Abstract
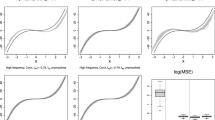
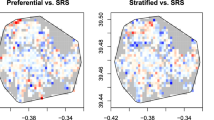
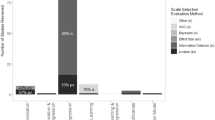
In a spatial regression context, scientists are often interested in a physical interpretation of components of the parametric covariance function. For example, spatial covariance parameter estimates in ecological settings have been interpreted to describe spatial heterogeneity or “patchiness” in a landscape that cannot be explained by measured covariates. In this article, we investigate the influence of the strength of spatial dependence on maximum likelihood (ML) and restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimates of covariance parameters in an exponential-with-nugget model, and we also examine these influences under different sampling designs—specifically, lattice designs and more realistic random and cluster designs—at differing intensities of sampling (n=144 and 361). We find that neither ML nor REML estimates perform well when the range parameter and/or the nugget-to-sill ratio is large—ML tends to underestimate the autocorrelation function and REML produces highly variable estimates of the autocorrelation function. The best estimates of both the covariance parameters and the autocorrelation function come under the cluster sampling design and large sample sizes. As a motivating example, we consider a spatial model for stream sulfate concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustine, D. J., and Frank, Douglas A. (2001), “Effects of Migratory Grazers on Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nitrogen Properties in a grassland Ecosystem,” Ecology, 82, 3149–3162.
Baker, L. A., Herlihy, A. T., Kaufmann, P. R., and Eilers, J. M. (1991), “Acidic Lakes and Streams in the United States: The Role of Acidic Deposition,” Science, 252, 1151–1154.
Banerjee, S., Carlin, B. P., and Gelfand, A. E. (2004), Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data, Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC Press.
Bellehumeur, C., and Legendre, P. (1998), “Multiscale Sources of Variatio in Ecological Variables: Modeling Spatial Dispersion, Elaborating Sampling Designs,” Landscape Ecology, 13, 15–25.
Chen, H.-S., Simpson, D. G., and Ying, Z. (2000), “Infill Asymptotics for a Stochastic Process Model With Measurement Error,” Statistica Sinica, 10, 141–156.
Cressie, N., and Majure, J. J. (1997), “Spatio-Temporal Statistical Modeling of Livestock Waste in Streams,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 2, 24–47.
Cressie, N. A. C. (1993), Statistics for Spatial Data, New York: Wiley.
Cressie, N. A. C., and Lahiri, S. N. (1996), “Asymptotics for REML Estimation of Spatial Covariance Parameters,” Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 50, 327–341.
Dalthorp, D., Nyrop, J., and Villani, M. (2000), “Foundations of Spatial Ecology: The Reification of Patches Through Quantitative Description of Patterns and Pattern Repetition,” Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 96, 119–127.
Franklin, R. B., Blum, L. K., McComb, A. C., and Mills, A. L. (2002), “A Geostatistical Analysis of Small-Scale Spatial Variability in Bacterial Abundance and Community Structure in Salt Marsh Creek Bank Sediments,” FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 42, 71–80.
Ganio, L. M., Torgensen, C. E., and Gresswell, R. E. (2005), “A Geostatistical Approach for Describing Spatial Pattern in Stream Networks,” Frontiers in Ecology and Environment, 3, 138–144.
Gardner, B., Sullivan, P. J., and Lembo, Jr., A. J. (2003), “Predicting Stream Temperatures: Geostatistical Model Comparison using Alternative Distance Metrics,” Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 60, 344–351.
Herlihy, A. T., Kaufmann, P. R., Church, M. R., Wigington, Jr., P. J., Webb, J. R., and Sale, M. J. (1993), “The Effects of Acidic Deposition on Streams in the Appalachain Mountain and Piedmont Region of the mid-Atlantic United States,” Water Resources Research, 29, 2687–2703.
Herlihy, A. T., Kaufmann, P. R., and Mitch, M. E. (1990), “Regional Estimates of Acid Mine Drainage Impact on Streams in the mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States,” Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 50, 91–107.
— (1991), “Stream Chemistry in the Eastern United States 2. Current Sources of Acidity in Acidic and Low Acid-Neutralizing Capacity Streams,” Water Resources Research, 27, 629–642.
Hoeting, J. A., Davis, R. A., Merton, A. A., and Thompson, S. E. (2006), “Model Selection for Geostatistical Models,” Ecological Applications, 16, 87–98.
Kaufmann, P. R., Herlihy, A. T., and Baker, L. A. (1992), “Sources of Acidity in Lakes and Streams of the United States,” Environmental Pollution, 77, 115–122.
Kaufmann, P. R., Herlihy, A. T., Mitch, M. E., Messer, J. J., and Overton, W. S. (1991), “Stream Chemistry in the Eastern United States 1. Synoptic Survey Design, Acid-Base Status, and Regional Patterns,” Water Resources Research, 27, 611–627.
Kennard, D. K., and Outcalt, K. (2006), “Modeling Spatial Patterns of Fuels and Fire Behavior in a Longleaf Pine Forest in the Southeastern USA,” Fire Ecology, 2, 31–52.
Lark, R. M. (2000), “Estimating Variograms of Soil Properties by the Method-of-Moments and Maximum Likelihood,” European Journal of Soil Science, 51, 717–728.
Madsen, L. J. (2000), “Comparing Two Parameterizations of the Exponential Variogram in REML Parameter Estimation and Spatial Prediction,” unpublished master’s thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York.
Mardia, K., and Marshall, R. (1984), “Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Models for Residual Covariance in Spatial Regression,” Biometrika, 71, 135–146.
Minasny, B., and McBratney, A. B. (2005), “The Matérn Function as a General Model for Soil Variograms,” Geoderma, 128, 192–207.
Muller, W. G., and Zimmerman, D. L. (1999), “Optimal Designs for Variogram Estimation,” Environmetrics, 10, 23–37.
Ollinger, S. V., Aber, J. D., Lovett, G. M., Millham, S. E., Lathrop, R. G., and Ellis, J. M. (1993), “A Spatial Model of Atmospheric Deposition for the Northeastern U.S.,” Ecological Applications, 3, 459–472.
Peterson, E. E., Merton, A. A., Theobald, D. M., and Urquhart, N. (2006), “Patterns of Spatial Autocorrelation in Stream Water Chemistry,” Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121, 569–594.
Pettitt, A. N., and McBratney, A. B. (1993), “Sampling Designs for Estimating Spatial Variance Components,” Applied Statistics, 42, 185–209.
Rossi, R. E., Mulla, D. J., Journel, A. G., and Franz, E. H. (1992), “Geostatistical Tools for Modeling and Interpreting Ecological Spatial Dependence,” Ecological Monographs, 62, 277–314.
Rufino, M. M., Maynou, F., Abello, P., and Yule, A. B. (2004), “Small-Scale Non-linear Geostatistical Analysis of Liocarcinus depurator (crustacea: brachyura) A bundance and Size Structure in a Western Mediterranean Population,” Marine Ecology Progress Series, 276, 223–235.
Saetre, P., and Baath, E. (2000), “Spatial Variation and Patterns of Soil Microbial Community Structure in a Mixed Spruce-Birch Stand,” Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32, 909–917.
Schabenberger, O., and Gotway, C. A. (2005), Statistical Methods for Spatial Data Analysis, Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC Press.
Schwarz, P. A., Fahey, T. J., and McCulloch, C. E. (2003), “Factors Controlling Spatial Variation of Tree Species Abundance in a Forested Landscape,” Ecology, 84, 1862–1878.
Stein, M. L. (1988), “Asymptotically Efficient Prediction of a Random Field with a Misspecified Covariance Function,” The Annals of Statistics, 16, 55–63.
Swallow, W. H., and Monahan, J. F. (1984), “Monte Carlo Comparison of ANOVA, MIVQUE, REML, and ML Estimators of Variance Components,” Technometrics, 26, 47–57.
Thompson, S. E. (2001), “Bayesian Model Averaging and Spatial Prediction,” unpublished PhD thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO.
Ver Hoef, J. (2004), Graybill Conference, June 16–18. In Short Course on Spatial Statistics, Fort Collins, CO.
Webster, R., and Oliver, M. A. (2001), Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, West Sussex, England: Wiley.
Xia, G., Miranda, M. L., and Gelfand, A. E. (2006), “Approximately Optimal Spatial Design Approaches for Environmental Health Data,” Environmentrics, 17, 363–385.
Zhang, H. (2004), “Inconsistent Estimation and Asymptotically Equal Interpolations in Model-Based Geostatistics,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 99, 250–261.
Zhang, H., and Zimmerman, D. L. (2005), “Towards Reconciling two Asymptotic Frameworks in Spatial Statistics,” Biometrika, 92, 921–936.
Zhu, Z., and Stein, M. L. (2005), “Spatial Sampling Design for Parameter Estimation of the Covariance Function,” Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 134, 583–603.
Zhu, Z., and Zhang, H. (2006), “Spatial Sampling Design Under the Infill Asymptotic Framework,” Environmetrics, 17, 323–337.
Zimmerman, D. L. (2006), “Optimal Network Design for Spatial Prediction, Covariance Parameter Estimation and Empirical Prediction,” Environmetrics, 17, 635–652.
Zimmerman, D. L., and Zimmerman, M. B. (1991), “A Comparison of Spatial Semivariogram Estimators and Corresponding Ordinary Kriging Predictors,” Technometrics, 33, 77–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irvine, K.M., Gitelman, A.I. & Hoeting, J.A. Spatial designs and properties of spatial correlation: Effects on covariance estimation. JABES 12, 450–469 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1198/108571107X249799
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1198/108571107X249799