Abstract
Seven gouge cores in the middle Sepik Plain (northern Papua New Guinea) were bored to clarify the depositional age and the chemical characteristics of the tropical peat. The weakly-acidic peat layer (3–4 m thick) is distributed around the south bank of the Blackwater Lakes. The peat layer consists mainly of sago palm and grass remains within a mineral matrix of very fine sand and clay. Radiocarbon dating indicates that the peat’s formation had commenced by 3,710–3,560 cal BP. Nitrogen and exchangeable potassium reach their highest values in the upper 60 cm of the peat column. Conversely, exchangeable sodium, calcium and magnesium, as well as carbon, increase their values with depth in the peat. These differences in the exchangeable cations’ contribution suggest changes in the plant species, which were decomposed during the peat’s formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Carbon dioxide storage in tropical peatlands has recently attracted significant international attention. Carbon dioxide emission from deforested tropical peatlands is a very important and controversial issue, in the context of global warming [1,2]. Tropical peatlands are widely distributed in south-east Asia and Oceania, but only a limited area has been studied, with regard to carbon dioxide storage and emission problems. The detailed distribution, formation process and chemical properties of tropical peats have been clarified in Indonesia and Malaysia (e.g. [3-6]). However, there have been relatively few studies of tropical peatlands in Oceania. Oceania’s largest peatland area, estimated at 290,000–500,000 ha [7,8], is situated in Papua New Guinea.
Previous research on Papua New Guinea included studies of highland peat in the mountain areas [9,10] and a few geomorphologic studies of the main peatlands, which are distributed in the floodplains of the Fly and Sepik Rivers [11,12]. Additional geological data in these regions is expected to clarify the details of tropical peat distribution, as well as the floodplains’ geomorphological development.
In the present study, an array coring survey was conducted around the south bank of the Blackwater Lakes, in the middle Sepik Plain. The peat layer’s thickness, its depositional age and chemical characteristics were identified to determine the formation process and the distribution range of tropical peats in the inland floodplains of Papua New Guinea.
Study area
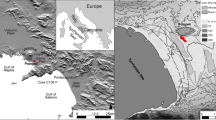
The study area comprises the water catchment of the Sepik River, extending over 77,700 km2 within a tectonic basin [13], in the northern part of Papua New Guinea (Figure 1). The river (1,126 km total length) flows eastwards through the basin and discharges into the Bismarck Sea [14]. The Sepik basin is filled with alluvial sediments originating from the Pleistocene rocks, which form the nearby mountains [15].
The physical environment of the middle Sepik Plain is divided into three land systems: ‘Sanai’, ‘Pandago’ and ‘Kabuk’ [16]. The Sanai component corresponds to floodplain swamps with minor low levees, scrolls and oxbow lakes; subject to severe flooding. These areas contain organic soils, alluvial black clays and plastic heavy clay and young alluvial soils covered with mixed grass. Phragmites swamps, in particular, also include minor herbaceous swamp vegetation. Such areas are widespread along the Sepik River. In contrast, the Kabuk and Pandago components are distributed on the edge of the flood plain. The Kabuk component refers to permanent floodplain swamps, consisting of organic soils and plastic, heavy clay, young alluvial soils, which cover the sago palm-Phragmites swamps. The Pandago component corresponds to seasonally-inundated floodplain swamps. These are very poorly drained and include swampy, plastic, heavy clay, young alluvial soils, occasionally with organic soils that are covered by sago palm forests and sago palm swamps.
Although the study area is located in a tropical region, rainfall is generally not heavy, and the monthly averages range from 203 to 356 mm in the wettest month, i.e. between October and March, to 51–127 mm in the driest month, i.e. between March and October. Rainfall causes water-level fluctuations in the rivers and lakes [17,18].
The field surveys conducted for the purposes of the present study focused on the south bank of the Blackwater Lakes, about 150 km upwards from the river mouth and about 10 m above sea level (Figure 2). The floodplain consists mainly of meander belts, backmarsh, abandoned channels and lakes. Most of the lakes are separated by the meander belts of a Sepik tributary. The Blackwater Lakes are vast lakes in the middle Sepik Plain, which expand to approximately 60 km2 during the rainy season. A village named ‘Kraimbit’ is located on the south bank of the lake. The typical micro-landscape of the middle Sepik Plain is observed on the southern bank of the Black Water Lakes. It can be divided into three main areas, based on their physical environment: permanent floodplain swamps, seasonally-inundated floodplains covered by grass (residential quarter and garden) and seasonally-inundated flood-plains covered by sago palm, corresponding to Sanai, Kabuk and Pandago.
Methods
A geological transect, from Blackwater Lakes to Sago Forest, was realised, extracting seven gouge cores (KB1: 4°32'19.37"S, 143°22'51.04"E; KB2: 4°32'20.94"S, 143°22'53.29"E, KB3: 4°32’21.73”S, 143°22’54.66”E; KB4: 4°32’18.87”S, 143°22’50.43”E; KB5: 4°32’20.94”S, 143°22’53.29”E; KB7: 4°32’23.32”S, 143°22’55.14”E; KB8: 4°32’25.55”S, 143°22’56.31”E) at 20–60 m intervals along the transect, to determine the distribution of the peat layer. In addition, observations on the village outcrops were recorded. The 250 m transect crosses the floodplain, from north to south, centred at Kraimbit village. The cores are 25 mm in diameter and range from 1.0 to 4.5 m in depth. The sedimentary features of the cores were logged in the field. The relative elevation of each coring site was determined using an automatic level, based on the water level of the Blackwater Lakes at 6:00 P.M. on 21 August 2011.
Samples from two cores were radiocarbon-dated using the accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) method. The ages were calibrated using Calib5.0 [19] and were converted from radiocarbon years (y BP) to calendar years (cal BP) using INTCAL04 [20].
From core KB1, 38 samples were collected for chemical analysis, at 0.1-metre depth-intervals. They were air-dried and then sieved through a 2-mm mesh. Un-decomposed pieces of wood, whenever present, were removed from the samples, in this step. Total carbon (TC) and total nitrogen (TN) content, as well as their ratio (C/N) were measured through a CN analyser (CN Corder MT-700, Yanaco) in the air-dried fine samples. The pH was determined by a glass electrode (pH/COND metre D-54, HORIBA) in suspension (the sample: deionized water = 1: 10 at mass ratio) after stirring for one hour. To determine the exchangeable cation contents, in the samples, they were stirred for one hour with 1 M ammonium acetate solution (pH 7) (sample: solution = 1: 20), and subsequently filtered through a 0.45-μm membrane-filter (A045A025A, ADVANTEC, Tokyo, Japan). The sodium (Na), potassium (K), calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) concentrations in the filtrates were then analysed using an ICP-AES (IRIS ICAP, Nippon Jarrell Ash).
Results
Stratigraphy and radiocarbon ages
The transected deposits are mainly composed of a 3–4 m thick peat layer (Figures 3 and 4). The peat layers consist of partially-decomposed organic matter and contain sago palm and grass remains in a mineral matrix of very fine sand and clay. Inorganic silty clay was located under the peat layer at coring sites KB1, KB3, KB4 and KB5. In addition, inorganic fine sand was detected under the silty clay at coring site KB5. The peat layer’s base is sharp and clear, wherever it is located. The peat layer has a greater thickness on the inland side. Three dates, 3,710–3,560 cal BP, 3,620–3,440 cal BP and 2,870–2,760 cal BP, were obtained from the lower and the middle part of the peat layer (Table 1).
Simplified geological cross-section along a NW-SE transect, including the columnar sections of the cores. Coring sites are indicated in Figure 3.
The peat layer was also detected beyond the studied transect, in river outcrops and artificial water-courses in the village. One particular artificial water-course, approximately 200 m south of the coring site KB1, presented the three-dimensional sedimentary characteristics of the peat layer (Figure 5), clearly indicating the progressive soil formation in the surface layer.
Chemical characterization
The results of the chemical analysis on the samples of core KB1 are presented in Figure 6. The average pH value is 5.73 in the silty clay (G.L. − 4.00 to −3.58 m) and 4.40 in the peat layer (G.L. − 3.58 to 0.00 m); the peat is weakly acidic. The total carbon-to-total nitrogen values range between 19.7 and 78.2, and are classified broadly into two groups: relatively high values in the middle part of the peat layer and relatively low values in the lower and upper parts.
The data on exchangeable cations exhibit strong variability through the core KB1, whereas the C content maintains high values from the depth of 3.5 m upwards. The exchangeable Na tends to decrease from around 3.5 m depth, whereas the exchangeable K remains constant between depths of 3.0 to 1.0 m and then increases abruptly above 1.0 m. Furthermore, the exchangeable Ca fluctuates at high values, from 3.5 m to 1.0 m depth, and then decreases. The profile of exchangeable Mg has two peaks, at the 3.5–3.0 m and the 2.0–1.0 m depth.
Discussion
Fluvial facies and radiocarbon dating indicate that the sedimentary environment, in the study area, changed around 3,710–3,560 cal BP. Inorganic silty clay and fine sand have been carried by rivers, accumulating sago palm and grass remains in the shallow swamp waters. This phenomenon can also be described as a reduction of the Sanai and an expansion of the Pandago and Kabuk components, possibly affecting the floodplains of middle Sepik. A mid-Holocene marine transgression followed by a late-Holocene marine regression occurred in the lower part of Sepik [12], inducing an expansion of the peat layer in the middle Sepik.
Important changes in the peat’s chemical characteristics, between its different levels, were observed. The variation in the exchangeable cations’ content is considered to correspond to a vegetation change in this area. Since the carbon content has remained at a high value from 3.5 m depth onwards, the area was probably covered with rich vegetation. However, the plant species assemblage might have changed. The K, Ca and Mg content, in plant tissues, varies between the different species. The nutrient contents in various plant species from valleys in Ghana; in the 15 species analysed, the highest Ca-content was measured at 27.0 g kg−1 in Mareya micrantha, with a K-content as low as 4.7 g kg−1, and the highest K-content was measured at 65.9 g kg−1 in Portulaca oleracea, corresponding to a low Ca-content of 4.6 g kg−1. Since their mobility in the peat layer varies among the elements, for example K and Na are more mobile than Ca and Mg, the cation ratios in the peat do not directly reflect the contribution of the past vegetation [21]. However, the high values of exchangeable Ca and Mg in specific layers suggest that other plants coexisted in the area, along with sago palm.
Conclusions
Tropical peat was investigated in the middle Sepik Plain, northern Papua New Guinea. The thickness of the peat layers 3–4 m, and the layers consist of partially-decomposed organic matter and contain sago palm and grass remains within a very fine sand and clayey mineral matrix. Tropical peat formed between 3,710–3,560 cal BP, as a result of a late-Holocene marine regression.
The peat’s chemical variability, especially regarding the exchangeable cations, may be due to a vegetation change in this area during the peat’s formation.
Despite the limited nature of the presented data, with regard to the carbon storage issue, the results provided here constitute a significant contribution to this region’s geological and geomorphological survey. The measured changes in the peat’s chemical characteristics certainly demand additional studies to investigate further the factors affecting them, making use of existing research results on sago palm from other areas. Conclusively, the focus of future studies should be to widen the survey area and to analyse the peatlands’ carbon storage parameters, including non-decomposed plant remains.
References
Hooijer A, Page S, Canadell JG, Silvius M, Kwadijk J, Wösten H, Jauhiainen J (2010) Current and future CO2 emissions from drained peatlands in Southeast Asia. Biogeosciences 7:1505–1514, doi:10.5194/bg-7-1505-2010
Page SE, Rieley JO, Banks CJ (2011) Global and regional importance of the tropical peatland carbon pool. Glob Chang Biol 17:798–818, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02279.x
Page SE, Rieley JO, Shotyk W, Weiss D (1999) Interdependence of peat and vegetation in a tropical peat swamp forest. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 354:1885–1897
Wüst RAJ, Bustin RM, Lavkulich L (2003) New classification systems for tropical organic-rich deposits based on studies of the Tasek Bera Basin, Malaysia. Catena 53:133–163, doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00022-5
Page SE, Wűst RAJ, Weiss D, Rieley JO, Shotyk W, Limin SH (2004) A record of Late Pleistocene and Holocene carbon accumulation and climate change from an equatorial peat bog (Kalimantan, Indonesia): implications for past, present and future carbon dynamics. J Quat Sci 19:625–635, doi:10.1002/jqs.884
Dommain R, Couwenberg J, Joosten H. (2011) Development and carbon sequestration of tropical peat domes in South-East Asia: links to post-glacial sea-level changes and Holocene climate variability. Quat Sci Rev 30:999–1010. doi:0.1016/j.quascirev.2011.01.018
Shier CW (1985) Tropical peat resources - an overview. Proceedings of the Symposium on Tropical Peat Resources - Prospects and Potential. International Peat society, Helsinki, Kingston, Jamaica, pp 29–46
Wayi BM, Freyne DF (1992) The distribution, characterization, utilization and management of the peat soils in Papua New Guinea. In: Aminuddin BY, Tan SL (eds), Tropical Peat: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Tropical Peatland. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, 1991, pp 28-29
Haberle SG, Hope GS, der Kaars V (2001) Biomass burning in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea: natural and human induced fire events in the fossil record. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 171:259–268, doi:0.1016/S0031-0182(01)00248-6
Hope G (2009) Environmental change and fire in the Owen Stanley Ranges, Papua New Guinea. Quat Sci Rev 28:2261–2276, doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.04.012
Swadling P (1997) Changing shorelines and cultural orientations in the Sepik‐Ramu, Papua New Guinea: Implications for Pacific prehistory. World Archaeol 29:1–14, doi:10.1080/00438243.1997.9980360
Chappell J (2005) Geographic changes of coastal lowlands in the Papuan past. In: Pawley A, Attenborough R, Golson J, Hide R (eds) Papuan Pasts: Cultural, Linguistic and Biological Histories of Papuan-Speaking Peoples. Pacific Linguistics, RSPAS, ANU, Canberra, pp 525–539
Chappell J (1993) Contrasting Holocene sedimentary geologies of lower Daly River, northern Australia, and lower Sepik-Ramu, Papua New Guinea. Sediment Geol 83:339–358, doi:10.1016/0037-0738(93)90020-6
Gascoigne I (1998) Papua New Guinea. Cavendish Square Publishing, New York
Löffler E (1977) Geomorphology of Papua New Guinea. CSIRO, ANU Press, Canberra
Haantjens HA, Reiner E, Robbins RG (1968) Land systems of the Wewak-lower Sepik area. In: Haantjens HA (ed) Lands of the Wewak-lower Sepik area, Territory of Papua and New Guinea. (CSIRO Land Use series 22). CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 15–48
Arnold JM (1968) Climate of the Wewak-lower Sepik area. In: Haantjens HA (ed) Lands of the Wewak-lower Sepik area, Territory of Papua and New Guinea. (CSIRO Land Use series 22). CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 49–60
Reiner E, Mabbutt A (1968) Geomorphology of the Wewak-lower Sepik area. In: Haantjens HA (ed) Lands of the Wewak-lower Sepik area, Territory of Papua and New Guinea. (CSIRO Land Use series 22). CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 61–71
Stuiver M, Reimaer PJ (1993) Extended 14C database and revised CALIB radiocarbon calibration program. Radiocarbon 35:215–230
Reimer PJ, Baillie MGL, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck JW, Bertrand CJH, Blackwell PG, Buck CE, Burr GS, Cutler KB, Damon PE, Edwards RL, Fairbanks RG, Friedrich M, Guilderson TP, Hogg AG, Hughen KA, Kromer B, McCormac G, Manning S, Bronk Ramsey C, Reimer RW, Remmele S, Southon JR, Stuiver M, Talamo S, Taylor FW, van der Plicht J, Weyhenmeyer CE (2004) IntCal04 terrestrial radiocarbon age calibration, 0–26 cal kyr BP. Radiocarbon 46:1029–1058
Annan-Afful E, Masunaga, Wakatsuki T (2005) Nutrient distribution in the profile of Valley bottom soils cultivated to rice in Ghana. J Plant Nutr 28:151–160, doi:10.1081/PLN-200042204
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Pamela Swadling and Robin Hide of Australian National Univ., Keichi Kumagai of Ochanomizu Univ., Kenichi Nonaka of Rikkyo Univ. and Mariko Shinmoto of Hiroshima Univ. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 22251002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
All authors have jointly drafted the manuscript and participated in interpretation and have read and approved the final manuscript. Both EO and MU collected core samples from the study area. MU and TI conducted the chemical analysis of the peat samples. Prof. CT proposed some of the ideas for the interpretation of the chemical data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, E., Umemura, M., Ishida, T. et al. Preliminary investigation of the formation age and chemical characterization of the tropical peat in the middle Sepik Plain, northern Papua New Guinea. Geosci. Lett. 2, 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-015-0021-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-015-0021-4