Abstract
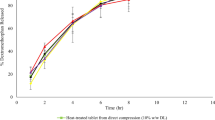
This study investigated the processing parameters and formulation factors on the bioadhesive properties, temperature stability properties, and drug release properties of miconazole in PolyOx® and Klucel® matrix systems produced by Hot-melt Extrusion (HME) technology. Miconazole incorporated into these matrix systems were found to be stable for 8 months by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The addition of miconazole increased area under the curve (AUC) at contact time intervals of 30 and 60 sec, while the bioadhesion decreased with an increase in processing temperatures. The release profiles suggest that a sustained release of miconazole was observed from all of the tested HME film formulations for approximately 10 h. The release from the optimal HME film extruded at 205°C was found to be significantly different than that extruded at 190°C. Therefore, this matrix system may address the present shortcomings of currently available therapy for oral and pharyngeal candidiasis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawyer PR, Brogden RN, Pinder RM, Speight TM, Avery GS. Miconazole: a review of its antifungal activity and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1975;9(6):406–23.
Chang HT, Chen WC, Chen JS, Lu YC, Hsu SS, Wang JL, et al. Effect of miconazole on intracellular Ca2+ levels and proliferation in human osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci. 2005;76(18):2091–101.
Devaraj A, O’Beirne JP, Veasey R, Dunk AA. Interaction between warfarin and topical miconazole cream. Bmj. 2002;325(7355):77.
Mohammed FA, Khedr H. Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of the buccal bioadhesive properties of slow-release tablets containing miconazole nitrate. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003;29(3):321–37.
Hynninen VV, Olkkola KT, Neuvonen PJ, Laine K. Oral voriconazole and miconazole oral gel produce comparable effects on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of etoricoxib. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;65(1):89–95.
Mandal TK. Swelling-controlled release system for the vaginal delivery of miconazole. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50:7.
Bioadhesion of Carbopol polymers, BF Goodrich Specialty Chemicals, Cleveland, Ohio. 1994: 7.
Repka MA, McGinity JW. Bioadhesive properties of hydroxypropylcellulose topical films produced by hot-melt extrusion. J Control Release. 2001;70(3):341–51.
Repka MA, ElSohly MA, Munjal M, Ross SA. Temperature stability and bioadhesive properties of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol incorporated hydroxypropylcellulose polymer matrix systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2006;32(1):21–32.
Thumma S, Majumdar S, ElSohly MA, Gul W, Repka MA. Chemical stability and bioadhesive properties of an ester prodrug of 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in poly(ethylene oxide) matrices: Effect of formulation additives. Int J Pharm. 2008;362:7.
Repka MA, McGinity JW. Physical-mechanical, moisture absorption and bioadhesive properties of hydroxypropylcellulose hot-melt extruded films. Biomaterials. 2000;21(14):1509–17.
Prodduturi, S., K.L. Urman, J.U. Otaigbe and M.A. Repka, Stabilization of hot-melt extrusion formulations containing solid solutions using polymer blends. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2007. 8(2): Article 50.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the project of Research Center of Drug-Delivery Systems in Universities of Guangdong Province (No.: GCZX-A0802). In addition, this research was supported by Grant Number P20GM104931 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NIGMS or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Lu, J., Deng, W. et al. Influence of Processing Parameters and Formulation Factors on the Bioadhesive, Temperature Stability and Drug Release Properties of Hot-Melt Extruded Films Containing Miconazole. AAPS PharmSciTech 15, 522–529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-0029-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-0029-z