Abstract
This work deals with the modeling of laminated composite and sandwich shells through a variable separation approach based on a Reissner’s Variational Mixed Theorem (RMVT). Both the displacement and transverse stress fields are approximated as a sum of products of separated functions of the in-plane coordinates and the transverse coordinate. This approach yields to a non-linear problem that is solved by an iterative process, in which 2D and 1D problems are separately considered at each iteration. In the thickness direction, a fourth-order expansion in each layer is used. For the in-plane description, classical Finite Element method is used. Numerical examples involving several representative shell configurations (deep/shallow, thick/thin) are addressed to show the accuracy of the present method. It is shown that it can provide quasi-3D results less costly than classical LW computations. In particular, the estimation of the transverse stresses, which are of major importance for damage analysis, is very good.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Composite shells are widely used in the industrial field (aerospace, automotive, marine, medical industries...) due to their excellent mechanical properties, especially their high specific stiffness and strength. For composite design, accurate knowledge of displacements and stresses is required. One way consists in considering the three-dimensional modelisation. However, due to the complexity of such numerical simulations, it is desirable to take advantage of the geometric ratios and to represent the problem as a two-dimensional model by referring to shell theories. There are two ways to define the approximation of the displacement field. A “pure shell” model can be considered in which the displacement is associated with the local curvilinear vectors, and strain and stress are deduced using the differential geometry [1]. Alternatively, the shell-like solid approach [2] is widely used to formulate shell Finite Element (FE), in particular in commercial software. In this case, the displacement vector is defined in the global cartesian frame. The jacobian matrix transformation is used to express strain and stress with respect to the reference frame defined on the middle surface in order to introduce the constitutive law. With respect to the “pure shell” approach, differentiation is simplified and the curvatures need to be directly calculated [3]. The development of efficient computational models for the analysis of shells appears thus of major interest.
According to the published research, various theories for composite shells have been implemented in the FEM framework. Most of the works mentioned in the subsequent literature overview will refer to “pure shell” models restricted to a linear analysis. Following Reddy [4], two families of models can be identified:
The Equivalent Single Layer Models (ESLM), to which belong the Classical Shell Theory (CST/Koiter) and First Order Shear Deformation Theory (FSDT/Nagdhi). The reader can refer to [5] for a detailed description of the assumptions on the strain field to derive different shell models. CST leads to inaccurate results for composites because both transverse shear and normal strains are neglected, see [6,7,8] for shallow laminated shells. FSDT is the most popular model due to the possibility to use a C\({}^0\) FE, but it needs shear correction factors and the transverse normal strain is still neglected (cf. [9,10,11,12]). So, Higher-order Shear Deformation Theories (HSDT) have been developed to overcome these drawbacks. Different kinematics including 7 [13, 14] or 9 parameters [15] have been proposed. Reddy has derived a 5 parameter model starting from a third-order theory by considering the homogeneous top/bottom conditions for the transverse shear stresses [16]. Note also the variable kinematics approach based on the Carrera’s Unified Formulation developed in [17, 18].
In the ESLM context, a simple way to improve the estimation of the mechanical quantities consists in adding one zig–zag function, called Murakami’s function, in the expression of the displacement. In this way, the slope discontinuity at the interface between two adjacent layers is introduced. It allows to describe the so-called zig–zag effect. It has been carried out in conjunction with the FSDT in [19] and [20] based on dedicated mixed formulation. It has been also used with the HSDT in [21] and [22] including 9 and 13 parameters, respectively.
The Layer-Wise Models (LWM), in which the expansion of the mechanical quantities is defined over each layer independently. Some of these works are based on a linear distribution of the in-plane displacements through each layer, without taking into account the transverse normal stress. The transverse displacement can be constant across the whole thickness, such as in [23, 24], or in each layer separately, as in [25]. But, this type of approach fails to predict accurate transverse stresses, unless using dedicated post-processing steps [24]. Thus, higher-order approaches taking into account the transverse normal effect have been developed. The three-dimensional constitutive law is used. Second-, third- and fourth-order expansions are discussed in [4, 26, 27]. In this framework, Kulikov [28] has developed the sampling surfaces method, see also the previously mentioned work [18]. In all the aforementioned LWM, the number of unknowns depends on the number of layers, which may thus affect the performance in terms of computational cost.
As an alternative, refined models have been developed in order to improve the accuracy of ESL models avoiding the additional computational cost of LW approach. Starting from a LW expansion, enforcing the interlaminar continuity of the displacement and transverse shear stresses, as well as the homogeneous top/bottom conditions, the number of unknowns becomes independent of the number of layers. The deduced model can be derived from the CST [29], as well as from an HSDT with a third-order theory [30,31,32,33] or the sinus model [1]. The number of parameters of the resulting displacement model varies from 5 to 15. We can also cite two other approaches where only the displacement continuity [34] or the top/bottom conditions [16] are satisfied. While the above references propose models still relying on the 2D constitutive law, the papers [35, 36] extend the zig–zag approach to include the transverse normal stress.
It should be noted that the mentioned works are based on the Finite Element method for linear elasticity problem in mechanics and applied to laminated composites, knowing that many other approaches (meshless, analytical, semi-analytical...) are involved in open literature. Furthermore, the fundamental subject about the shear and membrane locking of shell is not addressed here. So, this above literature deals with only some aspects of the broad research activity about composite shells. An extensive assessment of different approaches for various theories and/or finite element applications can be found in [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] and more recently in [46].
Nevertheless, in the framework of the failure analysis of composite structures, involving the free edge effect for instance, the prediction of the interlaminar stresses is of major interest. In particular, the difficulty is to well-describe the interlaminar continuous transverse stresses. Most of the ESLM fail to represent these in the most critical cases, unless using a post-processing treatment [11, 24, 47,48,49]. To overcome these drawbacks, alternative formulations to the displacement-based approach have been developed. On the one hand, several techniques have been devised to correct the transverse shear locking pathology affecting FSDT-based plate/shell elements, most of which can be stated from hybrid-mixed approaches [50]. For composites, an assumed strain approach has been adapted in a FSDT [51] or in a LWM [52]. On the other hand, assumed partial/complete stress field over the laminate thickness independently aims at increasing the accuracy of this one. Without considering the transverse normal stress, some authors [53, 54] have adopted a partial hybrid stress approach based on the HellingerReissner Variational Principle (HRVP). Using a HSDT approach for displacements, Yong [53] has developed a generalized stress assumption for the transverse shear stresses only, whereas in-plane stresses are also involved in [54]. Alternative hybrid approaches take into account the transverse normal effect. The Fraeijs de VeubekeHuWashizu multifield variational principle [55, 56] and the Reissner Mixed Variational Theorem [57] are used assuming the transverse shear stresses only. Note that Sgambitterra et al. [14] have introduced a mixed-field assumptions (\(\gamma _{\alpha 3}\) and \(\sigma _{33}\)) to derive a hybrid formulation enforcing the compatibility straindisplacement relations to be least-squares compatible through the shell thickness. As a complement to these hybrid methods, mixed formulations are addressed in conjunction with FSDT [58] (HRVP) or including the Murakami’s zig–zag function [20] (Jing and Liao’s functional [59]). An advanced method is proposed in [60] by considering all interlaminar stresses between two adjacent layers as primary variables and also a higher-order LW displacement.
In the same way, the partially Reissner’s Mixed Variational Theorem (RMVT) assuming two independent fields for all displacement and transverse stress variables allows to ensure a priori interlaminar continuous transverse stress fields. The consideration of the transverse normal stress as an independent assumed variable seems to be important to obtain accurate distributions through the thickness of the shell (see e.g. [55]). The RMVT approach comes from the works of Reissner, see [61, 62]. It was first applied for multilayered structures in [63] and then, in [64] with higher order displacement field and [65] with a Layerwise approach for both displacements and transverse stress fields. Afterwards, the approach was widely developed with a systematic approach based on the Carrrera’s Unified Formulation to provide a large panel of 2D models for composite structures based on ESL and/or LW descriptions of the unknowns [66,67,68]. It has been also applied for shell structures in [69,70,71]. Note that the reader can refer to [27] for a survey on RMVT in this framework, and to [37, 72] for a further discussion.
In the present work, the RMVT is considered because it is a natural variational tool for composite structures as it allows to formulate independent approximations for mechanical variables that are required to be continuous across the stacking direction. It is used in conjunction with a variable separation method, namely the Proper Generalized Decomposition (PGD). The main purpose consists in taking advantage of this promising approach to decrease the high computational cost of a LW approach. In fact, interesting features have been shown in the model reduction framework [73,74,75]. So, the aim of the present paper is to assess this particular representation of the unknowns in the framework of a mixed formulation to model cylindrical laminated and sandwich shells. Both displacements and transverse stresses are written under the form of a sum of products of bidimensional polynomials of \((\xi ^1,\xi ^2)\) and unidimensional polynomials of z. A piecewise fourth-order Lagrange polynomial of z is chosen across the thickness of each layer. As far as the variation with respect to the in-plane coordinates \((\xi ^1,\xi ^2)\) is concerned, a 2D eight-node quadrilateral FE is employed. With the PGD approach, each unknown function of \((\xi ^1,\xi ^2)\) is approximated using one degree of freedom (dof) per node of the mesh and the LW unknown functions of z are global for the whole shell. This process yields to two separate linear problems, i.e., a 2D problem in \((\xi ^1,\xi ^2)\) and a 1D problem in z, in which the number of unknowns is much smaller compared to a classical Layerwise approach. These two problems are solved successively within an iterative scheme. The interesting feature of this approach lies on the possibility to have a higher-order z-expansion and to refine the description of the mechanical quantities through the thickness without substantially increasing the computational cost. This is particularly suitable for the modeling of composite structures. Note that this method has been successfully applied to displacement-based plate/shell models in [76,77,78,79] and also to RMVT plate models in [80].
We now outline the remainder of this article. First, the shell definition and the differential geometry are recalled. The RMVT formulation is described and the separation of the in-plane and out-of-plane displacements/ transverse stresses is introduced. The principles of the PGD are precised in the framework of our study. The particular assumption on the assumed variables yields to a non-linear problem, that is solved within an iterative process. The FE discretization is also described and finally, numerical tests are addressed. A preliminary convergence study is performed. Then, the influence of classical shell assumptions on the strains and the number of numerical layers are studied. The approach is also assessed for a wide range of applications: deep/shallow shells, cross-ply/angle-ply configurations, different slenderness ratios and different degrees of anisotropy for a sandwich are considered. The accuracy of the results is evaluated by comparison with a 2D elasticity solution from [81], or results available in the open literature [79, 82, 83].
Shell definitions and differential geometry
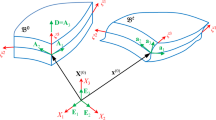
A shell \({\mathcal {C}}\) with a middle surface \({\mathcal {S}}\) and a constant thickness e, see Fig. 1, is defined by [84]:
where the middle surface can be described by a map \(\vec \Phi \) from a parametric bidimensional domain \(\Omega \) as:
In Fig. 1, the map \(\vec \Phi \) describing the shell middle surface (in grey) and the local basis vectors are presented. The basis vectors \(\vec a_i\) are defined for a point on \(\mathcal{S}\) and the basis vectors \(\vec g_i\) are defined for a generic point of the shell.
For a point on the shell middle surface, the covariant basis vectors defining the tangent plane to the middle surface are usually obtained as follows:
where \(\vec a_3\) is the unit normal vector to the surface \({\mathcal {S} }\), see Fig. 1. In Eq. (2) and further on, latin indices \(i, j, \ldots \) take their values in the set \(\{1,2,3\}\) while greek indices \(\alpha ,\beta , \ldots \) take their values in the set \(\{1,2\}\). The summation convention on repeated indices is used and partial derivative is denoted by \(()_{,\alpha }\). A shell is characterized by the first fundamental form \(a_{\alpha \beta }\) and the second one \(b_{\alpha \beta }\). Their covariant, contravariant and mixed form definitions are given by:
The contravariant vectors are constructed from the covariant ones using the following equations:
where \(\delta _\beta ^\alpha \) is the Kronecker symbol.
For a generic point of the shell, covariant basis vectors must be defined and we have
where \(b^\beta {}_\alpha \) is the mixed form of the second fundamental form. This basis \(\vec g_i\), illustrated in Fig. 1, must be used to define quantities for any point of the shell. The form \(\mu ^\beta {}_\alpha (z)\) introduced in Eq. (5) defines the transport from the shell middle surface to any point of the shell and is associated with the curvature variation along the thickness direction z of the shell. The inverse tensor of the mixed tensor \(\mu ^\beta {}_\alpha \) is denoted \(m^\beta {}_\alpha \) and is defined as:
where we have introduced the determinant of the mixed tensor \(\mu = det(\mu ^\beta {}_\alpha ) = 1 - 2 H \xi ^3 + (\xi ^3)^2 K \) and the invariants of the second fundamental form \(H ~=~ \frac{1}{2} tr(b^\beta {}_\alpha )\) and \(K = det(b^\beta {}_\alpha )\). Finally, the surface element \(d \mathcal{S}\) and the volume element \(d \mathcal{C}\) are given by:
where a is the determinant of the first fundamental form \(a_{\alpha \beta }\). The geometry of a shell can also be defined using contravariant or mixed forms. Furthermore, covariant and contravariant differentiation involving Christoffel symbols are not detailed here and readers can refer to the book [84].
Reference problem description
The definition of the strain field
For geometrically linear elastic analysis, the components of the strain tensor \(\varepsilon _{ij}\) expressed in the contravariant basis \(\vec a^i\) are obtained through covariant differentiation, denoted |, as follows:
The mixed tensor \(m^{\beta }{}_{\lambda }\) carries out the transport from any point of the shell to the shell middle surface, that is from \(\vec g^i\) to \(\vec a^i\).
Constitutive relation
The stress tensor is obtained from the strain tensor using the constitutive equations. For this purpose, all these tensors must be referred to the covariant and contravariant basis vectors, \(\vec a_i\) and \(\vec a^i\) respectively, associated with the middle surface of the shell. In case of laminated shells composed of orthotropic plies, this reference frame ensures to consistently take into account the different material orientations of the layers. The tensorial relation is:
It should be noted that the stress tensor is defined in the covariant reference frame, whereas the strain components are defined in the contravariant frame. If the frame is assumed to be orthonormal then covariant and contravariant components are equal, that is super-script and sub-script are interchangeable.
In the framework of the RMVT formulation, the Hooke’s law has to be rewritten under a convenient mixed form.
Firstly, stresses \({\varvec{\sigma }}\) and strains \({\varvec{\varepsilon }}\) are split into two groups:
where the subscripts n and p denote transverse and in-plane values, respectively.
The shell can be made of NC perfectly bonded orthotropic layers. Using the previous assumptions and the separation between transverse and in-plane components, the three dimensional constitutive law of the kth layer is given by:
In this equation, the subscript G indicates that the strain is issued from the geometrical relations, while H means that the quantities are calculated from the Hooke’s law. \({\mathbf {Q}}_{ij}^{(k)}\) are defined by
where \(Q_{ij}^{(k)}\) are the three-dimensional stiffness coefficients of the layer (k).
Finally, RMVT is associated to a mixed form of Hooke’s law, which can be written as
The assumed transverse stresses are denoted as \({\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM} \). The superscript \({}^{(k)}\) and the coordinates \((\xi ,z)\) are omitted for clarity reason.
The relations between the coefficients of the classical Hooke’s law Eq. (12) and the mixed one Eq. (13) are:
The weak form of the boundary value problem
The formulation of the problem is based on the Reissner’s partially Mixed Variational Theorem [61], denoted RMVT. In this formulation, the Principle of Virtual Displacement is modified by introducing the constraint equation to enforce the compatibility of the transverse strain components. This term also depends on the assumed transverse stresses, see also [17, 72]. Thus, the problem can be formulated as follows:
Find \({\varvec{u}}(M) \in U\) (space of admissible displacements) and \( {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}\) such that
where \({\varvec{t}} \) is the prescribed surface forces applied on \({\partial \mathcal{C}}_{F}\). The body force is not considered in this expression.
Application of the proper generalized decomposition to the cylindrical shell
In this section, we develop the application of the PGD for shell analysis with a mixed formulation. This work is an extension of a previous study on composite cylindrical shell structures [79].
The cylindrical geometry
A cylindrical shell (see Fig. 2) is described using the following map:
Following Eq. (3), the non-zero terms for the covariant and mixed forms are:
and \(\mu = 1 + \dfrac{z}{R}.\)
The displacement and transverse stress field
Let us denote \(u_{i}(\xi ^1,\xi ^2,\xi ^3=z)\) and \(\sigma _{i3}(\xi ^1,\xi ^2,\xi ^3=z)\) the curvilinear components of the displacement field and the transverse stresses respectively, associated with the contravariant basis vectors \(\vec a^i\). Let \(\Omega \) and \(\Omega _z\) be the bidimensional domain associated with the mid-surface of the shell [see Eq. (1)], and the unidimensional domain associated with the normal fiber, respectively. The displacement and transverse stress fields are constructed as the sum of N products of functions of in-plane coordinates and transverse coordinate (\(N \in \mathbb {N}\) is the order of the representation) according to
where \((f_{1}^{i}, f_{2}^{i}, f_{3}^{i})\), \((f_{\sigma _1}^{i}, f_{\sigma _2}^{i}, f_{\sigma _3}^{i})\) are defined in \(\Omega _{z}\) and \((v_{1}^{i}, v_{2}^{i}, v_{3}^{i})\), \((\tau _{1}^{i}, \tau _{2}^{i}, \tau _{3}^{i})\) are defined in \(\Omega \). The “\(\circ \)” operator is Hadamard’s element-wise product.
In this paper, a classical eight-node FE approximation is used in \(\Omega \) and a LW description is chosen in \(\Omega _{z}\) as it is particulary suitable for the modeling of composite structures.
The strain field for the cylindrical composite structure
The strain field in Eq. (8) is free of any approximated shell kinematics. These strain components are simplified using Eq. (17) and we recover the following relations:
where covariant derivative becomes classical derivative for the case of a cylindrical shell.
Equation (18) must be introduced at this level in order to obtain the compatible strain expansion along the normal coordinate z of the shell. So, we obtain:
where the prime stands for the derivative with respect to z (\(f'_i = \displaystyle \frac{df_i}{dz}\)), \(()_{,\alpha }\) indicates the partial derivative with respect to \(\xi ^\alpha \) (\(\alpha =1,2\)).
The problem to be solved
The resolution of Eq. (15) is based on a greedy algorithm. If we assume that the first m functions have been already computed, the trial function for the iteration \(m+1\) is written as
where \((v_{1}, v_{2}, v_{3})\), \((\tau _{1}, \tau _{2}, \tau _{3})\), \((f_{1}, f_{2}, f_{3})\) and \((f_{\sigma _1}, f_{\sigma _2}, f_{\sigma _3})\) are the functions to be computed and \({ {\mathbf {u}}^m}\), \( {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^{m}\) are the associated known sets at iteration m defined by
The test functions are
with
The test functions defined by Eqs. (26, 27), the trial functions defined by Eqs. (23, 24), and the mixed constitutive relation Eq. (13) are introduced into the weak form Eq. (15) to obtain the two following equations:
For the present work, \({\partial \mathcal C}_{F}\) is considered as the partial top or bottom surface of the shell, that is \(z=z_F\) with \(z_F = \pm e/2\).
From Eqs. (29) and (30), a coupled non-linear problem is derived whose solution is seeked by means of a fixed point method for simplicity reason. An initial function \({\varvec{f}}^{(0)}\), \({\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(0)}\) is set, and at each step, the algorithm computes two new pairs \(({\varvec{v}}^{(k+1)}, {\varvec{f}}^{(k+1)})\), \((\varvec{\tau }^{(k+1)}, {\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(k+1)})\) such that
\({\varvec{v}}^{(k+1)}, \, \varvec{\tau }^{(k+1)}\) satisfy Eq. (29) for \({\varvec{f}}\), \( {\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }\) set to \({\varvec{f}}^{(k)}\) and \({\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(k)}\)
\({\varvec{f}}^{(k+1)}\), \({\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(k+1)}\) satisfy Eq. (30) for \({\varvec{v}}\), \(\varvec{\tau }\) set to \({\varvec{v}}^{(k+1)}\), \(\varvec{\tau }^{(k+1)}\)
These two equations are linear. The first one is solved on \(\mathcal S\), while the second one is solved on \(\Omega _{z}\). As in [80], the fixed point algorithm is stopped when the distance between two consecutive solutions is smaller than a fixed value \(\varepsilon _0\).
Finite element discretization
To build the shell finite element approximation, a discrete representation of the functions \(({\varvec{v}},\varvec{\tau },{\varvec{f}},{\varvec{f}}_\sigma )\) must be introduced. In this work, a classical finite element approximation in \(\Omega \) and \(\Omega _{z}\) is used. The elementary vector of degrees of freedom (dof) associated with one element \(\Omega _e\) of the mesh in \(\Omega \) is denoted \({\varvec{q}}_{e}^{v\tau }\), while the elementary dof vector associated with one element \(\Omega _z{}_e\) of the mesh in \(\Omega _z\) is denoted \({\varvec{q}}_e^{ff_\sigma } \). The displacement, strain and transverse stress fields are determined from the values of \({\varvec{q}}_{e}^{v\tau }\) and \({\varvec{q}}_e^{f f_\sigma }\) by
where
and
The matrices \({{\varvec{N}}}_{\xi }\), \({{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi }\), \({{\varvec{N}}}_{z}\), \({{\varvec{B}}}_{z}\), \({{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi }\), \({{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z}\) contain the interpolation functions, their derivatives and the jacobian components, respectively.
Finite element problem to be solved on \(\Omega \)
For the sake of simplicity, the functions \({\varvec{f}}^{(k)}\), \( {\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(k)}\) which are assumed to be known, will be denoted \(\tilde{{\varvec{f}}}\), \(\tilde{{\varvec{f}}}_{\sigma }\), respectively, and the functions \({\varvec{v}}^{(k+1)}\), \(\varvec{\tau }^{(k+1)}\) to be computed will be denoted \({\varvec{v}}\) and \(\varvec{\tau }\), respectively. The strains and the assumed transverse stresses in Eq. (29) are defined as
with
The variational problem defined on \(\Omega \) from Eq. (29) is
with
Note that the units of \({\mathbf {C}}_{nn}\), \({\mathbf {C}}_{np}\), \({\mathbf {C}}_{pn}\) and \({\mathbf {C}}_{pp}\) are different.
The introduction of the finite element approximation Eq. (31) in the variational Eq. (36) leads to the linear system
where
\( {\varvec{q}}^{v\sigma }\) is the vector of the nodal displacements / transverse stresses associated with the finite element mesh in \(\Omega \),
\({\mathbf {K}}_{z}(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma })\) is the stiffness matrix obtained by summing the elements’ stiffness matrices \( \displaystyle {\mathbf {K}}_{z}^e(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma })= \int _{\Omega _{e}} \Big [ {{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi }^{T} {\varvec{k}}_{z}^v(\tilde{f}){{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi } + {{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi }^{T} {\varvec{k}}_{z}^{v\sigma }(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma }) {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi } + {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi }^T {\varvec{k}}_{z}^{\sigma v}(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma }) {{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi } + {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi }^T {\varvec{k}}_{z}^{\sigma \sigma }(\tilde{f}_{\sigma }) {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi } \Big ] \sqrt{a} d\Omega _e \)
\( {\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{v}(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) \) is the equilibrium residual obtained by summing the elements’ residual load vectors \( \displaystyle {\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{v}^e(\tilde{f},\tilde{f}_{\sigma }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) = \int _{\Omega _{e}} \Big [ {{\varvec{N}}}_{\xi }^T {\varvec{t}}_z(\tilde{f}) - {{\varvec{B}}}_{\xi }^{T} {\varvec{\sigma }}_z(\tilde{f}, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m)- {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma \xi }^T {\varvec{\varepsilon }}_z(\tilde{f}_{\sigma }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) \Big ] \sqrt{a} d\Omega _e.\)
Finite element problem to be solved on \(\Omega _{z}\)
For the sake of simplicity, the functions \({\varvec{v}}^{(k+1)}\), \(\varvec{\tau }^{(k+1)}\) which are assumed to be known, will be denoted \(\tilde{{\varvec{v}}}\), \(\tilde{\varvec{\tau }}\) and the functions \({\varvec{f}}^{(k+1)}\), \( {\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }^{(k+1)}\) to be computed will be denoted \({\varvec{f}}\), \({\varvec{f}}_{\sigma }\). The strain in Eq. (30) is defined as
with
The variational problem defined on \(\Omega _{z}\) from Eq. (30) is
with
and
The introduction of the finite element discretization Eq. (31) in the variational Eq. (44) leads to the linear system
where
\( {\varvec{q}}^{f f_\sigma }\) is the vector of degree of freedom associated with the F.E. approximations in \(\Omega _{z}\),
\( {\mathbf {K}}_{\xi }(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau })\) is obtained by summing the elements’ stiffness matrices:
$$\begin{aligned} {\mathbf {K}}_{\xi }^e(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau })= & {} \int _{\Omega _{ze}} \Big [{{\varvec{B}}}_{z}^{T} {\varvec{k}}_{\xi }^f(\tilde{v}) {{\varvec{B}}}_{z} + {{\varvec{B}}}_{z}^T {\varvec{k}}_{\xi }^{f f_\sigma }(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau }) {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z} \nonumber \\&+ {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z}^T {\varvec{k}}_{\xi }^{f_\sigma f}(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau }) {{\varvec{B}}}_{z} + {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z}^T {\varvec{k}}_{\xi }^{f_\sigma f_\sigma }(\tilde{\tau }) {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z} \Big ] \mu dz_e \end{aligned}$$(48)\({\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{f}(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m)={\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{f}^F(\tilde{v}) - {\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{f}^{Coup}(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m)\) is a equilibrium residual with \({\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{f}^F(\tilde{v}) = \left. {{\varvec{N}}}_{z}^T {\varvec{t}}_{\xi }(\tilde{v} ) \mu \right| _{z=z_F} \) and \( {\varvec{\mathcal {R}}}_{f}^{Coup}(\tilde{v},\tilde{\tau }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) \) is obtained by the summation of the elements’ residual vectors given by
$$\begin{aligned} \int _{\Omega _{ze}} \Big [ {{\varvec{B}}}_{z}^{T} {\varvec{\sigma }}_{\xi }(\tilde{v}, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) + {{\varvec{N}}}_{\sigma z}^T {\varvec{\varepsilon }}_{\xi }(\tilde{\tau }, {\varvec{u}}^m, {\varvec{\sigma }}_{nM}^m) \Big ] \mu dz_e \end{aligned}$$(49)
Numerical results
In this section, an eight-node quadrilateral FE based on the Serendipity interpolation functions is used for the unknowns depending on the in-plane coordinates. The geometry of the shell is approximated by this classical FE in the parametric space. The geometrical transformation is based on an explicit map \(\vec \Phi \). A Gaussian numerical integration with 3 \(\times \) 3 points is used to calculate the elementary matrices.
Several static tests are presented with the aim of validating our approach and evaluating its efficiency. First, a convergence study is carried out to determine the suitable mesh for the further analysis. Then, the influence of the approximation on the factor \(1/\mu \) is addressed [1, 85]. Three orders of expansion are considered. The influence of the numerical layers is also studied to illustrate the possibility to refine the transverse description of the displacements and the stresses. The present approach is assessed for deep/shallow and thick/thin cross-ply/angle-ply/sandwich shells to show the wide range of validity.
Unless otherwise mentioned, the numerical assessments are based on the test case proposed by Ren [81]. It concerns a semi-infinite simply-supported cylindrical shell submitted to a sinusoidal pressure, as detailed below:
Geometry: Composite cross-ply cylindrical shell, \(R = 10\), \(\phi \in \{ \pi /8, \pi /3, \pi /2\}\), with the following stacking sequences \([0^{\circ }]\), \([0^{\circ } / 90^{\circ }]\), \([0^{\circ } / 90^{\circ } / 0^{\circ }]\). All layers have the same thickness. \(\displaystyle S=\frac{R}{e} \in \{2, 4, 10, 40, 100\}\). The panel is supposed infinite along the \(x_2 = \xi ^2\) direction (\(b_{\mathcal {C}} = 8 a_{\mathcal {C}})\) (Cf. Fig. 2).
Boundary conditions: Simply-supported shell along its straight edges (transverse and tangential displacements are fixed on the \((\xi ^1,\xi ^2)\) mesh), sinusoidal pressure along the curvature: \(q(\xi ^1)= q_{0} \sin {\dfrac{\pi \xi ^1}{R \phi }}\)
Material properties: \( \begin{array}{lcl} E_{L} &{} = &{} 25 \, \text{ GPa } \; , \; E_{T} = 1 \, \text{ GPa } \; , \; G_{LT} = 0.2 \, \text{ GPa } \; , \\ G_{TT} &{} = &{} 0.5 \,\text{ GPa } \; , \; \nu _{LT} = \nu _{TT} = 0.25. \end{array}\) where L refers to the fiber direction, T refers to the transverse direction.
Mesh: Only a quarter of the structure is meshed. The mesh is constituted of \(N_x \times N_y\) elements in the \(\xi ^1\) and \(\xi ^2\) directions respectively. A space ratio is considered in these two directions (ratio between the size of the larger and the smaller element).
Numerical layers: \(N_z\) is the total number of numerical layers.
Number of dofs: \(Ndof_{xy} =6 (3 N_x N_y + 2 (N_x + N_y) +1)\) and \(Ndof_z = 24 \times \alpha NC +6\) are the number of dofs of the two problems associated with \(v_j^i\) and \(f_j^i\) respectively. \(\alpha \) is the number of numerical layers per physical layer. So the total number of dofs is \(Ndof_{xy} + Ndof_{z}\).
Results: The results are made nondimensional using:
\( \displaystyle \bar{u} =u_1(0,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z) \frac{E_T }{e q_0 S^3},\qquad \bar{w} = u_3(a_{\mathcal {C}}/2,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z) \frac{100 E_T }{e q_0 S^4} \)
\( \bar{\sigma }_{\alpha \alpha } = \dfrac{ \sigma _{\alpha \alpha }(a_{\mathcal {C}}/2,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z)}{q_{0} S^2}, \)
\( \bar{\sigma }_{13} = \dfrac{\sigma _{13}(0,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z) }{q_{0} S}, \quad \bar{\sigma }_{33} = \dfrac{ \sigma _{33}(a_{\mathcal {C}}/2,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z)}{q_{0}} \)
Reference values: The 2D exact elasticity results are obtained as in [81].
Few iterations are required to reach the convergence of the fixed point algorithm (cf. Section ). Moreover, for this test case, only one couple is needed to obtain the solution.
The present approach, denoted VS-LM4, is compared with results available in open literature:
LM4: It refers to the systematic work of Carrera and his “Carrera’s Unified Formulation” (CUF), see [37, 72, 86]. A LayerWise model based on a RMVT approach where each component is expanded until the fourth-order, is given. \(24 NC+6\) unknown functions per node are used in this kinematic.
VS-LD4: It refers to the work on the proper generalized decomposition with a spatial separation between (x, y) and z. A fourth-order expansion is used for the 1D problem associated to the z-direction. The formulation is based on a displacement approach (see [79]).
Convergence study
Firstly, a convergence study is performed to determine the suitable mesh to be used for the following test cases. A one-layered shell with \(S=40\) and \(\phi =\pi /3\) is considered. For the mesh, a space ratio is taken equal to 50 in the \(\xi ^2\)-direction, and a regular one is used in \(\xi ^1\)-direction. The results issued from the Navier approach which is the asymptotic value of the present model, are also given. The latter are quite similar to the reference 2D elasticity solution given by Ren [81]. Table 1 shows that a 26 \(\times \) 10 mesh (see Fig. 3) is adequate to model the structure. These results can be considered as converged values. The maximum error rate remains less than 0.9% for both displacements and stresses with respect to the reference solution. This mesh is used for the following investigations.
Influence of the expansion order for the factor \(1/\mu \)
In this section, the influence of the approximation on the factor \(1/\mu = 1/(1+z/R)\) is addressed for very thick to thin homogeneous shells and for deep or shallow shells, respectively. For this purpose, the results involving the zero, one and two-order expansions are compared in Tables 2 and 3. The zero-order approximation (thin shell hypothesis or Love’s hypothesis) seems to be suitable only for the thin structure with \(S \ge 40\). For \(S\le 10\), the order of the development of \(1/\mu \) should be increased to improve significantly the accuracy of the solution, including both the displacements and the stresses. Nevertheless, the use of the second-order expansion has a significant influence only for the thick shell.
Considering different opening angles of the structure in Table 3, it can be inferred from these results that the use of the two-order expansion allows us again to decrease significantly the error rate for both displacements and stresses. Nevertheless, the influence on the transverse normal stress does not appear for the shallow shells (\(\phi \le \pi /3\)).
It can be also noticed that the error rate on the transverse shear and normal stresses remains high for both the thick structures and the shallow shells (\(\phi \le \pi /3\)), regardless of the degree of the approximation of \(1/\mu \). Even for \(\phi =\pi /8\), the error rates associated to the displacement u and the normal stress \(\sigma _{11}\) are still high. Thus, a residual error remains. This problem is investigated in the following section.
Influence of the number of numerical layers
The influence of the number of numerical layers is studied for the homogeneous case. In Tables 4 and 5, four numerical layers per physical layer are considered for moderately thick to very thick cases and shallow shells, respectively. These configurations are the most representative ones. First, it can be observed that the accuracy of results with different opening angles (Table 5) are improved when compared with Table 3, regardless of the degree of approximation. In particular, the effect on the stresses is more pronounced. Then, the use of the second order expansion of \(1/\mu \) drives to a very good agreement with the reference solution (Tables 4, 5). The maximum error rate is 1%, even for the very thick case. Finally, a refinement in the z-direction in conjunction with a high-order expansion of \(1/\mu \) is required to obtain accurate results for the shallow shells (\(\phi \le \pi /3\)) or for the moderately to very thick cases (\(S \le 10\)).
In Table 6, the suitable number of numerical layers is given for different slenderness ratios so as to obtain an error rate of about 1% for \(\phi =\pi /8\) (the most critical test). As expected, it can be seen that the number of numerical layers increases with the thickness of the structure. Even considering a structure with only one physical layer, the refinement of the description of mechanical quantities is required as their distributions through the thickness could be very complex for a shell structure. For illustration, the distributions of the displacement \(\bar{u}\) and the stresses \(\bar{\sigma }_{11}\), \(\bar{\sigma }_{13}\) through the thickness are provided in Fig. 4. An oscillating behavior occurs for the displacement and the in-plane stress, which is quite different than the plate case. Moreover, an asymmetrical distribution can be observed. The maximum value of the transverse shear stress is obtained near the top of the homogeneous shell.
For the present approach, it should be also noted that the additional computational cost inducing by the z-refinement is negligible as only the number of dofs of the 1D problem increases (\(Ndof_z = 24 \times \alpha NC +6\), see Table 6). The size of the 2D problem remains unchanged. This is a main difference with respect to a LW approach where the total number of unknowns would be \(Ndof_{xy} \times Ndof_{z} = Ndof_{xy} \times (24 \times \alpha NC +6)\).
Thus, despite the simplicity of the stacking sequence, it is observed that the use of a higher-order theory involving numerical layers is required for thick or shallow shells.
Bending analysis of laminated shells under a sinusoidal pressure
Cross-ply test case
Firstly, a thick three-layer \([0^{\circ } / 90^{\circ } / 0^{\circ }]\) shell is considered, referring to the test case proposed by Ren [81] described in the preliminaries of the present section. Only distributions of the transverse normal and shear stresses through the thickness are provided for deep and shallow shells (see Fig. 5), as those are the most difficult to obtain. Only 1 couple is built and only one element per layer is used for the problem in \(\Omega _z\). It is inferred from this figure that the present model gives excellent results when compared to the exact solution. It can be noticed that the top/bottom surface conditions are fulfilled. Moreover, the maximum value of the transverse normal stress inside the structure increases for the deepest shell. It becomes greater than the applied load value on the top surface.
For further illustrations, a 24-layer case with \(S=4\) and \(\phi =\pi /3\) is addressed. The distributions of displacements and stresses are given in Figs. 6 and 7. This example shows the capability of the approach to provide accurate results for a significant number of layers. It is to be noted that the agreement of the present solutions with the exact one is very good. To achieve a solution with the same accuracy, it is needed to use a LW approach. To illustrate the interest of the present method in terms of computational cost, we can compare the number of dofs involved for each model. For the present one, the 2D and 1D problems imply \(Ndof_{xy} = 5118\) and \(Ndof_{z} = 582\), respectively, while, a LW approach with a fourth-order expansion induces \(Ndof_{LW} = 496,446\).
Angle-ply test case
In this section, a test case proposed by Bhaskar [82] involving a three-layer \([45^{\circ }/-45^{\circ }/45^{\circ }]\) with \(S=4\) and \(\phi =1\) is given. The material properties and the loads are the same as the Ren’s test. Numerical results for displacements and stresses are summarized in Table 7 and are compared with the exact solution. Again, the accuracy of the results is very satisfactory. The continuity of the transverse stresses is naturally fulfilled owing to the mixed formulation. We also note that the free boundary conditions are satisfied.
Bending analysis of a sandwich shell under a sinusoidal pressure
The approach is now assessed on a sandwich shell. The test is based on the Ren test and is proposed by Carrera in [83]. It is detailed below:
Geometry: Cylindrical shell with \(R = 10\), \(S=4\). The thickness of each face sheet is \(\frac{e}{10}\). The panel is supposed infinite along the \(x_2 = \xi ^2\) direction.
Boundary conditions: Simply-supported shell along its straight edges, subjected to a sinusoidal pressure along the curvature: \(q(\xi ^1)= q_{0} \sin {\dfrac{\pi \xi ^1}{R \phi }}.\)
Material properties: Face: \(E_{face}= 73\) GPa, \(\nu _{face} = 0.34\), \(G_{face} = 27.239\) GPa Core: \(E_{L} = E_{T} = \alpha 0.01 \) MPa, \(E_{zz} = \alpha 75.85 \) MPa, \(\nu = 0.01 \), \(G = \alpha 22.5 \) MPa, with \(\alpha = 1\) (B1) or \(\alpha = 10^{-2}\) (B2)
Mesh: Mesh 26 \(\times \) 10 with a space ratio 50 is used for the quarter of the plate.
Number of dofs: \(Ndof_{xy} = 5.118\) and \(Ndof_z = 24 \times NC +6 { = 78}\)
Results: The results are made nondimensional using:
$$\begin{aligned} \displaystyle \bar{w}= & {} u_3(a_{\mathcal {C}}/2,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z) \frac{10 E_{face} }{S^4 e q_0} \\ \bar{\sigma }_{13}= & {} \dfrac{\sigma _{13}(0,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z) }{q_{0} S}, \; \; \; \bar{\sigma }_{33} = \dfrac{ \sigma _{33}(a_{\mathcal {C}}/2,b_{\mathcal {C}}/2,z)}{q_{0}} \end{aligned}$$Reference values: the LM4 results are given in [83].
The parameter \(\alpha \) allows us to define different face-to-core stiffness ratios, i.e. \(\frac{E_{face}}{E_{Tcore}} =73.10^5 \) and \(\frac{E_{face}}{E_{Tcore}} =73.10^7 \) for \(\alpha = 1\) and \(\alpha = 10^{-2}\), respectively. This test case is discriminating for the assessment of composite models. In [83], the authors have shown that LayerWise models are needed to obtain accurate distributions of the transverse stresses through the thickness for this soft core sandwich shell. Moreover, the use of a mixed formulation with an order expansion greater than two, also increases the accuracy of the results. The present approach can be assessed for this discriminating test case. The distributions through the thickness of the transverse displacement and the transverse shear/normal stresses are given in Figs. 8 and 9. It can be noticed that the results are in very good agreement with the LM4 model. The localisation of the transverse stress in the faces of the sandwich is well-represented. Very high values are reached, contrary to the plate case where the maximum value occurs on the loading surface. The results issued from the VS-LD4 model are also provided for further comparison. For both cases, it shows that the transverse normal stress is very difficult to obtain by a displacement based formulation even with a higher-order theory.
Bending analysis of laminated shells under a constant pressure
In this section, the Ren configuration involving three layers is considered with a constant global pressure. To assess the present mixed model, the results of the displacement-based model with variable separation, denoted VS-LD4, are given. In this simulation, four numerical layers per physical layer with a fourth-order expansion through the thickness is used. Only the distribution of the transverse shear and normal stresses are given in Fig. 10 as these are the most difficult quantities to compute. It can be inferred from this figure that five couples are needed to obtain accurate results. Nevertheless, the convergence rate is higher for the transverse normal stress. For this later, only two couples allow us to recover the load value on the top surface of the shell.
Conclusion
In this paper, a variable separation method in the framework of Reissner’s Mixed Variational Theorem is proposed for the modeling of laminated composite and sandwich shells. A 8-node FE for the in-plane unknown approximation and a fourth-order LW description for the thickness unknown approximation are used. In this formulation, all interface conditions are exactly satisfied. The approach has been assessed through different benchmarks proposed in the open literature. The influence of classical strain assumptions (approximation of \(1/\mu \)) is discussed. We have shown the importance of the expansion of this term for thick shells. At the same time, the accuracy of the results could be also improved by using numerical layers in each physical layer without increasing significantly the computational cost. In fact, the number of layers has no influence on this cost as only the cost of the 1D problem is affected. This is particularly interesting in the framework of a mixed approach, where the number of unknowns involving both displacements and transverse stresses becomes very important in a classical LW method. Comparisons with exact reference solutions, results available in open literature have shown the very good accuracy of the method for a wide range of applications. Deep/shallow, very thick/thin shell structures with various stacking sequences and high anisotropy configurations can be modeled with an excellent accuracy. So, the present work can provide quasi-3D results avoiding expensive 3D FEM or LW computations. Therefore, this method seems to have very attractive features.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
Dau F, Polit O, Touratier M. A efficient c\(^1\) finite element with continuity requirements for multilayered/sandwich shell structures. Comput Struct. 2004;82:1889–99.
Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL. The finite element method, vol. 2. 5th ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2000.
Vidal P, D’Ottavio M, Thaier MB, Polit O. An efficient finite shell element for the static response of piezoelectric laminates. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2011;22(7):671–90. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X11402863.
Reddy JN. Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells—theory and analysis. New York: CRC Press Inc.; 2004.
Leissa AW. Vibration of shells. NASA SP-288, Nasa report, 1973.
Rao KP. A rectangular laminated anisotropic shallow thin shell finite element. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1978;15:13–33.
Jeyachandrabose C, Kirkhope J. Explicit formulation of two anisotropic, triangular, thin, shallow shell elements. Comput Struct. 1987;25:415–36.
Qatu MS, Leissa AW. Bending analysis of laminated plates and shells by different methods. Comput Struct. 1994;52:529–39.
Reddy JN. Bending of laminated anisotropic shells by a shear deformable finite element. Fibre Sci Technol. 1982;17:9–24.
Chakravorty D, Bandyopadhyay JN, Sinha PK. Finite element free vibration analysis of doubly curved laminated composite shells. J Sound Vibr. 1996;191:491–504.
Hossain SJ, Sinha PK, Sheikh AH. A finite element formulation for the analysis of laminated composite shells. Comput Struct. 2004;82:1623–38.
Asadi E, Wang W, Qatu MS. Static and vibration analyses of thick deep laminated cylindrical shells using 3d and various shear deformation theories. Compos Struct. 2012;94(2):494–500.
Balah M, Al-Ghamedy HN. Finite element formulation of a third order laminated finite rotation shell element. Comput Struct. 2002;80:1975–90.
Sgambitterra G, Adumitroaie A, Barbero EJ, Tessler A. A robust three-node shell element for laminated composites with matrix damage. Compos B. 2011;42:41–50.
Kant T, Menon MP. Estimation of interlaminar stresses in fibre reinforced composite cylindrical shells. Comput Struct. 1991;38:131–47.
Reddy JN, Liu CF. A higher-order shear deformation theory of laminated elastic shells. Int J Eng Sci. 1985;23:319–30.
Carrera E. Theories and finite elements for multilayered, anisotropic, composite plates and shells. Arch Comput Meth Eng. 2002;9:87–140.
Cinefra M, Carrera E. Shell finite elements with different through-the-thickness kinematics for the linear analysis of cylindrical multilayered structures. Int J Non-Newt Fluid Mech. 2013;93(2):160–82.
Brank B. On composite shell models with a piecewise linear warping function. Compos Struct. 2003;59:163–71.
Jing HS, Tzeng KG. Refined shear deformation theory of laminated shells. AIAA J. 1993;31(4):765–73.
Bhaskar K, Varadan TK. A higher-order theory for bending analysis of laminated shells of revolution. Comput Struct. 1991;40(4):815–9.
Ganapathi M, Patel BP, Patel HG, Pawargi DS. Vibration analysis of laminated cross-ply oval cylindrical shells. J Sound Vibr. 2003;262:65–86.
Botello S, Onate E, Canet JM. A layer-wise triangle for analysis of laminated composite plates and shells. Comput Struct. 1999;70:635–46.
Zinno R, Barbero EJ. A three-dimensional layer-wise constant shear element for general anisotropic shell-type structures. Int J Num Method Eng. 1994;37:2445–70.
Seide P, Chaudhuri RA. Triangular finite element for analysis of thick laminated shells. Int J Num Method Eng. 1987;24(8):1563–79.
Basar Y, Ding Y. Interlaminar stress analysis of composites: layer-wise shell finite elements including transverse strains. Comp Eng. 1995;5(5):485–99.
Grigolyuk EI, Kulikov GM. General direction of development of the theory of multilayered shells. Mech Compos Mater. 1988;24:231–41.
Kulikov GM, Plotnikova SV. Advanced formulation for laminated composite shells: 3d stress analysis and rigid-body motions. Compos Struct. 2013;95:236–46.
Soldatos KP, Timarci T. A unified formulation of laminated composite, shear deformable, five-degrees-of-freedom cylindrical shell theories. Compos Struct. 1993;25(1):165–71.
Cho M, Kim KO, Kim MH. Efficient higher-order shell theory for laminated composites. Compos Struct. 1996;34(2):197–212.
Shariyat M. Non-linear dynamic thermo-mechanical buckling analysis of the imperfect laminated and sandwich cylindrical shells based on a global-local theory inherently suitable for non-linear analyses. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2011;46:253–71.
Yasin MY, Kapuria S. An efficient layerwise finite element for shallow composite and sandwich shells. Compos Struct. 2013;98:202–14.
Shu X-P. A refined theory of laminated shells with higher order transverse shear deformation. Int J Solids Struct. 1997;34(6):673–83.
Versino D, Gherlone M, Di Sciuva M. four node shell element for doubly curved multilayered composites based on the refined zigzag theory. Compos Struct. 2014;118:392–402.
Zhen W, Wanji C. A global-local higher order theory for multilayered shells and the analysis of laminated cylindrical shell panels. Compos Struct. 2008;84(4):350–61.
Icardi U, Ferrero L. Multilayered shell model with variable representation of displacements across the thickness. Compos B. 2011;42:18–26.
Carrera E. Historical review of zig-zag theories for multilayered plates and shells. Appl Mech Rev. 2003;56(3):287–308.
Kapania R. A review on the analysis of laminated shells. J Pres Ves Technol. 1989;111:88–96.
Noor AK, Burton WS. Assessment of computational models for multilayered composite shells. Appl Mech Rev. 1990;43(4):67–97.
Gilewski W, Radwanska M. A survey of finite element models for the analysis of moderately thick shells. Finite Elem Anal Des. 1991;9:1–21.
Yang HTY, Saigal S, Masud A, Kapania RK. A survey of recent shell finite element. Int J Num Method Eng. 2000;47:101–27.
Carrera E. Theories and finite elements for multilayered, anisotropic, composite plates and shells. Arch Comput Method Eng. 2002;9(2):87–140.
Reddy JN, Arciniega RA. Shear deformation plate and shell theories: from stavsky to present. Mech Adv Mater Struct. 2004;11:535–82.
Hohe J, Librescu L. Advances in the structural modeling of elastic sandwich panels. Mech Adv Mater Struct. 2004;11(4–5):395–424.
Qatu MS, Asadi E, Wang W. Review of recent literature on static analyses of composite shells: 2000–2010. Open J Compos Mater. 2012;2:61–86.
Caliri MF, Ferreira AJM, Tita V. A review on plate and shell theories for laminated and sandwich structures highlighting the finite element method. Compos Struct. 2016;156:63–77.
Cho M, Kim JS. A postprocess method for laminated shells with a doubly curved nine-noded finite element. Compos B. 2000;31(1):65–74.
Tanov R, Tabiei A. Adding transverse normal stresses to layered shell finite elements for the analysis of composite structures. Compos Struct. 2006;76(4):338–44.
Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N. Static analysis of completely doubly-curved laminated shells and panels using general higher-order shear deformation theories. Compos Struct. 2013;101:59–93.
Pian THH, Sumihara K. State-of-the-art development of hybrid/mixed finite element method. Finite Elem Anal Des. 1995;21:5–20.
Haas DJ, Lee SW. A nine-node assumed-strain finite element for composite plates and shells. Comput Struct. 1987;26(3):445–52.
Liu ML, To CWS. Free vibration analysis of laminated composite shell structures using hybrid strain based layerwise finite elements. Finite Elem Anal Des. 2003;40:83–120.
Yong Y-K, Cho Y. Higher-order, partial hybrid stress, finite element formulation for laminated plate and shell analyses. Comput Struct. 1995;57:817–27.
Di S, Ramm E. Hybrid stress formulation for higher-order theory of laminated shell analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1993;109:359–76.
Vu-Quoc L, Tan XG. Efficient hybrid-eas solid element for accurate stress prediction in thick laminated beams, plates, and shells. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2013;253:337–55.
Rah K, Paepegem WV, Degrieck J. An optimal versatile partial hybrid stress solid-shell element for the analysis of multilayer composites. Int J Num Method Eng. 2013;93(2):201–23.
Feng W, Hoa SV. A partial hybrid degenerated plate/shell element for the analysis of laminated composites. Int J Num Method Eng. 1996;39:3625–39.
Noor AHK, Andersen CM. Mixed isoparametric finite element models of laminated composite shells. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1977;11(3):255–80.
Jing H-S, Liao ML. Partial hybrid stress element for the analysis of thick laminated composite plates. Int J Num Method Eng. 1989;28(12):2813–27.
Wu C-P, Liu C-C. Mixed finite-element analysis of thick doubly curved laminated shells. J Aerosp Eng. 1995;8(1):43–53.
Reissner E. On a certain mixed variational theorem and a proposed application. Int J Num Method Eng. 1984;20:1366–74.
Reissner E. On a mixed variational theorem and on a shear deformable plate theory. Int J Num Method Eng. 1986;23:193–8.
Murakami H. Laminated composite plate theory with improved in-plane responses. J Appl Mech ASME. 1986;53:661–6.
Toledano A, Murakami H. A high-order laminated plate theory with improved in-plane responses. Int J Solids Struct. 1987;23:111–31.
Toledano A, Murakami H. A composite plate theory for arbitrary laminate configurations. J Appl Mech ASME. 1987;24:181–9.
Carrera E. Evaluation of layerwise mixed theories for laminated plates analysis. AIAA J. 1998;36(5):830–9.
Carrera E, Demasi L. Classical and advanced multilayered plate elements based upon PVD and RMVT. part 1: derivation of finite element matrices. Int J Num Method Eng. 2002;55:191–231.
Carrera E, Demasi L. Classical and advanced multilayered plate elements based upon PVD and RMVT. part 2: numerical implementations. Int J Num Method Eng. 2002;55:253–91.
Brank B, Carrera E. Multilayered shell finite element with interlaminar continuous shear stresses: a refinement of the reissner-mindlin formulation. Int J Num Method Eng. 2000;48(6):843–74.
Brank B, Carrera E. A family of shear-deformable shell finite elements for composite structures. Comput Struct. 2000;76(1):287–97.
Cinefra M, Chinosi C, Croce LD, Carrera E. Refined shell finite elements based on rmvt and mitc for the analysis of laminated structures. Compos Struct. 2014;113:492–7.
Carrera E. Developments, ideas and evaluations based upon the reissner’s mixed theorem in the modeling of multilayered plates and shells. Appl Mech Rev. 2001;54:301–29.
Allix O, Vidal P. A new multi-solution approach suitable for structural identification problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2002;191(25–26):2727–58.
Ammar A, Mokdada B, Chinesta F, Keunings R. A new family of solvers for some classes of multidimensional partial differential equations encountered in kinetic theory modeling of complex fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech. 2006;139:153–76.
Chinesta F, Ammar A, Cueto E. Recent advances and new challenges in the use of the proper generalized decomposition for solving multidimensional models. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2010;17(4):327–50.
Savoia M, Reddy JN. A variational approach to three-dimensional elasticity solutions of laminated composite plates. J Appl Mech ASME. 1992;59:166–75.
Bognet B, Leygue A, Chinesta F. Separated representations of 3D elastic solutions in shell geometries. Adv Model Simul Eng Sci. 2014;1:4.
Vidal P, Gallimard L, Polit O. Proper generalized decomposition and layer-wise approach for the modeling of composite plate structures. Int J Solids Struct. 2013;50(14–15):2239–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.03.034.
Vidal P, Gallimard L, Polit O. Shell finite element based on the proper generalized decomposition for the modeling of cylindrical composite structures. Comput Struct. 2014;132:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2013.10.015.
Vidal P, Gallimard L, Polit O. Modeling of composite plates based on Reissners Mixed Variational Theorem with variables separation. Compos B. 2016;86:229–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.09.055.
Ren JG. Exact solutions for laminated cylindrical shells in cylindrical bending. Comp Sci Technol. 1987;29:169–87.
Bhaskar K, Varadan TK. Exact elasticity solution for laminated anisotropic cylindrical shells. J Appl Mech ASME. 1993;60:41–7.
Carrera E, Brischetto S. A comparison of various kinematic models for sandwich shell panels with soft core. J Comp Mater. 2009;43(20):2201–21.
Bernadou M. Finite element methods for thin shell problems. Chichester: Wiley; 1996.
Carrera E. The effects of shear deformation and curvature on buckling and vibrations of cross-ply laminated composite shells. J Sound Vibr. 1991;151:405–33.
D’Ottavio M, Ballhause D, Wallmersperger T, Kröplin B. Considerations on higher-order finite elements for multilayered plates based on a unified formulation. Comput Struct. 2006;84:1222–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal, P., Polit, O., Gallimard, L. et al. Modeling of cylindrical composite shell structures based on the Reissner’s Mixed Variational Theorem with a variable separation method. Adv. Model. and Simul. in Eng. Sci. 6, 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40323-019-0132-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40323-019-0132-0