Abstract
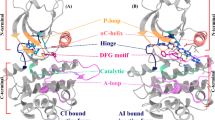
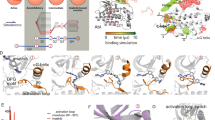
Aurora kinase B (AKB), a Ser/Thr kinase that plays a crucial role in mitosis, is overexpressed in several cancers. Clinical inhibitors targeting AKB bind to the active DFG “in” conformation of the kinase. It would be beneficial, however, to understand if AKB is susceptible to type II kinase inhibitors that bind to the inactive, DFG “out” conformation, since type II inhibitors achieve higher kinome selectivity and higher potency in vivo. The DFG “out” conformation of AKB is not yet experimentally determined which makes the design of type II inhibitors exceedingly difficult. An alternate approach is to simulate the DFG “out” conformation from the experimentally determined DFG “in” conformation using atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. In this work, we employed metadynamics (MTD) approach to simulate the DFG “out” conformation of AKB by choosing the appropriate collective variables. We examined structural changes during the DFG-flip and determined the interactions crucial to stabilize the kinase in active and inactive states. Interestingly, the MTD approach also identified a unique transition state (DFG “up”), which can be targeted by small molecule inhibitors. Structural insights about these conformations is essential for structure-guided design of next-generation AKB inhibitors. This work also emphasizes the usefulness of MTD simulations in predicting macromolecular conformational changes at reduced computational costs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–34.
Nolen B, Taylor S, Ghosh G. Review regulation of protein kinases: controlling activity through activation segment conformation. Mol Cell. 2004;15:661–75.
Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. Elsevier. 1987;50:823–9.
Kornev AP, Haste NM, Taylor SS, Ten Eyck LF. Surface comparison of active and inactive protein kinases identifies a conserved activation mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:17783–8.
Johnson LN, Noble ME, Owen DJ. Active and inactive protein kinases: structural basis for regulation. Cell. 1996;85:149–58.
Endicott JA, Noble MEM, Johnson LN. The structural basis for control of eukaryotic protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:587–613.
Cohen P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E127–30.
Dar AC, Shokat KM. The evolution of protein kinase inhibitors from antagonists to agonists of cellular signaling. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:769–95.
Vader G, Medema RH, Lens SMA. The chromosomal passenger complex: guiding Aurora-B through mitosis. J Cell Biol. 2006;173:833–7.
Carmena M, Wheelock M, Funabiki H, Earnshaw WC. The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC): from easy rider to the godfather of mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:789–803.
Takeshita M, Koga T, Takayama K, Ijichi K, Yano T, Maehara Y, et al. Aurora-B overexpression is correlated with aneuploidy and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2013;80:85–90.
Zhang Y, Jiang C, Li H, Lv F, Li X, Qian X, et al. Elevated Aurora B expression contributes to chemoresistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:751-7.
Tuncel H, Shimamoto F, Kaneko Guangying Qi H, Aoki E, Jikihara H, Nakai S, et al. Nuclear Aurora B and cytoplasmic Survivin expression is involved in lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2012;3:1109–14.
Fadri-Moskwik M, Weiderhold KN, Deeraksa A, Chuang C, Pan J, Lin S-H, et al. Aurora B is regulated by acetylation/deacetylation during mitosis in prostate cancer cells. FASEB J. 2012;26:4057–67.
Chieffi P, Cozzolino L, Kisslinger A, Libertini S, Staibano S, Mansueto G, et al. Aurora B expression directly correlates with prostate cancer malignancy and influence prostate cell proliferation. Prostate. 2006;66:326–33.
Hartsink-Segers SA, Zwaan CM, Exalto C, Luijendijk MWJ, Calvert VS, Petricoin EF, et al. Aurora kinases in childhood acute leukemia: the promise of aurora B as therapeutic target. Leukemia. 2013;27:560–8.
Porcelli L, Guida G, Quatrale AE, Cocco T, Sidella L, Maida I, et al. Aurora kinase B inhibition reduces the proliferation of metastatic melanoma cells and enhances the response to chemotherapy. J Transl Med. 2015;13:26.
Yamauchi T, Uzui K, Shigemi H, Negoro E, Yoshida A, Ueda T. Aurora B inhibitor barasertib and cytarabine exert a greater-than-additive cytotoxicity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:926-33.
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Popov VM, Scarsella L, Festuccia C, La Verghetta ME, et al. Close correlation between MEK/ERK and Aurora-B signaling pathways in sustaining tumorigenic potential and radioresistance of gynecological cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:285–94.
Wu X, Liu W, Cao Q, Chen C, Chen Z, Xu Z, et al. Inhibition of Aurora B by CCT137690 sensitizes colorectal cells to radiotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:13.
Treiber DK, Shah NP. Ins and outs of kinase DFG Motifs. Chem Biol. 2013;20:745–6.
Roskoski R. Classification of small molecule protein kinase inhibitors based upon the structures of their drug-enzyme complexes. Pharmacol Res. 2016;103:26–48.
Tang A, Gao K, Chu L, Zhang R, Yang J, Zheng J. Aurora kinases: novel therapy targets in cancers. Oncotarget. 2017;8:23937–54.
Sessa F, Villa F. Structure of Aurora B–INCENP in complex with barasertib reveals a potential transinhibitory mechanism. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014;70:294–8.
Zhou Y, Shan S, Li Z-B, Xin L-J, Pan D-S, Yang Q-J, et al. CS2164, a novel multi-target inhibitor against tumor angiogenesis, mitosis and chronic inflammation with anti-tumor potency. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:469–77.
Sessa F, Mapelli M, Ciferri C, Tarricone C, Areces LB, Schneider TR, et al. Mechanism of Aurora B activation by INCENP and inhibition by hesperadin. Mol Cell. 2005;18:379–91.
Sini P, Gurtler U, Zahn SK, Baumann C, Rudolph D, Baumgartinger R, et al. Pharmacological profile of BI 847325, an orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive inhibitor of MEK and Aurora kinases. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:2388–98.
Shaw DE, Maragakis P, Lindorff-Larsen K, Piana S, Dror RO, Eastwood MP, et al. Atomic-level characterization of the structural dynamics of proteins. Science. 2010;330:341–6.
Shan Y, Arkhipov A, Kim ET, Pan AC, Shaw DE. Transitions to catalytically inactive conformations in EGFR kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:7270–5.
Sugita Y, Okamoto Y. Replica-exchange molecular dynamics method for protein folding. Chem Phys Lett. 1999;314:141–51.
Meng Y, Gao C, Clawson DK, Atwell S, Russell M, Vieth M, et al. Predicting the conformational variability of Abl tyrosine kinase using molecular dynamics simulations and Markov state models. J Chem Theory Comput. 2018;14:2721–32.
Li Y, Li X, Ma W, Dong Z. Conformational transition pathways of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain from multiple molecular dynamics simulations and Bayesian clustering. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014;10:3503–11.
Zhang Y, Niu H, Li Y, Chu H, Shen H, Zhang D, et al. Mechanistic insight into the functional transition of the enzyme guanylate kinase induced by a single mutation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8405.
Laio A, Parrinello M. Escaping free-energy minima. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:12562–6.
Tribello GA, Ceriotti M, Parrinello M. A self-learning algorithm for biased molecular dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:17509–14.
Dodson CA, Kosmopoulou M, Richards MW, Atrash B, Bavetsias V, Blagg J, et al. Crystal structure of an Aurora-A mutant that mimics Aurora-B bound to MLN8054: insights into selectivity and drug design. Biochem J. 2010;427:19–28.
Bian Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang W. On the accuracy of metadynamics and its variations in a protein folding process. Mol Simul. 2015;41:752–63.
Park J, McDonald JJ, Petter RC, Houk KN. Molecular dynamics analysis of binding of kinase inhibitors to WT EGFR and the T790M Mutant. J Chem Theory Comput. 2016;12:2066–78.
Callegari D, Lodola A, Pala D, Rivara S, Mor M, Rizzi A, et al. Metadynamics simulations distinguish short- and long-residence-time inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2017;57:159–69.
Taylor SS, Kornev AP. Protein kinases: evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:65–77.
Knight JDR, Qian B, Baker D, Kothary R. Conservation, variability and the modeling of active protein kinases. Fugmann S, editor. PLoS One. 2007;2:e982.
Carrera AC, Alexandrov K, Roberts TM. The conserved lysine of the catalytic domain of protein kinases is actively involved in the phosphotransfer reaction and not required for anchoring ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:442–6.
Harrington EA, Bebbington D, Moore J, Rasmussen RK, Ajose-Adeogun AO, Nakayama T, et al. VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nat Med. 2004;10:262–7.
Meng Y, Lin Y, Roux B. Computational study of the “DFG-Flip” conformational transition in c-Abl and c-Src tyrosine kinases. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119:1443–56.
Ensing B, De Vivo M, Liu Z, Moore P, Klein ML. Metadynamics as a tool for exploring free energy landscapes of chemical reactions. Acc Chem Res. 2006;39(2):73-81.
Barducci A, Bussi G, Parrinello M. Well-tempered metadynamics: a smoothly converging and tunable free-energy method. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;100:020603.
Levinson NM, Kuchment O, Shen K, Young MA, Koldobskiy M, Karplus M, et al. A Src-like inactive conformation in the abl tyrosine kinase domain. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e144.
Sultan MM, Denny RA, Unwalla R, Lovering F, Pande VS. Millisecond dynamics of BTK reveal kinome-wide conformational plasticity within the apo kinase domain. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15604.
Zhang X, Gureasko J, Shen K, Cole PA, Kuriyan J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell. 2006;125:1137–49.
Shan Y, Seeliger MA, Eastwood MP, Frank F, Xu H, Jensen MØ, et al. A conserved protonation-dependent switch controls drug binding in the Abl kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:139–44.
Vashisth H, Maragliano L, Abrams CF. DFG-flip in the insulin receptor kinase is facilitated by a helical intermediate state of the activation loop. Biophys J. 2012;102:1979–87.
Schindler T, Bornmann W, Pellicena P, Miller WT, Clarkson B, Kuriyan J. Structural mechanism for STI-571 inhibition of Abelson tyrosine kinase. Science. 2000;289:1938–42.
Funding
This work was supported by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under grant number “P20 GM109005.” BF was supported by the UAMS Seeds of Science Grant, the UAMS COP Seed Grant, and a grant from the American Thyroid Association (ATA/Thyca). HL was supported by NIH grants (NIH 1R01CA194094 and 1R01CA197178). MB was supported by Inglewood Scholars Program and NIA/NIH grant 2P01AG012411-17A1 (W.S.T. Griffin, P.I.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editors: Shraddha Thrakkar and Cesar Compadre
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 442 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakkaniga, N.R., Balasubramaniam, M., Zhang, S. et al. Structural Characterization of the Aurora Kinase B “DFG-flip” Using Metadynamics. AAPS J 22, 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-019-0399-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-019-0399-6