Abstract
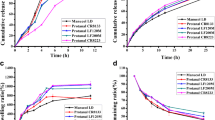
This research investigated the use of sodium alginate for the preparation of hydrophylic matrix tablets intended for prolonged drug release using ketoprofen as a model drug. The matrix tablets were prepared by direct compression using sodium alginate, calcium gluconate, and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) in different combinations and ratios. In vitro release tests and erosion studies of the matrix tablets were carried out in USP phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). Matrices consisting of sodium alginate alone or in combination with 10% and 20% of HPMC give a prolonged drug release at a fairly constant rate. Incorporation of different ratios of calcium gluconate leads to an enhancement of the release rate from the matrices and to the loss of the constant release rate of the drug. Only the matrices containing the highest quantity of HPMC (20%) maintained their capacity to release ketoprofen for a prolonged time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timmins P, Delargy AM, Minchom CM, Howard R. Influence of some process variables on product properties for a hydrophilic matrix controlled release tablet.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1992;38:113–118.
Aslani P, Kennedy RA. Studies on diffusion in alginate gels. I. Effect of cross-linking with calcium or zinc ions on diffusion of acetaminophen.J Controlled Release. 1996;42:75–82.
Yotsuyanagi T, Yoshioka I, Segi N, Ikeda K. Acidinduced and calcium-induced gelation of alginic acid: bead formation and pH dependent swelling.Chem. Pharm Bull. 1991;39:1072–1074.
Rubio MR, Ghaly ES. In vitro release of acetaminophen from sodium alginate controlled release pellets.Durg Dev Ind Pharm. 1994;20:1239–1251.
Timida H, Mizuo C, Nakamura C, Kiryu S. Imipramine release from Ca-alginate gel beads.Chem. Pharm Bull. 1993;41:1475–1477.
Mumper RJ, Hoffinan AS, Poulakkainen PA, Bouchard LS, Gombotz WR. Calcium-alginate beads for the oral delivery of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1): stabilization of TGF-β1 by the addition of polyacrylic acid within acid-treated beads.J Controlled Release. 1994;30:241–251.
Kim C-K, Lee E-J. The controlled release of blue dextran from alginate beads.Int J Pharm. 1992;79:11–19.
Bowersock TL, Hogenesch H, Suckow M, et al. Oral vaccination with alginate microsphere systems.Int J Pharm. 1996;39:209–220.
Grant GT, Morris ER, Rees DA, Smith PJC, Thom D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: the egg box model.FEBS Lett. 1973;32:195–198.
Badwan AA, Abumalooh A, Sallam E, Abukalaf A, Jawan O. A sustained release drug delivery system using calcium alginate beads.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1985;11:239–256.
Kikuchi A, Kawabuchi M, Sugihara M, Sakurai Y, Okano T. Controlled release of macromolecular dextran from calcium-alginate gel beads.Proceed Intern Symp Control Rel Bioact Mater. 1996;23:737–738.
Jamali F, Brocks DR. Pharmacokinetics of ketoprofen and its enantiomers,Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990;19:197–217.
Ranga Rao KV, Padmalatha Devi K, Buri, P. Cellulose matrices for zero-order release of soluble drugs.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1988;14:2299–2320.
Ritger PL, Peppas NA. A simple equation for description of solute release. II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J Controlled Release. 1987;5:37–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giunchedi, P., Gavini, E., Moretti, M.D.L. et al. Evaluation of alginate compressed matrices as prolonged drug delivery systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 1, 19 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt010319
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt010319