Abstract
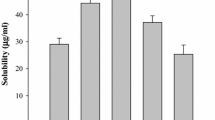
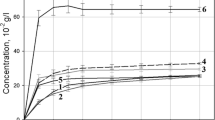
This study focused on an investigation of a high drug-loaded solid dispersion system consisting of drug, carrier, and surfactant. Solid dispersions of a water-insoluble ofloxacin (OFX) with polyethylene glycol (PEG) of different molecular weights, namely binary solid dispersion systems, were prepared at drug to carrier not less than 5∶5. Polysorbate 80, a nonionic surfactant, was incorporated into the binary solid dispersion systems as the third component to obtain the ternary solid dispersion systems. The powder x-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetric studies indicated that crystalline OFX existed in the solid dispersions with high drug loading. However, a decreased crystallinity of the solid dispersions obtained revealed that a portion of OFX was in an amorphous state. The results indicated a remarkably improved dissolution of drug from the ternary solid dispersion systems when compared with the binary solid dispersion systems. This was because of polysorbate 80, which improved wettability and solubilized the non-molecularly dispersed or crystalline fraction of OFX.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiou WL, Riegelman S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion system. J Pharm Sci. 1971;60:1281–1302.
Craig DQM. The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int J Pharm. 2002;231:131–144.
Owusu-Ababio G, Ebube NK, Reams R, Habib M. Comparative dissolution studies for mefenamic acid-polyethylene glycol solid dispersion systems and tablets. Pharm Dev Technol. 1998;3:405–412.
Schachter DM, Xiong J. Solid state NMR perspective of drug-polymer solutions: a model system based on poly(ethylene oxide). Int J Pharm. 2004;281:89–101.
Sethia S, Squillante E. Solid dispersion of carbamazepine in PVP K30 by conventional solvent evaporation and supercritical methods. Int J Pharm. 2004;272:1–10.
Suzuki H, Sunada H. Influence of water-soluble polymers on the dissolution of nifedipine solid dispersions with combined carriers. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1998;46:482–487.
Mura P, Faucci MT, Manderioli A, Bramanti G, Parrini P. Thermal behavior and dissolution properties of naproxen from binary and ternary solid dispersions. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1999;25:257–264.
Okonogi S, Oguchi T, Yonemochi E, Puttipipatkhachorn S, Yamamoto K. Improved dissolution of ofloxacin via solid dispersion. Int J Pharm. 1997;156:175–180.
Craig DQM. Polyethylene glycol and drug release. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1990;16:2514–2515.
Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P, Blaton N, Kinget R. Physicochemical charaterization of solid dispersions of temazepam with polyethylene glycol 6000 and PVP K30. Int J Pharm. 1998;164:67–80.
Puttipipatkhachorn S, Nunthanid J, Yamamoto K, Peck GE. Drug physical state and drug-polymer interaction on drug release from chitosan matrix films. J Control Release. 2001;75:143–153.
Morris KR, Knipp GT, Serajuddin ATM. Structural properties of polyethylene glycol-polysorbate 80 mixture, a solid dispersion vehicle. J Pharm Sci. 1992;81:1185–1188.
Jachowicz R, Nurnberg E, Pieszczek B, Kluczykowska B, Maciejewska A. Solid dispersion of ketoprofen in pellets. Int J Pharm. 2000;206:13–21.
Okonogi S, Puttipipatkhachorn S, Yamamoto K. Thermal behavior of ursodeoxycholic acid in urea: identification of anomalous peak in thermal analysis. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2001;27:819–823.
Corrigan OI, Murphy CA, Timoney RP. Dissolution properties of polyethylene glycols and polyethylene glycol-drug systems. Int J Pharm. 1979;4:67–74.
Luner PE, Babu SR, Mehta SC. Wettability of a hydrophobic drug by surfactant solution. Int J Pharm. 1996;128:29–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: June 2, 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okonogi, S., Puttipipatkhachorn, S. Dissolution improvement of high drug-loaded solid dispersion. AAPS PharmSciTech 7, 52 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070252
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070252