Abstract
Purpose
Important underlying mechanisms of nitroglycerine tolerance development include oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction, and there is paucity of information on how to reduce the tolerance during long-term administration. Taurine, a sulfonic amino acid, was reported to possess antioxidant, cardio-regulatory, neuro-modulatory, and membrane-stabilizing effect. The present study was designed to investigate the potential ability of taurine to prevent nitroglycerine-induced tolerance.
Methods
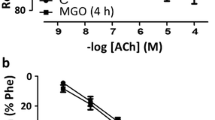
The effect of taurine on nitroglycerin-induced tolerance was investigated in endothelium intact and endothelium-denuded aortic ring preparations. In the in vivo study, male Wistar rats were pre-treated with taurine for ten days and co-treated with nitroglycerin (GTN) 50 mg/kg for 3 days. Then, the aortic ring was harvested and tested in vitro for GTN tolerance. The serum was used to test for oxidative stress parameter (malondialdehyde, reduced glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT)).
Results
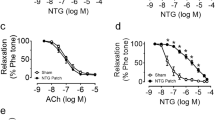
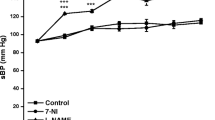
Taurine (20 mM) co-incubated with GTN significantly augmented vasodilatory response to nitroglycerin (GTN) in endothelial-denuded aortic rings. Pre-treatment with taurine (100 and 200 mg/kg) also ameliorated GTN (50 mg/kg)-induced tolerance in isolated aortic ring in rats. Also, taurine (100 and 200 mg/kg) significantly (p < 0.05) increased serum nitrite, GSH, and CAT levels while reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration.
Conclusion
Taurine could prevent nitroglycerin-induced tolerance by increasing serum nitric oxide level and decreasing oxidative stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and material for this study will be provided upon request.
Code availability
Not Applicable.
Abbreviations
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- GTN:
-
Nitroglycerine
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- NO2 − :
-
Nitrite
- GSH-Px:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- cyt P450:
-
Cytochrome P450
- L-NAME:
-
N-nitro-L-arginine methylester
References
Daiber A, Wenzel P, Oelze M, Schuhmacher S, Jansen T, Munzel T. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH-2)—maker of and marker for nitrate tolerance in response to nitroglycerin treatment. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;178:40–7.
Daiber A, Munzel T. Organic nitrate therapy, nitrate tolerance, and nitrate-induced endothelial dysfunction: emphasis on redox biology and oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;23:899–942.
Sydow K, Daiber A, Oelze M, Chen Z, August M, Wendt M, et al. Central role of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and reactive oxygen species in nitroglycerin tolerance and cross-tolerance. J Clin Investig. 2004;113:482–9.
Cai H, Griendling KK, Harrison DG. The vascular NADPH oxidases as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:471–8.
Jurt U, Gori T, Ravandi A, Babaei S, Zeman P, Parker JD. Differential effects of pentaerythritol tetranitrate and nitroglycerin on the development of tolerance and evidence of lipid peroxidation: a human in vivo study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38:854–9.
Fukatsu A, Hayashi T, Miyazaki-Akita A, Matsui-Hirai H, Furutate Y, Ishitsuka A, Hattori Y, Iguchi A. Possible usefulness of apocynin, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, for nitrate tolerance: prevention of NO donor-induced endothelial cell abnormalities. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293:H790–7.
Daiber A, August M, Baldus S, Wendt M, Oelze M, Sydow K, Kleschyov AL, Munzel T. Measurement of NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide with the luminol analogue L-012. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;36:101–11.
Daiber A, Oelze M, Ulyok S, Coldewey M, Schulz E, Treiber N, et al. Heterozygous deficiency of manganese superoxide dismutase in mice (Mn-SOD+/-): a novel approach to assess the role of oxidative stress for the development of nitrate tolerance. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:579–88.
Munzel T, Daiber A, Gori T. More answers to the still unresolved question of nitrate tolerance. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2666–73.
Wenzel P, Hink U, Oelze M, Schuppan S, Schaeuble K, Schildknecht S, et al. Role of reduced lipoic acid in the redox regulation of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH-2) activity. Implications formitochondrial oxidative stress and nitrate tolerance. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:792–9.
Sayed N, Kim DD, Fioramonti X, Iwahashi T, Duran WN, Beuve A. Nitroglycerin-induced S-nitrosylation and desensitization of soluble guanylyl cyclase contribute to nitrate tolerance. Circ Res. 2008;103:606–14.
Dudek M, Bednarski M, Bilska A, Iciek M, Sokołowska-Jeżewicz M, Filipek B, Włodek L. The role of lipoic acid in prevention of nitroglycerin tolerance. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;591:203–10.
Munzel T, Kurz S, Rajagopalan S, Thoenes M, Berrington WR, Thompson JA, et al. Hydralazine prevents nitroglycerin tolerance by inhibiting activation of a membrane-bound NADH oxidase. A new action for an old drug. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:1465–70.
Wang T, Zhou Q, Jiang X, Li P, Tan W, Sun Y, et al. Dropping pill prevents nitroglycerin-induced tolerance in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016;9(7):13793–801.
Zhou Q, Sun Y, Tan W, Liu X, Qian Y, Ma X, et al. Effect of Shenmai injection on preventing the development of nitroglycerin- induced tolerance in rats. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(4):e0176777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176777.
Wójcik OP, Koenig KL, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Costa M, Chen Y. The potential protective effects of taurine on coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 2010;208:19–25.
Huxtable RJ. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev. 1992;72:101–63.
Hanson SH. The role of taurine in diabetes and the development of diabetes complications. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001;17:330–46.
Abebe W, Mahmood S, Mozaffari S. Role of taurine in the vasculature: an overview of experimental and human studies. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;1(3):293–311.
Azuma J, Hasegawa H, Sawamura A. Taurine for treatment of congestive heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 1982;2:303–4.
Mizushima S, Nara Y, Sawamura M, Yamori Y. Effects of oral taurine supplementation on lipids and sympathetic nerve tone. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996;403:615–22.
Militante JD, Lombardini JB. Treatment of hypertension with oral taurine: experimental and clinical studies. Amino Acids. 2002;23:381–93.
Xu YJ, Saini HK, Zhang M, Elimban V, Dhalla NS. MAPK activation and apoptotic alterations in hearts subjected to calcium paradox are attenuated by taurine. Cardivas Res. 2006;72:163–74.
Yamauchi-Takihara K, Azuma J, Kishimoto S, Onishi S, Sperelakis N. Taurine prevention of calcium paradox-related damage in cardiac muscle. Its regulatory action on intracellular cation contents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;37:2651–8.
Hayes KC, Pronczuk A, Addesa AE, Stephan ZF. Taurine modulates platelet aggregation in cats and humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49:1211–6.
Mozaffari MS, Miyata N, Schaffer SW. Effects of taurine and enalapril on kidney function of the hypertensive glucose-intolerant rat. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:673–80.
Zhu J, Kang L, Ye Q, Fan G, Liang Y, Yan C, et al. Effects of Shenfu injection and its main components on the contraction of isolated rat thoracic aortic rings. PloS one. 2013;8(10):e78026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078026.
Azarmi Y, Babaei H, Alizadeh F, Gharebageri A, Fouladi DF, Nikkhah E. Allopurinol prevents nitroglycerin-induced tolerance in rat thoracic aorta. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013;63:113–9.
Zhou Q, Sun Y, Tan W, Liu X, Qian Y, Ma X, et al. Effect of Shenmai injection on preventing the development of nitroglycerin-induced tolerance in rats. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(4): e0176777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176777.
Green LC, Wagner DA, Godowsky J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982;126:131–8.
Nagababu E, Rifkind JM, Sesikeran B, Lakshmaiah N. Assessment of antioxidant activities of eugenol by in vitro and in vivo methods. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ). 2010;610:165–80.
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR. Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4, bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology. 1974;11:151–69.
Goth L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta. 1991;196:143–52.
Alabi B, Omobowale T, Badejo J, Adedapo A, Fagbemi O, Iwalewa O. Protective effects and chemical composition of Corchorus olitorius leaf fractions against isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury through p65NFkB-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway in rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020; 31(5). https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0108.
Wang X, Chen L, Wang T, Jiang X, Zhang H, Li P. Ginsenoside Rg3 antagonizes Adriamycin induced cardiotoxicity by improving endothelial dysfunction from oxidative stress via upregulating the Nrf2-ARE pathway through the activation of akt. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. 2015;22(10):875–84.
Ristori MT, Verdetti J. Effects of taurine on rat aorta in vitro. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991;5:245–58.
Xue W, Zhang M, Li J, Wu D, Niu L, Liang Y. Effect of taurine on aortic rings isolated from fructose-fed insulin resistance Sprague-Dawley rat are changed. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2008;22:461–8.
Niu LG, Zhang MS, Liu Y, Xue WX, Liu DB, Zhang J, Liang YQ. Vasorelaxant effect of taurine is diminished by tetraethylammonium in rat isolated arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;580:169–74.
Bakker AJ, Berg HM. Effect of taurine on sarcoplasmic reticulum function and force in skinned fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibers of the rat. J Physiol. 2002;538:185–94.
Kurz S, Hink U, Nickenig G, Borthayre AB, Harrison DG, Munzel T. Evidence for a causal role of the renin-angiotensin system in nitrate tolerance. Circulation. 1999;99:3181–7.
Munzel T, Daiber A, Gori T. Nitrate therapy, new aspects concerning molecular action and tolerance. Circulation. 2011;123:2132–44.
Munzel T, Sayegh H, Freeman BA, Tarpey MM, Harrison DG. Evidence for enhanced vascular superoxide anion production in nitrate tolerance. A novel mechanism underlying tolerance and cross-tolerance. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:187–94.
Oelze M, Knorr M, Kroller-Schon S, Kossmann S, Gottschlich A, Rummler R, et al. Chronic therapy with isosorbide-5-mononitrate causes endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and a marked increase in vascular endothelin-1 expression. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3206–16.
Harada H, Kitazaki K, Tsujino T, Watarai Y, Iwata S, Nonaka H, et al. Oral taurine supplementation prevents the development of ethanol induced hypertension in rats. Hypertens Res. 2000;23:277–84.
Fennessy EM, Monelet MB, Wang JH, Kelly CJ, Bouchier-Hayes DJ. Taurine and vitamin C modify monocyte and endothelial dysfunction in young smokers. Circulation. 2003;107:410–5.
Sugamura K, Keaney JF. Reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular disease. Free Radical Biol Med. 2011;51:978–92.
Daiber A, Wenzel P, Oelze M, Munzel T. New insights into bioactivation of organic nitrates, nitrate tolerance and cross-tolerance. Clin Res Cardiol. 2008;97:12–20.
Das J, Vasan V, Sil PC. Taurine exerts hypoglycemic effect in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, improves insulin-mediated glucose transport signaling pathway in heart and ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;258:296–308.
Das J, Sil PC. Taurine ameliorates alloxan-induced diabetic renal injury, oxidative stress-related signaling pathways and apoptosis in rats. Amino Acids. 2012;43:1509–23.
Adedara IA, Alake SE, Adeyemo MO, Olajide LO, Ajibade TO, Farombi EO. Taurine enhances spermatogenic function and antioxidant defense mechanisms in testes and epididymis of L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:181–9.
Li X, Catalina F, Grundy SM, Patel S. Method to measure apolipoprotein B-48 and B-100 secretion rates in an individual mouse: evidence for a very rapid turnover of VLDL and preferential removal of B-48-relative to B-100-containing lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1996;37:210–20.
Nandhini AT, Thirunavukkarasu V, Anuradha CV. Stimulation of glucose utilization and inhibition of protein glycation and AGE products by taurine. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004;181(3):297–303.
Parvez S, Tabassum H, Banerjee BD, Raisuddin S. Taurine prevents tamoxifen induced Mitochondrial oxidative damage in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;102:382–7.
Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Ramila KC, Azuma J. Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. J Biomed Sci. 2010;17:2–8.
Schaffer SW, Azuma J. Taurine attenuates hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;403:181–8.
Michael AM, Ronan GC, David HO, Patricia F, Chris T, David JB. Two weeks taurine supplementation reverses endothelial dysfunction in young male type 1 diabetics. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2010;7(4):300–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was carried out in collaboration among all authors. The following authors OO, JAB, and OSF designed the study. OO, BAA, AAM, and JAB performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol and the first draft of the manuscript. EOI and OSF managed the managed literature searches and supervised the experiment. All authors read and approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All of the experiments were conducted according to the approved guidelines set by the University of Ibadan Animal Care and Use Research Ethics Committee (UI-ACUREC), which is in agreement with the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” prepared by the National Academy of Science and published by the National Institutes of Health. The ethical approval number assigned for animal use in this study by UI-ACUREC was UI-ACUREC/17/0071.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odebiyi, O., Badejo, J., Alabi, B. et al. Evaluation of modulatory effects of taurine in the aortic and myocardial tissue of nitroglycerin-induced tolerance Wistar rats. Nutrire 46, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-021-00141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-021-00141-9