Abstract
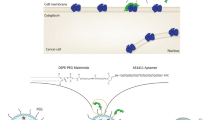
Lung cancer is the leading cancer and has the highest death rate. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) erlotinib has had a promising response in lung cancer therapy. Unfortunately, individuals with TKI-resistant EGFR mutations often develop acquired resistance against erlotinib. To overcome this resistance, in the present study, we developed liposomes anchored with anti-EGFR aptamer (Apt)-conjugated chitosan (Apt-Cs) as stable carriers to deliver erlotinib to the target. We loaded erlotinib into Apt-Cs-anchored liposomal complexes (Apt-CL-E) and characterized the physicochemistry of Apt-CL-E. The nanoparticles showed good biostability and a binding specificity for EGFR-mutated cancer cells guided by the Apt. The specific binding facilitated the uptake of Apt-CL-E into EGFR-mutated cancer cells. A cytotoxicity study showed an advantage of Apt-CL-E over their nontargeted liposomal counterparts in delivering erlotinib to EGFR-mutated cancer cells, resulting in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. These results provide a good platform for future in vivo animal studies with Apt-CL-E.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Gu H, Zhang DS, Li F, Liu T, Xia W. Highly effective inhibition of lung cancer growth and metastasis by systemic delivery of siRNA via multimodal mesoporous silica-based nanocarrier. Biomaterials. 2014;35(38):10058–69.
Peng L, Feng L, Yuan H, Benhabbour SR, Mumper RJ. Development of a novel orthotopic non-small cell lung cancer model and therapeutic benefit of 2′-(2-bromohexadecanoyl)-docetaxel conjugate nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(7):1497–506.
Nascimento AV, Singh A, Bousbaa H, Ferreira D, Sarmento B, Amiji MM. Mad2 checkpoint gene silencing using epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted chitosan nanoparticles in non-small cell lung cancer model. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(10):3515–27.
Sukumar UK, Bhushan B, Dubey P, Matai I, Sachdev A, Packirisamy G. Emerging applications of nanoparticles for lung cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int Nano Lett. 2013;3(1):1–17.
Pore N, Jiang Z, Gupta A, Cerniglia G, Kao GD, Maity A. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors decrease VEGF expression by both hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1-independent and HIF-1-dependent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2006;66(6):3197–204.
Peng X-H, Wang Y, Huang D, Wang Y, Shin HJ, Chen Z, et al. Targeted delivery of cisplatin to lung cancer using ScFvEGFR-heparin-cisplatin nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2011;5(12):9480–93.
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(8):786–92.
Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Troiani T, Martinelli E, Morgillo F, Ciardiello F. Erlotinib in cancer treatment. Ann Oncol. 2007;18 Suppl 6:vi35–41.
Srinivasan AR, Shoyele SA. Influence of surface modification and the pH on the release mechanisms and kinetics of erlotinib from antibody-functionalized chitosan nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2014;53(8):2987–93.
Regales L, Gong Y, Shen R, de Stanchina E, Vivanco I, Goel A, et al. Dual targeting of EGFR can overcome a major drug resistance mutation in mouse models of EGFR mutant lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(10):3000–10.
Jänne PA. Challenges of detecting EGFR T790M in gefitinib/erlotinib-resistant tumours. Lung Cancer. 2008;60:S3–9.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(3):169–81.
Walter AO, Sjin RT, Haringsma HJ, Ohashi K, Sun J, Lee K, et al. Discovery of a mutant-selective covalent inhibitor of EGFR that overcomes T790M-mediated resistance in NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2013;3(12):1404–15.
Key J, Kim YS, Tatulli F, Palange AL, O’Neill B, Aryal S, et al. Opportunities for nanotheranosis in lung cancer and pulmonary metastasis. Clin Transl Imaging. 2014;2(5):427–37.
Godugu C, Patel AR, Doddapaneni R, Marepally S, Jackson T, Singh M. Inhalation delivery of telmisartan enhances intratumoral distribution of nanoparticles in lung cancer models. J Control Release. 2013;172(1):86–95.
Long JT, Cheang TY, Zhuo SY, Zeng RF, Dai QS, Li HP, et al. Anticancer drug-loaded multifunctional nanoparticles to enhance the chemotherapeutic efficacy in lung cancer metastasis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2014;12:37.
Maniganda S, Sankar V, Nair JB, Raghu KG, Maiti KK. A lysosome-targeted drug delivery system based on sorbitol backbone towards efficient cancer therapy. Org Biomol Chem. 2014;12(34):6564–9.
Xiao Z, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Alexis F, Lupták A, Teply BA, Chan JM, et al. Engineering of targeted nanoparticles for cancer therapy using internalizing aptamers isolated by cell-uptake selection. ACS Nano. 2012;6(1):696–704.
Chittasupho C, Lirdprapamongkol K, Kewsuwan P, Sarisuta N. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to A549 lung cancer cells by CXCR4 antagonist conjugated PLGA nanoparticles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014;88(2):529–38.
Conde J, Tian F, Hernandez Y, Bao C, Cui D, Janssen KP, et al. In vivo tumor targeting via nanoparticle-mediated therapeutic siRNA coupled to inflammatory response in lung cancer mouse models. Biomaterials. 2013;34(31):7744–53.
Ghasemi Z, Dinarvand R, Mottaghitalab F, Esfandyari-Manesh M, Sayari E, Atyabi F. Aptamer decorated hyaluronan/chitosan nanoparticles for targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil to MUC1 overexpressing adenocarcinomas. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;121:190–8.
Farokhzad OC, Cheng J, Teply BA, Sherifi I, Jon S, Kantoff PW, et al. Targeted nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(16):6315–20.
Li X, Zhao Q, Qiu L. Smart ligand: aptamer-mediated targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA for cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2013;171(2):152–62.
Bouchard PR, Hutabarat RM, Thompson KM. Discovery and development of therapeutic aptamers. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:237–57.
Gao H, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Jiang X, He Q. Tumor homing cell penetrating peptide decorated nanoparticles used for enhancing tumor targeting delivery and therapy. Int J Pharm. 2015;478(1):240–50.
Farokhzad OC, Jon S, Khademhosseini A, Tran T-NT, LaVan DA, Langer R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates a new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(21):7668–72.
Qiang F, Shin HJ, Lee BJ, Han HK. Enhanced systemic exposure of fexofenadine via the intranasal administration of chitosan-coated liposome. Int J Pharm. 2012;430(1–2):161–6.
Yang Z, Liu J, Gao J, Chen S, Huang G. Chitosan coated vancomycin hydrochloride liposomes: characterizations and evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2015;495(1):508–15.
Chen D, Xia D, Li X, Zhu Q, Yu H, Zhu C, et al. Comparative study of Pluronic((R)) F127-modified liposomes and chitosan-modified liposomes for mucus penetration and oral absorption of cyclosporine A in rats. Int J Pharm. 2013;449(1–2):1–9.
Allen TM, Cullis PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(1):36–48.
Kaminski GA, Sierakowski MR, Pontarolo R, Santos LA, de Freitas RA. Layer-by-layer polysaccharide-coated liposomes for sustained delivery of epidermal growth factor. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;140:129–35.
Mady MM, Darwish MM, Khalil S, Khalil WM. Biophysical studies on chitosan-coated liposomes. Eur Biophys J. 2009;38(8):1127–33.
Yang KK, Kong M, Wei YN, Liu Y, Cheng XJ, Li J, et al. Folate-modified–chitosan-coated liposomes for tumor-targeted drug delivery. J Mater Sci. 2012;48(4):1717–28.
Venturini M. Analysis of operating conditions influencing the morphology and in vitro behaviour of chitosan coated liposomes. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2014;5(4).
Diebold Y, Jarrin M, Saez V, Carvalho EL, Orea M, Calonge M, et al. Ocular drug delivery by liposome-chitosan nanoparticle complexes (LCS-NP). Biomaterials. 2007;28(8):1553–64.
Zhang S, Bai H, Luo J, Yang P, Cai J. A recyclable chitosan-based QCM biosensor for sensitive and selective detection of breast cancer cells in real time. Analyst. 2014;139(23):6259–65.
Nguyen TX, Huang L, Liu L, Elamin Abdalla AM, Gauthier M, Yang G. Chitosan-coated nano-liposomes for the oral delivery of berberine hydrochloride. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(41):7149–59.
Chen MX, Li BK, Yin DK, Liang J, Li SS, Peng DY. Layer-by-layer assembly of chitosan stabilized multilayered liposomes for paclitaxel delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;111:298–304.
Mobed M, Chang T. Comparison of polymerically stabilized PEG-grafted liposomes and physically adsorbed carboxymethylchitin and carboxymethyl/glycolchitin liposomes for biological applications. Biomaterials. 1998;19(13):1167–77.
Tan Y, Shi Y-s, Wu X-d, Liang H-y, Gao Y-b, Li S-j, et al. DNA aptamers that target human glioblastoma multiforme cells overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor variant III in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(12):1491–8.
Park SN, Jo NR, Jeon SH. Chitosan-coated liposomes for enhanced skin permeation of resveratrol. J Ind Eng Chem. 2014;20(4):1481–5.
Okazawa A, Maeda H, Fukusaki E, Katakura Y, Kobayashi A. In vitro selection of hematoporphyrin binding DNA aptamers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2000;10(23):2653–6.
Gao Y, Gu S, Zhang Y, Xie X, Yu T, Lu Y, et al. The architecture and function of monoclonal antibody-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with mifepristone: repurposing abortifacient for cancer metastatic chemoprevention. Small. 2016;12(19):2595–608.
Xie X, Li F, Zhang H, Lu Y, Lian S, Lin H, et al. EpCAM aptamer-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient colon cancer cell-targeted drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016;83:28–35.
Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S, Takahashi M, Chirieac LR, et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008;27(34):4702–11.
Baek SE, Lee KH, Park YS, Oh DK, Oh S, Kim KS, et al. RNA aptamer-conjugated liposome as an efficient anticancer drug delivery vehicle targeting cancer cells in vivo. J Control Release. 2014;196:234–42.
Yang H, Liu H, Kang H, Tan W. Engineering target-responsive hydrogels based on aptamer–target interactions. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(20):6320–1.
Famulok M, Hartig JS, Mayer G. Functional aptamers and aptazymes in biotechnology, diagnostics, and therapy. Chem Rev. 2007;107(9):3715–43.
Cao Z, Tong R, Mishra A, Xu W, Wong GC, Cheng J, et al. Reversible cell-specific drug delivery with aptamer-functionalized liposomes. Angew Chem. 2009;48(35):6494–8.
Hatakeyama H, Akita H, Harashima H. The polyethyleneglycol dilemma: advantage and disadvantage of PEGylation of liposomes for systemic genes and nucleic acids delivery to tumors. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(6):892–9.
Laouini A, Jaafar-Maalej C, Sfar S, Charcosset C, Fessi H. Liposome preparation using a hollow fiber membrane contactor—application to spironolactone encapsulation. Int J Pharm. 2011;415(1–2):53–61.
Han HD, Lee A, Song CK, Hwang T, Seong H, Lee CO, et al. In vivo distribution and antitumor activity of heparin-stabilized doxorubicin-loaded liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2006;313(1–2):181–8.
Kulkarni SA, Feng SS. Effects of particle size and surface modification on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Pharm Res. 2013;30(10):2512–22.
Wolterbeek A, Oosterwijk T, Schneider S, Landsiedel R, de Groot D, van Ee R, et al. Oral two-generation reproduction toxicity study with NM-200 synthetic amorphous silica in Wistar rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2015;56:147–54.
de Pinho Neves AL, Milioli CC, Müller L, Riella HG, Kuhnen NC, Stulzer HK. Factorial design as tool in chitosan nanoparticles development by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2014;445:34–9.
de Jesus MB, Radaic A, Zuhorn IS, de Paula E. Microemulsion extrusion technique: a new method to produce lipid nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2013;15(10).
Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010;7(9):1063–77.
Müller R, Jacobs C, Kayser O. Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy: rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):3–19.
Palakurthi S, Yellepeddi VK, Vangara KK. Recent trends in cancer drug resistance reversal strategies using nanoparticles. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012;9(3):287–301.
Li N, Nguyen HH, Byrom M, Ellington AD. Inhibition of cell proliferation by an anti-EGFR aptamer. PLoS One. 2011;6(6), e20299.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2015CB931804), the Natural Science Foundation of China (U150520007, 81571802, and 81273548), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2016J06020), and the Fujian Development and Reform Commission (2014/168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental 1
(DOCX 93 kb)
Supplemental 2
(DOCX 201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Mei, H., Xie, X. et al. Aptamer-Conjugated Chitosan-Anchored Liposomal Complexes for Targeted Delivery of Erlotinib to EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer Cells. AAPS J 19, 814–826 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0057-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0057-9