1bstract
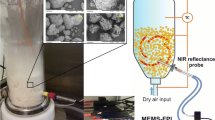
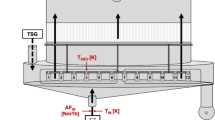
1 system for fluidized bed granulator automation with in-line multichannel near infrared (NIR) moisture measurement and a unique air flow rate measurement design was assembled, and the information gained was investigated. The multivariate process data collected was analyzed using principal component analysis (PCA). The test materials (theophylline and microcrystalline cellulose) were granulated and the calibration behavior of the multichannel NIR set-up was evaluated against full Fourier Transform (FT) NIR spectra. Accurate and reliable process air flow rate measurement proved critical in controlling the granulation process. The process data describing the state of the process was projected in two dimensions, and the information from various trend charts was outlined simultaneously. The absorbence of test material at correction wavelengths (NIR region) and the nature of material-water interactions affected the detected in-line NIR water signal. This resulted in different calibration models for the test materials. Development of process analytical methods together with new data visualization algorithms creates new tools for in-process control of the fluidized bed granulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browne HJ and Olsson KI. Discussion of control systems in pharmaceutical manufacturing.Pharm Eng. 1998;18(4):84–92.
López O. Qualification of supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.J Valid Technol. 1999;5(2):148–160.
Workman J, Veltkamp DJ, Doherty S, Anderson BB, Creasy, KE, Koch M, Tatera JF, Robinson AL, Bond L, Burgess LW, Bokerman GN, Ullman AH, Darsey, GP, Mozayeni F, Bamberger JA, and Greenwood MS. Process analytical chemistry.Anal Chem. 1999;71:121R-180R.
Watano S, Terashita K, and Miyanami K. Development and application of infrared moisture sensor to complex granulation.Bull Univ Osaka Pref. 1990;Series A. 39:187–197.
White JG. On-line moisture detection for a microwave vacuum dryer.Pharm Res. 1994;11(5):728–732.
List K and Steffens K-J. Überwachung und Steuerung von Granulationsprozessen mit Hilfe der Nah-Infrarot-Spektroskopie.Pharm Ind. 1996;58:347–353.
Frake, P., Greenhalgh, D., Grierson, S.M., Hempenstall, J.M. and Rudd, D.R., 1997. Process control and end-point determination of a fluid bed granulation by application of near infra-red spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 151. 75–80.
Goebel SG and Steffens K-J. Online-messung der Produktfeuchte und Korngröße in der Wirbelschnicht mit der Nah-Infrarot-Spektroskopie.Pharm Ind. 1998;60:889–895.
Rantanen J, Lehtola S, Rämet P, Mannermaa J-P. and Yliruusi J. On-line monitoring of moisture content in an instrumented fluidized bed granulator with a multi-channel NIR moisture sensor.Powd Technol. 1998;99:163–170.
Rantanen J, Antikainen O, Mannermaa J.-P., and Yliruusi J. Use of the near-infrared reflectance method for measurement of moisture content during granulation.Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000;5:209–217.
Hailey PA, Doherty P, Tapsell P, Oliver T, and Aldridge PK. Automated system for the on-line monitoring of powder blending processes using near-infrared spectroscopy: Part I. System development and control.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1996;14:551–559.
Sekulic SS, Ward HW, Brannegan DR, Stanley ED, Evans CL, Sciavolino ST, Hailey PA, and Aldridge PK. On-line monitoring of powder blend homogeneity by near-infrared spectroscopy.AnalChem. 1996;68:509–513.
Kirsch JD and Drennen JK. Determination of film-coated tablet parameters by near-infrared spectrscopy.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1995;13:1273–1281.
Kirsch JD and Drennen JK. Near-infrared spectroscopic monitoring of the film coating process.Pharm Res. 1996;13:234–237.
Hammond J, Jee RD, and Moffat AC. Monitoring reactions in combinatorial chemistry using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999:51(Suppl.):22, abstract.
Niskanen T, Yliruusi J, Niskanen M, and Kontro O. Granulation of potassium chloride in fluidized bed granulator: Part I. Effect of flow rate.Acta Pharm Fenn. 1990; 99:13–22.
Merkku P, Yliruusi J, and Hellen L. Testing of an automated laboratory scale fluidized bed granulator using different bed loads.Acta Pharm Fenn. 1992;101:173–180.
Wold S, Albano C, Dunn WJ, Edlund U, Esbensen K, Geladi P, Hellberg S, Johansson E, Lindberg W, and Sjöströn M. Multivariate data analysis in chemistry. In BR Kowalski (ed.),Chemometrics: Mathematics and Statistics in Chemistry. Dordrecht, Holland: D Reidel, 1984.
Jackson JE.A User's Guide to Principal Components. New York: John Wiley, 1991.
Wold S, Kettaneh N, Fridén H, and Holmberg A. Modelling and diagnostics of batch processes and analogous kinetic experiments.Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 1998;44:331–340.
Mercer PG. A method of measuring the content of a substance in a film comprising at least one other substance. GB Patent 2 044 443. 1980.
Niemelä P. Integrated infrared detectors for industrial process analyzers.Proc SPIE 1988;918:80–84.
Schaefer T and Worts O. Control of fluidized bed granulation. III. Effect of inlet air temperature and liquid flow rate on granule size and size distribution. Control of moisture content of granules in the drying phase.Arch. Pharm Chem Sci. 1978;6:1–13.
Björn IN, Folestad S, Ström D, Âberg C, and Andersson M. In-line NIR spectrometry—a tool for quality control during fluidized bed coating. 9th International Conference on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, Verona, Italy, Abstract book O. 5-5. 1999.
Herman J, Remon JP, Visavarungroj N, Schwartz JB, and Klinger GH. Formation of theophylline monohydrate during the pelletisation of microcrystalline celluloseanhydrous theophylline blends.Int J Pharm. 1988;151:75–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rantanen, J., Känsäkoski, M., Suhonen, J. et al. Next generation fluidized bed granulator automation. AAPS PharmSciTech 1, 10 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1208/pt010210
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt010210