Abstract
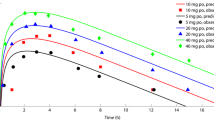
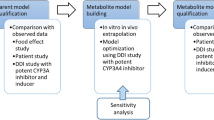
Disease-mediated therapeutic protein–drug interactions have recently gained attention from regulatory agencies and pharmaceutical industries in the development of new biological products. In this study, we developed a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model using SimCYP to predict the impact of elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels on cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and the treatment effect of an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody, sirukumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A virtual RA patient population was first constructed by incorporating the impact of systemic IL-6 level on hepatic and intestinal expression of multiple CYP enzymes with information from in vitro studies. Then, a PBPK model for CYP enzyme substrates was developed for healthy adult subjects. After incorporating the virtual RA patient population, the PBPK model was applied to quantitatively predict pharmacokinetics of multiple CYP substrates in RA patients before and after sirukumab treatment from a clinical cocktail drug interaction study. The results suggested that, compared with observed clinical data, changes in systemic exposure to multiple CYP substrates by anti-IL-6 treatment in virtual RA patients have been reasonably captured by the PBPK model, as manifested by modulations in area under plasma concentration versus time curves for midazolam, omeprazole, S-warfarin, and caffeine. This PBPK model reasonably captured the modulation effect of IL-6 and sirukumab on activity of CYP3A, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP1A2 and holds the potential to be utilized to assess the modulation effect of sirukumab on the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of concomitant small-molecule drugs in RA patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Morgan ET. Impact of infectious and inflammatory disease on cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;85(4):434–8. doi:10.1038/clpt.2008.302.
Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, Nijsten T. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(2):266–82. doi:10.1111/bjd.12355.
Kishimoto T. IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications. Int Immunol. 2010;22(5):347–52. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxq030.
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N, Gerald WL, et al. Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(12):3846–56. doi:10.1172/JCI31871.
Dickmann LJ, Patel SK, Rock DA, Wienkers LC, Slatter JG. Effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody on drug-metabolizing enzymes in human hepatocyte culture. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(8):1415–22. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.038679.
Dallas S, Sensenhauser C, Batheja A, Singer M, Markowska M, Zakszewski C, et al. De-risking bio-therapeutics for possible drug interactions using cryopreserved human hepatocytes. Curr Drug Metab. 2012;13(7):923–9.
Dickmann LJ, Patel SK, Wienkers LC, Slatter JG. Effects of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) and IL-1beta/interleukin 6 (IL-6) combinations on drug metabolizing enzymes in human hepatocyte culture. Curr Drug Metab. 2012;13(7):930–7.
Schmitt C, Kuhn B, Zhang X, Kivitz AJ, Grange S. Disease-drug-drug interaction involving tocilizumab and simvastatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;89(5):735–40. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.35.
Actemra (package insert). South San Francisco CG, Inc; 2014.
Zhuang Y, de Vries DE, Xu Z, Marciniak SJ, Chen D, Leon F, et al. Evaluation of disease-mediated therapeutic protein-drug interactions between an anti-lnterleukin-6 monoclonal antibody (sirukumab) and cytochrome P450 activities in a phase I study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using a cocktail approach. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. doi:10.1002/jcph.561.
Huang SM, Rowland M. The role of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in regulatory review. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(3):542–9. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.320.
Rowland M, Peck C, Tucker G. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetics in drug development and regulatory science. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;51:45–73. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100540.
Machavaram KK, Almond LM, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Gardner I, Jamei M, Tay S, et al. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling approach to predict disease-drug interactions: suppression of CYP3A by IL-6. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013;94(2):260–8. doi:10.1038/clpt.2013.79.
Ogata A, Tanimura K, Sugimoto T, Inoue H, Urata Y, Matsubara T, et al. Phase III study of the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous versus intravenous tocilizumab monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014;66(3):344–54. doi:10.1002/acr.22110.
Perry MG, Kirwan JR, Jessop DS, Hunt LP. Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(1):63–8. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.086561.
Chung SJ, Kwon YJ, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK. The correlation between increased serum concentrations of interleukin-6 family cytokines and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(1):113–20. doi:10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.113.
Crofford LJ, Kalogeras KT, Mastorakos G, Magiakou MA, Wells J, Kanik KS, et al. Circadian relationships between interleukin (IL)-6 and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones: failure of IL-6 to cause sustained hypercortisolism in patients with early untreated rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(4):1279–83. doi:10.1210/jcem.82.4.3852.
Dasgupta B, Corkill M, Kirkham B, Gibson T, Panayi G. Serial estimation of interleukin 6 as a measure of systemic disease in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992;19(1):22–5.
Hirano T, Matsuda T, Turner M, Miyasaka N, Buchan G, Tang B, et al. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988;18(11):1797–801. doi:10.1002/eji.1830181122.
Knudsen LS, Christensen IJ, Lottenburger T, Svendsen MN, Nielsen HJ, Nielsen L, et al. Pre-analytical and biological variability in circulating interleukin 6 in healthy subjects and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Biomarkers. 2008;13(1):59–78. doi:10.1080/13547500701615017.
Sakamoto K, Arakawa H, Mita S, Ishiko T, Ikei S, Egami H, et al. Elevation of circulating interleukin 6 after surgery: factors influencing the serum level. Cytokine. 1994;6(2):181–6.
Roytblat L, Rachinsky M, Fisher A, Greemberg L, Shapira Y, Douvdevani A, et al. Raised interleukin-6 levels in obese patients. Obes Res. 2000;8(9):673–5. doi:10.1038/oby.2000.86.
Arican O, Aral M, Sasmaz S, Ciragil P. Serum levels of TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in patients with active psoriasis and correlation with disease severity. Mediat Inflamm. 2005;5:273–9. doi:10.1155/MI.2005.273.
Ataseven H, Bahcecioglu IH, Kuzu N, Yalniz M, Celebi S, Erensoy A, et al. The levels of ghrelin, leptin, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma due to HBV and HDV infection. Mediat Inflamm. 2006;2006(4), 78380. doi:10.1155/MI/2006/78380.
Wang H, Moser M, Schiltenwolf M, Buchner M. Circulating cytokine levels compared to pain in patients with fibromyalgia—a prospective longitudinal study over 6 months. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(7):1366–70.
Haas CE, Kaufman DC, Jones CE, Burstein AH, Reiss W. Cytochrome P450 3A4 activity after surgical stress. Crit Care Med. 2003;31(5):1338–46. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000063040.24541.49.
Jamei M, Marciniak S, Feng K, Barnett A, Tucker G, Rostami-Hodjegan A. The Simcyp population-based ADME simulator. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009;5(2):211–23. doi:10.1517/17425250802691074.
Rowland Yeo K, Jamei M, Yang J, Tucker GT, Rostami-Hodjegan A. Physiologically based mechanistic modelling to predict complex drug-drug interactions involving simultaneous competitive and time-dependent enzyme inhibition by parent compound and its metabolite in both liver and gut—the effect of diltiazem on the time-course of exposure to triazolam. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010;39(5):298–309. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2009.12.002.
Sanada H, Sekimoto M, Kamoshita A, Degawa M. Changes in expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 subfamily enzymes during development of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J Toxicol Sci. 2011;36(2):181–90.
Uno S, Kawase A, Tsuji A, Tanino T, Iwaki M. Decreased intestinal CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activities in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2007;22(4):313–21.
Evers R, Dallas S, Dickmann LJ, Fahmi OA, Kenny JR, Kraynov E, et al. Critical review of preclinical approaches to investigate cytochrome p450-mediated therapeutic protein drug-drug interactions and recommendations for best practices: a white paper. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(9):1598–609. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.052225.
Gardner D, Lacy E, Wu S, Shealy D. Preclinical characterization of sirukumab, a human monoclonal antibody that targets human interleukin-6 signaling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:207. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.5124.
Zhuang Y, Xu Z, de Vries DE, Wang Q, Shishido A, Comisar C, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of sirukumab following a single subcutaneous administration to healthy Japanese and Caucasian subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013;51(3):187–99. doi:10.5414/CP201785.
Xu Z, Bouman-Thio E, Comisar C, Frederick B, Van Hartingsveldt B, Marini JC, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of a human anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody (sirukumab) in healthy subjects in a first-in-human study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;72(2):270–81. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03964.x.
Chai X, Zeng S, Xie W. Nuclear receptors PXR and CAR: implications for drug metabolism regulation, pharmacogenomics and beyond. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013;9(3):253–66. doi:10.1517/17425255.2013.754010.
Zhou SF, Wang B, Yang LP, Liu JP. Structure, function, regulation and polymorphism and the clinical significance of human cytochrome P450 1A2. Drug Metab Rev. 2010;42(2):268–354. doi:10.3109/03602530903286476.
Kimura A, Naka T, Nohara K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates Stat1 activation and participates in the development of Th17 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(28):9721–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804231105.
Jiang XL, Zhao P, Barrett JS, Lesko LJ, Schmidt S. Application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to predict acetaminophen metabolism and pharmacokinetics in children. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2013;2, e80. doi:10.1038/psp.2013.55.
Hsu V, de LT Vieira M, Zhao P, Zhang L, Zheng JH, Nordmark A, et al. Towards quantitation of the effects of renal impairment and probenecid inhibition on kidney uptake and efflux transporters, using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling and simulations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53(3):283–93. doi:10.1007/s40262-013-0117-y.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. The authors thank Robert Achenbach of Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, for the manuscript preparation and submission support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors Jiang, Zhuang, Xu, Wang, and Zhou are employees of Janssen Research & Development, LLC, at the time of the study. All authors own stock in Johnson & Johnson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Zhuang, Y., Xu, Z. et al. Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Predict Disease-Mediated Therapeutic Protein–Drug Interactions: Modulation of Multiple Cytochrome P450 Enzymes by Interleukin-6. AAPS J 18, 767–776 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-016-9890-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-016-9890-5