solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for loratadin by extrusion-spheronization. Adv Pharm Bull. 2014;4(2):113–9. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2014.018.
Abdalla A, Klein S, Mäder K. A new self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for poorly soluble drugs: characterization, dissolution, in vitro digestion and incorporation into solid pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008;35(5):457–64.
Madan J, Sudarshan B, Kadam V, Kamal D. Formulation and development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of pioglitazone hydrochloride. Asian J Pharm. 2014; Available from: http://www.asiapharmaceutics.info/text.asp 2014/8/1/27/134097.
Kanaujia P, Ng WK, Tan RBH. Solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SEDDS) for improved dissolution rate of fenofibrate. J Microencapsul. 2014. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2013.843601.
Mcconville C, Friend D. Development and characterisation of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems ( SMEDDSs ) for the vaginal administration of the antiretroviral UC-781. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;83:322–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.10.007.
Tsinontides SC, Rajniak P, Pham D, Hunke WA, Placek J, Reynolds SD. Freeze drying—principles and practice for successful scale-up to manufacturing. Int J Pharm. 2004;280:1–16.
Gaidhani KA, Harwalkar M, Bhambere D. Lyophilization / freeze drying—a review. World J Pharm Res. 2015;4(8):516–43.
Yang X, Li F, Guo Y, Zhang X, Pan W, Zhao Q, et al. Preparation and pharmacokinetics evaluation of oral self-emulsifying system for poorly water-soluble drug Lornoxicam. Drug Deliv. 2014. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.885615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, S.R.D., Tippavajhala, V.K. A Rundown Through Various Methods Used in the Formulation of Solid Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SEDDS). AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 323 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1550-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1550-5