Abstract
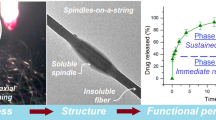
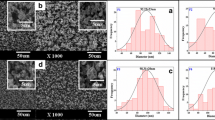
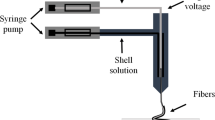
This study investigated the preparation of drug-loaded fibers using a modified coaxial electrospinning process, in which only unspinnable solvent was used as sheath fluid. With zein/ibuprofen (IBU) co-dissolving solution and N, N-dimethylformamide as core and sheath fluids, respectively, the drug-loaded zein fibers could be generated continuously and smoothly without any clogging of the spinneret. Field emission scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy observations demonstrated that the fibers had ribbon morphology with a smooth surface. Their average diameters were 0.94 ± 0.34 and 0.67 ± 0.21 μm when the sheath-to-core flow rate ratios were taken as 0.11 and 0.25, respectively. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry verified that IBU was in an amorphous state in all fiber composites. Fourier transform infrared spectra showed that zein had good compatibility with IBU owing to hydrogen bonding. In vitro dissolution tests showed that all the fibers could provide sustained drug release files via a typical Fickian diffusion mechanism. The modified coaxial electrospinning process reported here can expand the capability of electrospinning in generating fibers and provides a new manner for developing novel drug delivery systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Klein S, Kuhn J, Avrahami R, Tarre S, Beliavski M, Green M, et al. Encapsulation of bacterial cells in electrospun microtubes. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10:1751–6.
Xu L, Zheng R, Liu S, Song J, Chen J, Dong B, et al. NiO@ZnO heterostructured nanotubes: coelectrospinning fabrication, characterization, and highly enhanced gas sensing properties. Inorg Chem. 2012;51:7733–40.
Shaikh RP, Pillay V, Choonara YE, du Toit LC, Ndesendo VMK, Bawa P, et al. A review of multi-responsive membranous systems for rate-modulated drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11:441–59.
Yu DG, Branford-White C, White K, Li XL, Zhu LM. Dissolution improvement of electrospun nanofiber-based solid dispersions for acetaminophen. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11:809–17.
Brettmann BK, Tsang S, Forward KM, Rutledge GC, Myerson AS, Trout BL. Free surface electrospinning of fibers containing microparticles. Langmuir. 2012;28:9714–21.
Chiscan O, Dumitru I, Tura V, Stancu A. PVC/Fe electrospun nanofibers for high frequency applications. J Mater Sci. 2012;47:2322–7.
Brettmann BK, Cheng K, Myerson AS, Trout BL. Electrospun formulations containing crystalline active pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharm Res. 2013;30:238–46.
Yu M, Sun L, Li W, Lan Z, Li B, Tan L, et al. Investigation of structure and dissolution properties of a solid dispersion of lansoprazole in polyvinylpyrrolidone. J Mol Struct. 2011;1005:70–7.
Nagy ZK, Balogh A, Vajna B, Farkas A, Patyi G, Kramarics A, et al. Comparison of electrospun and extruded Soluplus® -based solid dosage forms of improved dissolution. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:322–32.
Brettmann B, Bell E, Myerson A, Trout B. Solid-state NMR characterization of high-loading solid solutions of API and excipients formed by electrospinning. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:1538–45.
Liu X, Lin T, Gao Y, Xu Z, Huang C, Yao G, et al. Antimicrobial electrospun nanofibers of cellulose acetate and polyester urethane composite for wound dressing. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100:1556–65.
Liu X, Lin T, Fang J, Yao G, Zhao H, Dodson M, et al. In vivo wound healing and antibacterial performances of electrospun nanofibre membranes. J Biomed Mater Res. 2010;94A:499–508.
Yu DG, Yu JH, Chen L, Williams GR, Wang X. Modified coaxial electrospinning for the preparation of high-quality ketoprofen-loaded cellulose acetate nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;90:1016–23.
Yu DG, White K, Yang JH, Wang X, Qian W, Li Y. PVP nanofibers prepared using co-axial electrospinning with salt solution as sheath fluid. Mater Lett. 2012;67:78–80.
Yu DG, Chatterton NP, Yang JH, Wang X, Liao YZ. Coaxial electrospinning with triton X-100 solutions as sheath fluids for preparing PAN nanofibers. Macromol Mater Eng. 2012;297:395–401.
Kanjanapongkul K, Wongsasulak S, Yoovidhya T. Prediction of clogging time during electrospinning of zein solution: scaling analysis and experimental verification. Chem Eng Sci. 2010;65:5217–25.
Yu DG, Li X, Wang X, Chian W, Liao Y, Li Y. Zero-order drug release cellulose acetate nanofibers prepared using coaxial electrospinning. Cellulose. 2013;20:379–89.
Zenis Y. Spinning continuous fibers for nanotechnology. Science. 2004;304:1917–9.
Moghe K, Gupta BS. Co-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: preparation and applications. Polym Rev. 2008;48:353–77.
Yarin AL. Coaxial electrospinning and emulsion electrospinning of core–shell fibers. Polym Adv Technol. 2011;22:310–7.
Díaz JE, Barrero A, Márquez M, Loscertales IG. Controlled encapsulation of hydrophobic liquids in hydrophilic polymer nanofibers by co-electrospinning. Adv Funct Mater. 2006;16:2110–211.
Yu DG, Wang X, Li X, Chian W, Li Y, Liao Y. Electrospun biphasic drug release polyvinylpyrrolidone/ethyl cellulose core/sheath nanofibers. Acta Biomater. 2013;9:5665–72.
Samarasinghe SR, Balasubramanian K, Edirisinghe MJ. Encapsulation of silver particles using co-axial jetting. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2008;19:33–8.
Yu DG, Williams GR, Gao LD, Bligh SWA, Yang JH, Wang X. Coaxial electrospinning with sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate solution for high quality polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspect. 2012;396:161–8.
Yu DG, Lu P, Branford-White C, Yang JH, Wang X. Polyacrylonitrile nanofibers prepared using co-axial electrospinning with LiCl solution as sheath fluid. Nanotechnology. 2011;22:435301.
Yu DG, Yang JM, Li L, Lu P, Zhu LM. Obtaining finer polymer nanofibers using two different electrospinning processes. Fiber Polym. 2012;13:450–5.
Lai LF, Guo HX. Preparation of new 5-fluorouracilloaded zein nanoparticles for liver targeting. Int J Pharm. 2011;404:317–23.
Torres-Giner S, Ocio MJ, Lagaron JM. Novel antimicrobial ultrathin structures of zein/chitosan blends obtained by electrospinning. Carbohydr Polym. 2009;77:261–6.
Tiwari SK, Tzezana R, Zussman E, Venkatraman SS. Optimizing partition-controlled drug release from electrospun core-shell fibers. Int J Pharm. 2010;392:209–17.
Jiang HL, Zhao PC, Zhu KJ. Fabrication and characterization of zein-based nanofibrous scaffolds by an electrospinning method. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7:517–25.
Jiang QR, Reddy N, Yang YQ. Cytocompatible crosslinking of electrospun zein fibers for the development of waterstable tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:4042–51.
Nie W, Yu DG, Branford-White C, Shen XX, Zhu LM. Electrospun Zein/PVP fiber composite and its application in drug delivery. Mater Res Innov. 2012;16:14–8.
Blundell TL, Jenkins JA. The binding of heavy metals to proteins. Chem Soc Rev. 1977;6:139–71.
Li D, Xia Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv Mater. 2004;16:1151–70.
Yu DG, Zhu LM, Branford-White C, Yang JH, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Solid dispersions in the form of electrospun core-sheath nanofibers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:3271–80.
Woods KK, Selling GW, Cooke PH. Compatible blends of zein and polyvinylpyrrolidone. J Polym Environ. 2009;17:115–22.
Peppas NA. Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm Acta Helv. 1985;60:110–1.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We gratefully thank Prof. Deng-Guang Yu for his help in carrying out the modified coaxial electrospinning. This research was supported by the Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Project No. XD20100774), the Hubei Key Laboratory Foundation (Project No.2012107) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei (Project No. 2010CDB05901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Zou, T., Li, S. et al. Drug-Loaded Zein Nanofibers Prepared Using a Modified Coaxial Electrospinning Process. AAPS PharmSciTech 14, 675–681 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9953-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9953-1