Abstract
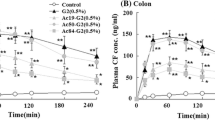
We aimed to investigate the absorption-enhancing effect (AEE) of caproyl-modified G2 PAMAM dendrimer (G2-AC) on peptide and protein drugs via the pulmonary route. In this study, G2 PAMAM dendrimer conjugates modified with caproic acid was synthesized, the pulmonary absorption of insulin as models with or without G2-AC were evaluated. The results indicated that G2-AC6 exhibited a greatest AEE for insulin in various caproylation levels of G2-AC. G2-AC6 could significantly enhance the absorption of insulin, and the AEE of G2-AC6 was concentration-dependent. In toxicity tests, G2-AC6 displayed no measurable cytotoxicity to the pulmonary membranes over a concentration range from 0.1% (w/v) to 1.0% (w/v). Measurements of the TEER and permeability showed that G2-AC6 significantly reduced the TEER value of CF and increased its Papp value. The results suggested that G2-AC6 could cross epithelial cells by means of a combination of paracellular and transcellular pathways. These findings suggested G2-AC6 at lower concentrations (below 1.0%, w/v) might be promising absorption enhancers for increasing the pulmonary absorption of peptide and protein drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agu RU, Ugwoke MI, Armand M, Kinget R, Verbeke N. The lung as a route for systemic delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides. Respir Res. 2001;2:198–209.
Paranjpe M, Müller-Goymann CC. Nanoparticle-mediated pulmonary drug delivery: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:5852–73.
Price DF, Luscombe CN, Eddershaw PJ, Edwards CD, Gumbleton M. The differential absorption of a series of P-glycoprotein substrates in isolated perfused lungs from Mdr1a/1b genetic knockout mice can be attributed to distinct physico-chemical properties: an insight into predicting transporter-mediated. Pulmonary Specific Disposition. Pharm Res. 2017;34:2498–516.
Patel LN, Wang J, Kim KJ, Borok Z, Crandall E, Shen WC. Conjugation with cationic cell-penetrating peptide increases pulmonary absorption of insulin. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:492–503.
Bruno BJ, Miller GD, Lim CS. Basics and recent advances in peptide and protein drug delivery. Ther Deliv. 2013;4:1443–67.
Esfand R, Tomalia DA. Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers: from biomimicry to drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discov Today. 2001;6:427–36.
Svenson S, Tomalia DA. Dendrimers in biomedical applications-reflections on the field. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:2106–29.
Yang H. Targeted nanosystems: advances in targeted dendrimersor cancer therapy. Nanomedicine. 2016;12:309–16.
Mendes LP, Pan J, Torchilin VP. Dendrimers as nanocarriers for nucleic acid and drug delivery in cancer therapy. Molecules. 2017;22:1401–4.
Bugno J, Hsu HJ, Hong S. Tweaking dendrimers and dendritic nanoparticles for controlled nano-bio interactions: potential nanocarriers for improved cancer targeting. J Drug Target. 2015;23:642–50.
Serramía MJ, Álvarez S, Fuentes-Paniagua E, Clemente MI, Sánchez-Nieves J, Gómez R, et al. In vivo delivery of siRNA to the brain by carbosilane dendrimer. J Control Release. 2015;200:60–70.
Bai S, Thomas C, Ahsan F. Dendrimers as a carrier for pulmonary delivery of enoxaparin, a low-molecular weight heparin. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96:2090–106.
Kaminskas LM, McLeod VM, Ascher DB, Ryan GM, Jones S, Chan LJ, et al. Methotrexate-conjugated PEGylated dendrimers show differential patterns of deposition and activity in tumor-burdened lymph nodes after intravenous and subcutaneous administration in rats. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:432–43.
Hubbard D, Enda M, Bond T, Moghaddam SP, Conarton J, Scaife C, et al. Transepithelial transport of PAMAM dendrimers across isolated human intestinal tissue. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:4099–107.
Black PN, Ahowesso C, Montefusco D, Saini N, Concetta C, DiRusso CC. Fatty acid transport proteins: targeting FATP2 as a gatekeeper involved in the transport of exogenous fatty acids. Medchemcomm. 2016;7:612–22.
Abdullah D, Ping QN, Liu GJ. Enhancing effect of essential oils on the penetration of 5-fluorouracil through rat skin. Acta Pharma Sin. 1996;31:214–6.
Jevprasesphant R, Penny J, Jalal R, Attwood D, McKeown NB, D’Emanuele A. The influence of surface modification on the cytotoxicity of PAMAM dendrimers. Int J Pharm. 2003;252:263–6.
Dong Z, Hamid KA, Gao Y, Lin Y, Katsumi H, Sakane T, et al. Polyamidoamine dendrimers can improve the pulmonary absorption of insulin and calcitonin in rats. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100:1866–78.
Chengyun Y, jing W, Jiwei G, Daping H. The influence of molecular parameters of chitosan on pulmonary absorption of insulin loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Lat Am J Pharm. 2013;32:860–8.
Ho W, Furst A. Intratracheal instillation method for mouse lungs. Oncology. 1973;27:385–93.
Okumura S, Fukuda Y, Takahashi K, Fujita T, Yamamoto A. Transport of drugs across the Xenopus pulmonary membrane and their absorption enhancement by various absorption enhancers. Pharmaceutical Research. 1996;13:1247–51.
Sadekar S, Ghandehari H. Transepithelial transport and toxicity of PAMAM dendrimers: implications for oral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:571–88.
Jevprasesphant R, Penny J, Attwood D, McKeown NB, D’Emanuele A. Engineering of dendrimer surfaces to enhance transepithelial transport and reduce cytotoxicity. Pharm Res. 2003;20:1543–50.
Yang Y, Sunoqrot S, Stowell C, Ji J, Lee C, Kim JW, et al. Effect of size, surface charge and hydrophobicity of poly(amidoamine) dendrimers on their skin penetration. Biomacromolecules. 2012;13:2154–62.
Bharatwaj B, Mohammad AK, Dimovski R, Cassio FL, Bazito RC, Conti D, et al. Dendrimer nanocarriers for transport modulation across models of the pulmonary epithelium. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:826–38.
Mendes LP, Pan J, Torchilin VP. Dendrimers as nanocarriers for nucleic acid and drug delivery in cancer therapy. Molecules. 2017;22:1401.
Zhong Q, Merkel OM, Reineke JJ, Rocha SRP. Effect of the route of administration and PEGylation of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers on their systemic and lung cellular biodistribution. Mol Pharm. 2016;13:1866–78.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support of these programs.
Funding
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31860266). This study was also supported in part by Guangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2018GXNSFAA281125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, C., Gu, J., Lv, Y. et al. Caproyl-Modified G2 PAMAM Dendrimer (G2-AC) Nanocomplexes Increases the Pulmonary Absorption of Insulin. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1505-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1505-x