Abstract
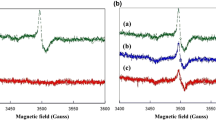
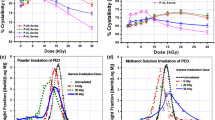
The purpose of this research was to evaluate how the presence of oxygen can affect irradiation-induced degradation reactions of PEGd,lPLA and PEG-PLGA multiblock copolymers submitted to gamma irradiation and to investigate the radiolytic behavior of the polymers. PEGd,lPLA, PEG-PLGA, PLA, and PLGA were irradiated by using a 60Co irradiation source in air and under vacuum at 25 kGy total dose. Mw and Mn were evaluated by gel permeation chromatography. The stability study was carried out on three samples sets: (a) polymer samples irradiated and stored in air, (b) polymer samples irradiated and stored under vacuum, and (c) polymer samples irradiated under vacuum and stored in air. The thermal and radiolytic behavior was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), respectively. Samples irradiated in air showed remarkable Mw and Mn reduction and Tg value reduction due to radiation-induced chain scission reactions. Higher stability was observed for samples irradiated and stored under vacuum. EPR spectra showed that the presence of PEG units in multiblock copolymer chains leads to: (a) decrease of the radiolytic yield of radicals and (b) decrease of the radical trapping efficiency and faster radical decay rates. It can be concluded that the presence of oxygen during the irradiation process and the storage phase significantly increases the entity of irradiation-induced damage.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Medicines Agency. The use of ionizing radiation in the manufacture of medicinal products European Guidelines 3AQ4a. (1991).
J. S. C. Loo, C. P. Ooi, and F. Y. C Boey. Degradation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) and poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) by electron beam radiation. Biomaterials. 26:1359–1367 (2005).
K. J. Hemmerich. Radiation sterilization, Polymer materials selection for radiation-sterilized products. Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry MDDI Feb. 2000, p. 78.
J. A. Bushell, M. Claybourn, H. E. Williams, and D. M. Murphy. An EPR and ENDOR study of gamma and beta-radiation sterilization in poly(lactide-co-glycolide) polymers and microspheres. J. Control. Release. 110(1):49–57 (2005).
R. Dorati, I. Genta, L. Montanari, A. Buttafava, A. Faucitano, and B. Conti. The effect of γ-irradiation on PLGA/PEG microspheres containing ovalbumin. J. Control. Release. 107:78–90 (2005).
A. Faucitano, A. Buttafava, L. Montanari, F. Cilurzo, B. Conti, I. Genta, and L. Valvo. Radiation induced free radical reactions in polymer/drug systems for controlled release: an EPR investigation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 67:61–72 (2003).
L. Montanari, M. Costantini, E.C. Signoretti, L. Valvo, M. Santucci, M. Bortolomei, P. Fattibene, S. Onori, A. Faucitano, B. Conti, and I. Genta. Gamma-irradiations effects on poly(d,l-lactie-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Control. Release. 56(2):219–229 (1998).
H. J. Haugen, M. Brunner, F. Pellkofer, J. Aigner, J. Will, and E. Wintermantel. Effect of different γ-irradiation doses on cytotoxicity and material properties of porous polyether–urethane polymer. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomate. 80B(2):415–423 (2006).
M. Claybourn, H. Gray, D. M. Murphy, I. J. Purnell, and C. C. Rowlands. Electron magnetic resonance study of gamma-irradiated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Control. Release. 91(3):431–438 (2003).
M. M. B. Sintzel, A. Merkli, C. Tabatabay, and R. Gurny. Influence of irradiation sterilization on polymers used as drug carriers—a review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 23(9):857–878 (1997).
L. Martini, J. H. Collett, and D. Attwood. The influence of gamma irradiation on the physicochemical properties of a novel triblock copolymer of ε-caprolactone and ethylene oxide. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49(6):601–605 (1997).
R. Garcia, B. Howard, R. LaRue, G. Parton, and J. Walke. Strategies for Gamma Sterilization of Pharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutical & Medical Packaging News. PMPN May 2004.
M. Bernkopf. Sterilisation of Bioresorbable Polymer Implants. Medical Device Technology MDT May/June 2007.
M. A. Al-Ma’adeed, I. Y. Al-Qaradawi, N. Madi, and N. J. Al-Thani. The effect of gamma irradiation and shelf aging in air on the oxidation of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(9):292 (2006).
R. Dorati, C. Colonna, M. Serra, I. Genta, T. Modena, F. Pavanetto, P. Perugini, and B. Conti. γ-irradiation of PEGd,lPLA and PEG-PLGA multiblock copolymers: I Effect of irradiation doses. AAPS PharmSciTech. 9(2):718–725 (2008).
A. Gèze, M. C. Venier-Julienne, J. Cottin, N. Faisant, and J. P. Benoit. PLGA microsphere bioburden evaluation for radiosterilization dose selection. J. Microencapsul. 18(5):627–636 (2001).
L. Woo, and C. L. Sandford. Comparison of electron beam irradiation with gamma processing for medical packaging materials. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 63:845–850 (2002).
C. Ahlneck, and G. Zografi. The molecular basis of moisture effects on the physical and chemical stability of drugs in the solid state. Int. J. Pharm. 62(2–3):87–95 (1990).
C. A. Oksanen, and G. Zografi. Molecular mobility in mixtures of absorbed water and solid poly(vinylpyrrolidone). Pharm. Res. 10(6):791–799 (1993).
B. C. Hancock, and G. Zografi. The relationship between the glass transition temperature and the water content of amorphous pharmaceutical solids. Pharm. Res. 11(4):471–477 (1994).
F. J. Buchanan, J. R. White, B. Sim, and S. Downes. The influence of gamma irradiation and aging on degradation mechanisms of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med. 12(1):29–37 (2001).
M. Z. Heydari, E. Malinen, E. O. Hole, and E. Sagstuen. Alanine radicals 2. The composite polycrystalline alanine EPR spectrum studied by ENDOR, thermal annealing, and spectrum simulation. J. Phys. Chem. A. 106:8971–8977 (2002).
D. Becker, S. Swart, and M. D. Sevilla. Electron spin resonance investigation of intramolecular hydrogen transfer and alkyl attack in ester cation radicals. J. Phys. Chem. 89(12):2638–2646 (1985).
A. Faucitano, A. Buttafava, F. Martinotti, P. Ferloni, and A. Magistris. The mechanism of gamma-radiolysis of polymethylene, polypropylene and poly-n-butylene oxides: an ESR investigation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 40(5):347–355 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorati, R., Colonna, C., Tomasi, C. et al. γ-irradiation of PEGd,lPLA and PEG-PLGA Multiblock Copolymers: II. Effect of Oxygen and EPR Investigation. AAPS PharmSciTech 9, 1110–1118 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9150-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9150-9