Abstract
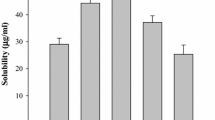
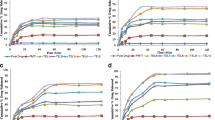
The release of verapamil hydrochloride from tablets with Eudragit RLPO or Kollidon®SR with different drug-to-polymer ratios were investigated with a view to develop twice-daily sustained-release dosage form by solid dispersion (SD) technique. The SDs containing Eudragit RLPO or Kollidon®SR at drug-polymer ratios of 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 with verapamil hydrochloride were developed using solvent evaporation technique. The physical mixtures of drug and both polymers were prepared by using simple mixing technique at the same ratio as solid dispersion. The physicochemical properties of solid dispersion were evaluated by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The study of DSC, XRD, and FTIR could not show significant interaction between verapamil HCl and Kollidon®SR or Eudragit RLPO. The solid dispersions or physical mixtures were compressed to tablets. The tablets were prepared with solid dispersions containing Eudragit RLPO or Kollidon®SR, with all the official requirements of tablet dosage forms fulfilled. Tablets prepared were evaluated for the release of verapamil hydrochloride over a period of 12 h in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer using US Pharmacopoeia type II dissolution apparatus. The in vitro drug release study revealed that the tablet containing Eudragit has extended the release rate for 12 h whereas the tablet containing Kollidon®SR at the same concentration has extended the release rate up to 8 h. The in vitro release profile and the mathematical models indicate that release of verapamil hydrochloride can be effectively controlled from a tablet containing solid dispersions of Eudragit RLPO. The reduction of size fraction of the SD system from 200–250 to 75–125 μm had a great effect on the drug release.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. J. Elliott. Circadian variation in the timing of stroke onset. A metaanalysis. Stroke. 29:992–996 (1998).
M. Gallerani, R. Manfredini, L. Ricci, E. Grandi, R. Cappato, G. Calò, P. L Pareschi, and C. Fersini. Sudden death from pulmonary thromboembolism: chronobiological aspects. Eur. Heart J. 6:305–323 (1992).
M. Lovrecich, F. Nobile, F. Rubessa, and G. Zingone. Effect of ageing on the release of indomethacin from solid dispersion with eudragits. Int. J. Pharm. 131:247–255 (1996).
A. A. Karnachi, R. A. De Hon, and M. A. Khan. Compression of indomethacin coprecipitates with polymer mixtures: effect of preparation methodology. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2112:1473–14483 (1995).
A. H. Goldberg, M. Gibaldi, and J. L. Kanig. Increasing dissolution rates and gastrointestinal absorption of drugs via solid solutions and eutectic mixtures. I. Theoretical considerations and discussion of literature. J. Pharm. Sci. 54:1145–1148 (1965).
W. L. Chiou, and S. Riegelman. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1281–1302 (1971).
F. Sadeghi, H. Afrasiabi Garekani, and A. Sadr. Influence of polymer viscosity and plasticizer addition on ethylcellulose matrix characteristics prepared from solid dispersion system. STP Pharma. Sci. 13:105–110 (2003).
J. I. Hernandez, E. S. Ghalj, A. Malave, and A. Marti. Controlled release matrix of acetaminophen ethylcellulose solid dispersion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 20:1253–1265 (1994).
K. Goracinova, L. J. Klisarova, and A. Simov. Physical characterization and dissolution properties of verapamil HCl coprecipitates. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 21:383–391 (1995).
M. A. Dabbagh, J. L. Ford, M. H. Rubinstein, and J. E. Hogan. Effect of polymer particle size, compaction pressure and hydrophilic polymers on drug release from matrices containing ethylcellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 140:85–95 (1996).
P. R. Katikaneni, S. M. Upadrashta, S. H. Neau, and A. K. Mitra. Ethylcellulose matrix controlled release tablets of a water-soluble drug. Int. J. Pharm. 123:119–125 (1995).
M. A. Khan, A. A. Karnachi, S. K. Singh, S. V. Sastry, S. M. Kislalioglu, and S. Bolton. Controlled release coprecipitates: formulation considerations. J. Cont. Rel. 37:131–141 (1995).
S. Benita, A. Hoffman, and M. Donbrow. Microencapsulation of paracetamol using polyacrylate resins (eudragit retard), Kinetics of drug release and evaluation of kinetic model. J. Pharm. Pharmcol. 37:391–395 (1985).
C. Ho, and G. C. C. Hwang. Development of extended release solid dispersion of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with aqueous polymeric dispersions: optimization of drug release via a curve-fitting technique. Pharm. Res. 9:206–210 (1992).
Technical Information, Kollidon®SR; BASF Aktiengesellschaft, Germany. 1–10 (1999).
W. Daniels. Vinyl ester polymers, In transitions and relaxations to Zwitterionic Polymerisation, 2nd Ed., Encyclopedia of polymer science and Engineering, John Wiley and sons, New York. 17:402–425 (1989).
J. Sahoo, P. N. Murthy, S. Biswal, A. K. Mahapatra, and S. K. Sahoo. Comparative study of propranolol hydrochloride release from matrix tablets with Kollidon®SR or hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. AAPS Pharma. SciTech. 9(2):577–582 (2008).
R. N. Saha, C. Sanjeev, and J. Sahoo. A comparative study of controlled release matrix tablets of diclofenac sodium, ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, and theophylline. Drug Delivery. 8:149–154 (2001).
J. Sahoo, P. N. Murthy, S. Biswal, A. K. Mahapatra, and S. K. Sahoo. Preparation and release rate study of controlled release matrix tablets of verapamil hydrochloride using hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. Int. J. Pharma. Ex. In press.
J. Sahoo, P. N. Murthy, S. Biswal, A. K. Mahapatra, and S. K. Sahoo. Preparation and release rate study of controlled release matrix tablets of verapamil hydrochloride using Kollidon®SR. Pharm. BIT. XVI(2):119–124 (2007).
S. Biswal, J. Sahoo, P. N. Murthy, P. R. Giradkar, and J. G. Avari. Enhancement of dissolution rate of gliclazide using solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 6000. AAPS Pharma. SciTech. 9(2):563–570 (2008).
P. Costa, and J. M. S. Lobo. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13:123–133 (2001).
C. Rustichelli, M. C. Gamberini, V. Ferioli, and G. Gamberini. Properties of the racemic species of verapamil hydrochloride and gallopamil hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. 178:111–120 (1999).
M. P. Oth, and A. J. Moes. Sustained release solid dispersions of indomethacin with Eudragit RS and RL. Int. J. Pharm. 55:157–164 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, J., Murthy, P.N., Biswal, S. et al. Formulation of Sustained-Release Dosage Form of Verapamil Hydrochloride by Solid Dispersion Technique Using Eudragit RLPO or Kollidon®SR. AAPS PharmSciTech 10, 27–33 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9175-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9175-0