Abstract
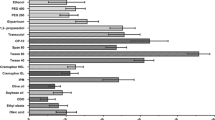
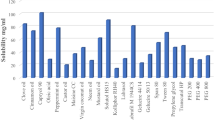
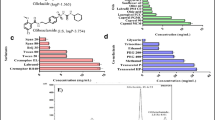
The goal of the present investigation is to formulate febuxostat (FXT) self-nanoemulsifying delivery systems (liquid SNEDDS, solid SNEDDS, and pellet) to ameliorate the solubility and bioavailability. To determine the self-nanoemulsifying region, ternary plot was constructed utilizing Capmul MCM C8 NF® as an oil phase, Labrasol® as principal surfactant, and Transcutol HP® being the co-surfactant. Liquid SNEDDS (L-SNEDDS) were characterized by evaluating droplet size, zeta potential, % transmission, and for thermodynamic stability. In vitro dissolution study of FXT loaded L-SNEDDS (batch F7) showed increased dissolution (about 48.54 ± 0.43% in 0.1 N HCl while 86.44 ± 0.16% in phosphate buffer pH 7.4 within 30 min) compared to plain drug (19.65 ± 2.95% in 0.1 N HCl while about 17.61 ± 2.63% in phosphate buffer pH 7.4 within 30 min). Single pass intestinal permeability studies revealed fourfold increase in the intestinal permeability of F7 compared to plain drug. So, for commercial aspects, F7 was further transformed into solid SNEDDS (S-SNEDDS) as readily nanoemulsifying powder form (SNEP) as well as pellets prepared by application of extruder spheronizer. The developed formulation was found superior to pure FXT with enhanced oral bioavailability and anti-gout activity (with reduced uric acid levels), signifying a lipidic system being an efficacious substitute for gout treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Love BL, Barrons R, Veverka A, Snider KM. Urate-lowering therapy for gout: focus on febuxostat. Pharmacotherapy. 2010;30:594–608.
Khosravan R, Grabowski B, Wu JT, Joseph-Ridge N, Vernillet L. Effect of food or antacid on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65:355–63.
Varsha M, Divekar B. Solubility enhancement and formulation of rapid disintegrating tablet of febuxostat cyclodextrin complex. BioMedRxBioMedRx [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2019 Jan 26];11:168–75. Available from: http://jprsolutions.info/files/final-file-56971b34f08349.53345893.pdf. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Maddileti D, Jayabun SK, Nangia A. Soluble cocrystals of the xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat. Cryst Growth Des. 2013;13:3188–96.
Kumar K, Srinivas L, Kishore V, Basha S. Formulation and evaluation of poorly soluble febuxostat orodispersable tablet. AjaddCoUk. 2014;2:191–202.
Ahuja BK, Jena SK, Paidi SK, Bagri S, Suresh S. Formulation, optimization and in vitro-in vivo evaluation of febuxostat nanosuspension. Int J Pharm. 2015;478:540–52.
Seo YG, Kim DH, Ramasamy T, Kim JH, Marasini N, Oh YK, et al. Development of docetaxel-loaded solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for enhanced chemotherapeutic effect. Int J Pharm. 2013;452:412–20.
Christophersen PC, Christiansen ML, Holm R, Kristensen J, Jacobsen J, Abrahamsson B, et al. Fed and fasted state gastro-intestinal in vitro lipolysis: in vitro in vivo relations of a conventional tablet, a SNEDDS and a solidified SNEDDS. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014;57:232–9.
Islambulchilar Z, Valizadeh H, Zakeri-Milani P. Systematic development of DoE optimized SNEDDS of sirolimus with enhanced intestinal absorption. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2014;24:620–7.
Mahmoud DB, Shukr MH, Bendas ER. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of cilostazol for oral and parenteral administration. Int J Pharm. 2014;476:60–9.
Akhtar N, Talegaonkar S, Ahad A, Khar RK, Jaggi M. Potential of a novel self nanoemulsifying carrier system to overcome P-glycoprotein mediated efflux of etoposide: in vitro and ex vivo investigations. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2015;28:18–27.
Kuentz M. Lipid-based formulations for oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2012;9.
Hassan TH, Metz H, Mäder K. Novel semisolid SNEDDS based on PEG-30-dipolyhydroxystearate: development and characterization. Int J Pharm. 2014;477:506–18.
Woo JS, Song YK, Hong JY, Lim SJ, Kim CK. Reduced food-effect and enhanced bioavailability of a self-microemulsifying formulation of itraconazole in healthy volunteers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008;33:159–65.
Balakrishnan P, Lee BJ, Oh DH, Kim JO, Hong MJ, Jee JP, et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability of dexibuprofen by a novel solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72:539–45.
Vohra AM, Patel CV, Kumar P, Thakkar HP. Development of dual drug loaded solid self microemulsifying drug delivery system: exploring interfacial interactions using QbD coupled risk based approach. J Mol Liq. 2017;242:1156–68.
Inugala S, Eedara BB, Sunkavalli S, Dhurke R, Kandadi P, Jukanti R, et al. Solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) of darunavir for improved dissolution and oral bioavailability: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2015;74:1–10.
Abbaspour M, Jalayer N, Makhmalzadeh BS. Development and evaluation of a solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for loratadin by extrusion-spheronization. Adv Pharm Bull. 2014;4:113–9.
Zeng L, Zhang Y. Development, optimization and in vitro evaluation of norcantharidin loadedself-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (NCTD-SNEDDS). Pharm Dev Technol. 2017;22:399–408.
Park JH, Kim DS, Mustapha O, Yousaf AM, Kim JS, Kim DW, et al. Comparison of a revaprazan-loaded solid dispersion, solid SNEDDS and inclusion compound: physicochemical characterisation and pharmacokinetics. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces [Internet. 2018 [cited 2019 Jun 25;162:420–6 Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0927776517308573. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Elkasabgy NA. Ocular supersaturated self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (S-SNEDDS) to enhance econazole nitrate bioavailability. Int J Pharm [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2019 Jun 25];460:33–44. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0378517313009393. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Craig DQM, Lievens HSR, Pitt KG, Storey DE. An investigation into the physico-chemical properties of self-emulsifying systems using low frequency dielectric spectroscopy, surface tension measurements and particle size analysis. Int J Pharm. 1993;96:147–55.
Nazzal S, Khan MA. Response surface methodology for the optimization of ubiquinone self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2004;3:23–31.
Chavda H, Patel J, Chavada G, Dave S, Patel A, Patel C. Self-nanoemulsifying powder of isotretinoin: preparation and characterization. J Powder Technol [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2019 Jan 26];2013:1–9. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jpt/2013/108569/abs/
Sunkavalli S, Eedara BB, Janga KY, Velpula A, Jukanti R, Bandari S. Preparation and characterization of docetaxel self-nanoemulsifying powders (SNEPs): a strategy for improved oral delivery. Korean J Chem Eng [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2019 Jan 26];33:1115–24. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0205-9
Mohamed DA, Al-okbi SY. Evaluation of anti-gout activity of some plant food extracts. Pol J Food Nutr Sci [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2019 Jan 26];58:389–95. Available from: http://agro.icm.edu.pl/agro/element/bwmeta1.element.agro-article-32e1e33d-8431-4edd-a82c-92fe8c8d814c. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Miao Y, Chen G, Ren L, Pingkai O. Characterization and evaluation of self-nanoemulsifying sustained-release pellet formulation of ziprasidone with enhanced bioavailability and no food effect. Drug Deliv. 2016;23:2163–72.
Patel J, Patel A, Raval M, Sheth N. Formulation and development of a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of irbesartan. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2013;2:9.
Pund S, Shete Y, Jagadale S. Multivariate analysis of physicochemical characteristics of lipid based nanoemulsifying cilostazol—quality by design. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 2014;115:29–36.
Rahman MA, Iqbal Z, Hussain A. Formulation optimization and in vitro characterization of sertraline loaded self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral administration. J Pharm Investig. 2012;42:191–202.
Kallakunta VR, Bandari S, Jukanti R, Veerareddy PR. Oral self emulsifying powder of lercanidipine hydrochloride: formulation and evaluation. Powder Technol. 2012;221:375–82.
Elkordy AA, Essa EA, Dhuppad S, Jammigumpula P. Liquisolid technique to enhance and to sustain griseofulvin dissolution: effect of choice of non-volatile liquid vehicles. Int J Pharm. 2012;434:122–32.
Gera S, Talluri S, Rangaraj N, Sampathi S. Formulation and evaluation of naringenin nanosuspensions for bioavailability enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017;18:3151–62.
Patel P, Pailla SR, Rangaraj N, Cheruvu HS, Dodoala S, Sampathi S. Quality by design approach for developing lipid-based nanoformulations of gliclazide to improve oral bioavailability and anti-diabetic activity. AAPS PharmSciTech [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2019 Jan 26];20:45. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1214-x
Sarvaiya VN, Sadariya KA, Pancha PG, Thaker AM, Patel AC, Prajapati AS. Evaluation of antigout activity of Phyllanthus emblica fruit extracts on potassium oxonate-induced gout rat model. Vet World. 2015;8:1230–6.
Taha EI, Al-Saidan S, Samy AM, Khan MA. Preparation and in vitro characterization of self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of all-trans-retinol acetate. Int J Pharm. 2004;285:109–19.
Singh AK, Chaurasiya A, Awasthi A, Mishra G, Asati D, Khar RK, et al. Oral bioavailability enhancement of exemestane from self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS). AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10:906–16.
Adel S, Elkasabgy NA. Design of innovated lipid-based floating beads loaded with an antispasmodic drug: in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. J Liposome Res [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2019 Jun 25];24:136–49. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3109/08982104.2013.857355
Basalious EB, Shawky N, Badr-Eldin SM. SNEDDS containing bioenhancers for improvement of dissolution and oral absorption of lacidipine. I: development and optimization. Int J Pharm. 2010;391:203–11.
Constantinides PP, Scalart JP, Lancaster C, Marcello J, Marks G, Ellens H, et al. Formulation and intestinal absorption enhancement evaluation of water-in-oil microemulsions incorporating medium-chain glycerides. Pharm Res An Off J Am Assoc Pharm Sci. 1994;11:1385–90.
Porter CJH, Trevaskis NL, Charman WN. Lipids and lipid-based formulations: optimizing the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:231–48.
Nielsen FS, Petersen KB, Müllertz A. Bioavailability of probucol from lipid and surfactant based formulations in minipigs: influence of droplet size and dietary state. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69:553–62.
Weerapol Y, Limmatvapirat S, Nunthanid J, Sriamornsak P. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of nifedipine: impact of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and molecular structure of mixed surfactants. AAPS PharmSciTech [Internet]. 2014;15:456–64. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24452500%0A http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=PMC3969497. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Gupta S, Chavhan S, Sawant KK. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for adefovir dipivoxil: design, characterization, in vitro and ex vivo evaluation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2011;392:145–55.
Zhao Y, Wang C, Chow AHL, Ren K, Gong T, Zhang Z, et al. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of zedoary essential oil: formulation and bioavailability studies. Int J Pharm. 2010;383:170–7.
Newton M, Petersson J, Podczeck F, Clarke A, Booth S. The influence of formulation variables on the properties of pellets containing a self-emulsifying mixture. J Pharm Sci. 2001;90:987–95.
Mohd AB, Sanka K, Bandi S, Diwan PV, Shastri N. Solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) for oral delivery of glimepiride: development and antidiabetic activity in albino rabbits. Drug Deliv. 2015;22:499–508.
Payghan SA. Potential investigation of Peceol for formulation of ezetimibe self nano emulsifying. Allied Acad. 2016:21–32.
Janga KY, Jukanti R, Sunkavalli S, Velpula A, Bandari S, Kandadi P, et al. In situ absorption and relative bioavailability studies of zaleplon loaded self-nanoemulsifying powders. J Microencapsul. 2013;30:161–72.
Gershanik T, Benita S. Self-dispersing lipid formulations for improving oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50:179–88.
Venkata Ramana Rao S, Shao J. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for oral delivery of protein drugs. I. Formulation development. Int J Pharm. 2008;362:2–9.
Singh B, Bandopadhyay S, … RK-CR in, 2009 26(5); 427–521. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): formulation development, characterization, and applications. dl.begellhouse.com [Internet]. [cited 2019 Jan 26]; Available from: http://www.dl.begellhouse.com/journals/3667c4ae6e8fd136,7bc13fbe52b73e32,3ecc45285b4b6014.html. Accessed 20 Jul 2019.
Thanki K, Gangwal RP, Sangamwar AT, Jain S. Oral delivery of anticancer drugs: challenges and opportunities. J Control Release. 2013;170:15–40.
Fernandez S, Jannin V, Chevrier S, Chavant Y, Demarne F, Carrière F. In vitro digestion of the self-emulsifying lipid excipient Labrasol® by gastrointestinal lipases and influence of its colloidal structure on lipolysis rate. Pharm Res. 2013;30:3077–87.
Zhao X, Zhu JX, Mo SF, Pan Y, Kong LD. Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103:357–65.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to NIPER Hyderabad for the support towards infrastructure and state-of-the art facilities for conducting research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors disclosed absence of any conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rangaraj, N., Shah, S., A J, M. et al. Quality by Design Approach for the Development of Self-Emulsifying Systems for Oral Delivery of Febuxostat: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1476-y