Abstract
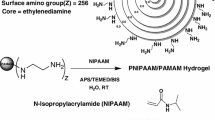
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of ethylenediamine core PAMAM dendrimers, on the release of nifedipine suspended in aqueous gels and to correlate release to the increase in solubility afforded by the dendrimers. Drug release from aqueous 5% HPMC gels containing nifedipine (2% wt/vol) through 0.2-μm membranes was measured using Enhancer cells and 50% ethanolic solution as the receptor medium. The release from gels containing PAMAM G-3 and G-5 (0.25%–1% wt/vol) was compared with gels containing the cosolvent isopropyl alcohol (10%–80% vol/vol). PAMAM dendrimers significantly increased the solubility of nifedipine. This caused a significant increase in the release rate of nifedipine from the gel suspensions. The increase in drug release depended on the concentration and generation size of the dendrimers added. For higher generations (G-5) lower concentrations were needed to obtain equivalent increases in release. Although the increase in solubility and release was not as high as from gels containing high concentrations of the cosolvent isopropyl alcohol, the dendrimers prevented the recrystallization of the drug that was observed when the gels containing isopropyl alcohol were left open.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SL. Nifedipine. In: Florey K, ed.Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances. New York, NY: Academic Press; 1989:223–228.
Perrotti P, Antropoli C, Molino D, De Stefano G, Antropoli M. Conservative treatment of acute thrombosed external hemorrhoids with topical nifedipine.Dis Col Rec. 2001;44:405–409.
Ezri T, Susmallian S. Topical nifedipine vs topical glyceryl trinitrate for treatment of chronic anal fissure.Dis Col Rec. 2003;46: 805–808.
Israel A. Topical gel for the treatment of refractory leg ulcer.Int J Pharm Comp. 2003;7:176–178.
Merenstein D, Rosenbaum D. Is topical nifedipine effective for chronic anal fissures?.J Fam Prac. 2003;52:190–192.
Slawson D. Topical nifedipine plus lidocaine gel effective for anal fissures.Am Fam Physiol. 2003;67:1781.
Segarra J, Santafe J, Garrido M, Martinez de Ibarreta MJ. The topical application of verapamil and nifedipine lowers intraocular pressure in conscious rabbits.Gen Pharmacol. 1993;24:1163–1171.
Michaels AS, Chandrasekaran SK, Shaw JE. Drug permeation through human skin: theory and in vitro experimental measurement.J AIChE. 1975;21:985–996.
Kondo S, Mizuno T, Sugimoto I. Effects of penetration enhancers on percutaneous absorption of nifedipine. Comparison between DDET and Azone.J Pharmacobiodyn. 1988;11:88–95.
Chauhan AS, Sridevi S, Chalasani KB, et al. Dendrimer-mediated transdermal delivery: enhanced bioavailability of indomethacin.J Cont Rel. 2003;90:335–343.
El-Sayed M, Kiani MF, Naimark MD, Hikal AH, Gandhehari H. Extravasation of poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers across microvascular network endothelium.Pharm Res. 2001;18:23–28.
El-Sayed M, Ginski M, Rhodes C, Ghandehari H. Transepithelial transport of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers across Caco-2 cell monolayers.J Cont Rel. 2002;8:355–365.
Kolhe P, Misra E, Kannan RM, Kanna S, Lieh-Lai M. Drug complexation, in vitro release and cellular entry of dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers.Int J Pharm. 2003;259:143–160.
Wang Z, Itoh Y, Hosaka Y, et al. Novel transdermal drug delivery system with polyhydroxyalkanoate and starburst polyamidoamine dendrimer.J. Biosci Bioeng. 2003;95:541–543.
Purohit G, Sakthivel T, Florence AT. The interaction of cationic dendrons with albumin and their diffusion through cellulose membranes.Int J Pharm. 2003;254:37–41.
Vandamme TF, Brobeck L. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers as ophthalmic vehicles for ocular delivery of pilocarpine and tropicamide.J Cont Rel. 2005;102:23–38.
Boje KM, Sak M, Fung HL. Complexation of nifedipine with substituted phenolic ligands.Pharm Res. 1988;5:655–659.
Vippagunta SR, Maul KA, Tallavajhala S, Grant DJW. Solid-state characterization of nifedipine solid dispersions.Int J Pharm. 2002;236:111–123.
Devarakonda B, Hill RA, De Villiers MM. The effect of PAMAM dendrimer generation size and surface functional group on the aqueous solubility of nifedipine.Int J Pharm. 2004;284:133–140.
Higuchi T, Conners KA. Phase-solubility techniques. In: Reilly CN, ed.Advances in analytical chemistry and instrumentation. New York: John Wiley; 1965:117–212.
Jain NK, Patel VV, Taneja LN. Hydrotropic solubilation of nifedipine.Pharmazie 1988;43(3):194–196.
Loftsson T, Fridriksdottir H, Olafsdottir B, Gudmundson O. Solubilization and stabilization of drugs through cyclodextrin complexation.Acta Pharm Nord. 1991;3:215–217.
Larrucea E, Arellano A, Santoyo S, Ygartua P. Interaction of tenoxicam with cyclodextrins and its influence on the in vitro percutaneous penetration of the drug.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2001;27:251–260.
Esfand R, Tomalia DA.Dendrimers and other dendritic polymers. New York: John Wiley; 2001:589–604.
Campbell PS, Chandrasekaran SKUS. Dosage for administrating and percutaneous absorption enhancer. US patent 4379454. April 13, 1983.
Berner B, Mazzenga GC, Otter JH, Steffens RJ, Juang RH, Ebert CD. Ethanol:water mutually enhanced transdermal therapeutic system II: skin permeation of ethanol and nitroglycerin.J Pharm Sci. 1989;78:402–407.
Caira MR, Robbertse Y, Bergh JJ, Song M, De Villiers MM. Structural characterization, physicochemical properties, and thermal stability of three crystal forms of nifedipine.J Pharm Sci. 2003;92:2519–2533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: October 24, 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devarakonda, B., Li, N. & de Villiers, M.M. Effect of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers on the in vitro release of water-insoluble nifedipine from aqueous gels. AAPS PharmSciTech 6, 63 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt060363
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt060363