Abstract
Background
Obesity and dental caries are global public health problems which can impact in childhood and throughout the life course. In simple terms, childhood dental caries and body weight are linked via the common risk factor of diet. An association between dental caries and obesity has been described in a number of studies and reviews. However, similarly, a relationship has also been noted between low body weight and caries experience in children. This protocol will provide the framework for an umbrella review to address the following question: Does the available evidence support a relationship between dental caries experience and body weight in the child population?
Methods
This review protocol outlines the process to carry out an umbrella systematic review which will synthesise previous reviews of childhood dental caries experience and body weight. An umbrella review methodology will be used to examine the methodological and reporting quality of existing reviews.
Discussion
The final umbrella review aims to aggregate the available evidence in order to provide a summary for policymakers and to inform healthcare interventions.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO CRD42016047304
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
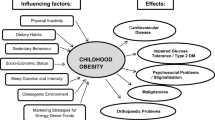
An increase in the number of individuals who are overweight or obese is proving to be one of the most challenging public health problems of the modern era [1]. Research suggests that there is a positive relationship between childhood obesity and obesity in adulthood [2, 3]. Dental caries (decay) in children is consistently found to be one of the most common non-communicable diseases worldwide [4, 5]. The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2010 Study found untreated dental caries in permanent teeth to be the most prevalent oral condition globally with around 35% of the population affected [5]. The consumption of excess free sugar has been implicated in the development of a number of non-communicable and chronic conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and dental caries [6]. In simple terms, dental caries and body weight are linked via the shared risk factor of diet [7]. If free sugars are a common risk factor for both dental caries and body weight, what then is the relationship between dental caries and body weight?
An association between these two conditions have been reported in a number of individual studies; however, the results and methodologies are mixed and provide contradictory evidence [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The relationship between dental caries and body weight in children and adolescents has been looked at in three systematic reviews [21,22,23]. These reviews suggested that a relationship could exist, but that it is far from simplistic. The Hooley et al. review also found evidence which suggests that a converse, dental caries and low body weight relationship may exist [21]. In 2015, Public Health England released an evidence summary entitled “The relationship between dental caries and obesity in children” [24]. This made use of published literature and routine public health monitoring data to review and summarise what is known about the relationship between dental caries and obesity in individuals and populations. The review also found that much of the available evidence was in relation to the obesity and caries relationship in childhood. The results of this evidence summary describe four systematic reviews, the three detailed previously [21,22,23] and an additional paper by Kantovitz et al [25]. Again, an equivocal relationship between dental caries and body weight was found. The authors made use of the recently available ROBIS tool which found several of the reviews to be at high risk of bias [24, 26].
This wealth of varying quality and contradictory evidence suggests the need for an umbrella review to bring together the accessible evidence to permit an understanding of the relationship between dental caries and body weight in children in order to inform policy and potential healthcare intervention. It is expected that this work will be significant in defining the degree of adequacy in the methodological quality and reporting of systematic reviews of observational studies which look at the association between body weight and childhood caries experience.
Objectives
The aim of this umbrella review is to summarise what is already known about the relationship between body weight and childhood dental caries experience in order to make recommendations for policy and to inform healthcare interventions which adopt the Common Risk Factor Approach (CRFA) [7].
Research question
What is the relationship between dental caries experience and body weight in children?
Methods
Protocol development
This protocol has regarded for the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) checklist [27] and is registered with the PROSPERO database for systematic reviews [28]. A completed PRISMA-P checklist for the protocol is attached as an additional file (see Additional file 1). The protocol has been revised by the authors; all updates and amendments can be found within the PROSPERO record.
Review methodology
In 2007, Moher et al. reported that “whilst systematic reviews are now produced in large numbers, the quality of their reporting is inconsistent” [29]. Given that a number of systematic reviews have been published on this topic, we will adopt a review of reviews or umbrella review method as described in Grand and Booth’s typology of reviews [30]. Umbrella review is the term applied to systematic reviews that draw together evidence from a series of other systematic reviews and meta-analyses [30, 31]. They are a means of reporting evidence other than that derived from randomised controlled trials and have been proposed as a way to provide a clear picture of a broad healthcare topic area [31,32,33]. The review will have regarded for the umbrella review methodology as outlined by Aromataris et al. in 2015 [31, 32].
This umbrella systematic review will specifically look at the quality of systematic reviews which have previously been carried out. It will appraise both the methodological and reporting characteristics of multiple reviews making use two available quality assessment tools: AMSTAR and PRISMA [29, 34]. In 2014, Pieper et al. tested the use of AMSTAR tool in appraising systematic reviews of non-randomised studies [35]. They found the tool to be reliable with only items 6 to 9 requiring further discussion between the reviewers. It was felt that this mainly arose due to the lack of standards for non-randomised studies when compared with randomised control trials, rather than an inherent problem with the questions themselves [35]. This review will focus on a quality assessment of the methodology and reporting of the reviews themselves, rather than the individual studies.
Inclusion criteria
Types of participants
Participants will be children defined as those under 18 years of age.
Phenomena of interest
The phenomena of interest in terms of the relationship with dental caries experience are body weight. Body weight as measured by weight, BMI, waist circumference or any other recognised methods will be included.
Outcomes
Outcomes for the primary, mixed and secondary dentition will be considered for inclusion. Any measure of dental caries including, but not limited to, DMFT (Decayed, Missing and Filled Teeth), DMFS (Decayed, Missing and Filled Surfaces), and caries incidence will be included.
Context
No limitations will be made in relation to cultural factors such as geographic location, specific racial or gender-based interests.
Types of studies
Studies will be systematic reviews or meta-analyses of observational studies in humans. Systematic reviews or meta-analyses which include cross-sectional, case series, case-control, cohort studies, or aetiology studies using data from an existing database will be included. All systematic reviews which look at the association between dental caries and body weight in children in the same individuals and populations will be considered.
A summary of the main study inclusion and exclusion criteria are provided in Table 1.
Review characteristics
Only full articles available in English will be reviewed. A list of possibly relevant titles in other languages will be provided as an appendix. As the availability and methodology of systematic reviews has increased since 1990 [33], it has been decided a priori to limit the search to systematic reviews from 1990 onwards.
Search strategy
Database search
The following electronic databases will be searched: MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE, PsycINFO and Scopus. Additional systematic review databases, the JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports, the Cochrane Register of Systematic Reviews and PROSPERO will also be searched. Manual screening of the reference lists of retrieved articles will also be carried out. A search for both black and unpublished grey literature will include databases which contain published reports from government and non-government organisations as well as additional material which have otherwise not been published [31, 36]. The Open Grey system for information on grey literature, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality database and the National Health and Medical Research Council database and Google Scholar will be used to aid in this search. The search process will be tailored to the specific host site.
Search terms
We will conduct a search of electronic databases using MeSH terms and selected free-text terms (including those retrieved from published reviews which can be found in Table 2) as well as terms for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (Table 3). A search strategy has been drafted in collaboration with a Medical Librarian and has been trialled in MEDLINE; Additional file 2 shows this in more detail. This included planned limits so that the search could be repeated.
Study selection
The initial search will be carried out by the lead reviewer. Screening of titles and abstracts will be carried out independently by two reviewers. Any disagreement will be resolved by discussion and, if necessary, by a third reviewer. If a decision on inclusion cannot to be made based on the title or abstract, the full text will be considered and any reasons for exclusion which are based on this will be provided.
Data extraction and management
Data from published reviews to be included will be abstracted into Endnote X7. Duplicates of individual systematic reviews will be deleted. A data extraction form has been designed to reflect the reporting standards for umbrella systematic reviews as outlined in the JBI methodology. Two reviewers will independently review the data, and any unresolved discrepancies will be settled through discussion with the review group. This tool is formed of the existing AMSTAR tool with additional reporting items from the PRISMA tool included [29, 34]. As this tool contains items derived from existing guidelines, it is believed the validity of the tool should be retained [34, 35]. The article flow and number of included studies will be described in a PRISMA flow diagram in the final report [29].
Assessment of methodological quality
The AMSTAR [34] checklist will be used to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that are eligible for inclusion. The methodological quality assessment will be carried out by two of the review team independently. Any unresolved discrepancies will be resolved through discussion and consensus agreement within the review group. The methodological quality of each retrieved review will be graded as good, fair or poor using the guidance criteria within the AMSTAR tool [34].
Assessment of reporting bias
A risk of bias assessment is included within the AMSTAR tool [34]. If more than 10 studies with the same outcome measure are available for review, a funnel plot will be used to explore the potential of publication bias. Selective reporting within systematic reviews or of review findings will be recorded. This will be assessed through the comparison of actual reported outcomes with those stated within the review protocol.
Reporting of findings
The PRISMA checklist will be used to assess the reporting quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that are eligible for inclusion [29]. The findings and conclusions from existing reviews will be presented in narrative form including tables and figures to aid in data presentation where appropriate. The limitations of each review will be reported and will include any confounders and potential moderating or mediating factors. It is anticipated that statistical pooling will not be possible due to variations in the outcome measure reporting. No subgroup analyses are planned; however, these will be presented as provided by the authors if appropriate. The whole umbrella review will be reported according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [29].
Discussion
This review protocol outlines the process to carry out an umbrella systematic review which will look at existing reviews on childhood dental caries and body weight in order to compare and contrast their findings. The overall aim is to synthesise the available evidence in order to provide an updated summary for policymakers and to better inform healthcare interventions which make use of the CRFA.
Abbreviations
- AMSTAR:
-
A measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews
- CRFA:
-
Common Risk Factor Approach
- DMFS:
-
Decayed, Missing and Filled (tooth) Surfaces
- DMFT:
-
Decayed, Missing and Filled Teeth
- GBD:
-
Global Burden of Disease
- MeSH:
-
Medical Subject Headings
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analyses
- PRISMA-P:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis Protocols
References
Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS. Childhood obesity: public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet. 2002;360(9331):473–82.
Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(13):869–73.
Freedman DS, Khan LK, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Relationship of childhood obesity to coronary heart disease risk factors in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):712–8.
United States National Library of Medicine. Physical activity and health: a report of the Surgeon General. 1996. https://profiles.nlm.nih.gov/ps/access/NNBBHB.pdf. Accessed 18 May 2017.
Marcenes W, Kassebaum NJ, Bernabé E, Flaxman A, Naghavi M, Lopez A, et al. Global burden of oral conditions in 1990-2010: a systematic analysis. J Dent Res. 2013;92(7):592–7.
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377(9765):557–67.
Sheiham A, Watt RG. The common risk factor approach: a rational basis for promoting oral health. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2000;28(6):399–406.
Vázquez-Nava F, Vázquez-Rodríguez EM, Saldívar-González AH, Lin-Ochoa D, Martínez-Perales GM, Joffre-Velázquez VM. Association between obesity and dental caries in a group of preschool children in Mexico. J Public Health Dent. 2010;70(2):124–30.
Kumar S, Kroon J, Lalloo R, Kulkarni S, Johnson NW. Relationship between body mass index and dental caries in children, and the influence of socio-economic status. Int Dent J. 2016;67(2):91–7.
Sharma A, Hegde A. Relationship between body mass index, caries experience and dietary preferences in children. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2009;34(1):49–52.
Willershausen B, Moschos D, Azrak B, Blettner M. Correlation between oral health and body mass index (BMI) in 2071 primary school pupils. Eur J Med Res. 2007;12(7):295.
Gerdin EW, Angbratt M, Aronsson K, Eriksson E, Johansson I. Dental caries and body mass index by socio-economic status in Swedish children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2008;36(5):459–65.
Hong L, Ahmed A, McCunniff M, Overman P, Mathew M. Obesity and dental caries in children aged 2-6 years in the United States: national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2002. J Public Health Dent. 2008;68(4):227–33.
Oliveira LB, Sheiham A, Bönecker M. Exploring the association of dental caries with social factors and nutritional status in Brazilian preschool children. Eur J Oral Sci. 2008;116(1):37–43.
Hilgers KK, Kinane DF, Scheetz JP. Association between childhood obesity and smooth-surface caries in posterior teeth: a preliminary study. Pediatr Dent 2006;28(1):23–8.
Chen W, Chen P, Chen S-C, Shih W-T, Hu H-C. Lack of association between obesity and dental caries in three-year-old children. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1997;39(2):109–11.
Macek MD, Mitola DJ. Exploring the association between overweight and dental caries among US children. Pediatr Dent. 2006;28(4):375–80.
Sadeghi M, Alizadeh F. Association between dental caries and body mass index-for-age among 6-11-year-old children in Isfahan in 2007. J Dent Res, Dent Clin, Dent Prospects. 2007;1(3):119–24.
Granville-Garcia AF, VAd M, PId L, Ferreira JM, Leite-Cavalcanti A. Obesity and dental caries among preschool children in Brazil. Rev Salud Pública. 2008;10(5):788–95.
Narksawat K, Tonmukayakul U, Boonthum A. Association between nutritional status and dental caries in permanent dentition among primary schoolchildren aged 12-14 years, Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2009;40(2):338–44.
Hooley M, Skouteris H, Boganin C, Satur J, Kilpatrick N. Body mass index and dental caries in children and adolescents: a systematic review of literature published 2004 to 2011. Syst Rev. 2012;1(1):1.
Hayden C, Bowler JO, Chambers S, Freeman R, Humphris G, Richards D, et al. Obesity and dental caries in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2013;41(4):289–308.
Silva AER, Menezes AMB, Demarco FF, Vargas-Ferreira F, Peres MA. Obesity and dental caries: systematic review. Rev Saude Publica. 2013;47(4):799–812.
Public Health England. The relationship between dental caries and obesity in children: an evidence summary. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/466334/Caries_obesity_Evidence_SummaryOCT2015FINAL.pdf (2015). Accessed 18 May 2017.
Kantovitz KR, Pascon FM, Rontani RMP, Gaviao MBD. Obesity and dental caries—a systematic review. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2006;4(2):137.
Whiting P, Savović J, Higgins JPT, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al. ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;69:225–34.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4(1):1–9.
Booth A, Clarke M, Dooley G, Ghersi D, Moher D, Petticrew M, et al. The nuts and bolts of PROSPERO: an international prospective register of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2012;1(1):1.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf L J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13(3):132–40.
Joanna Briggs I. 2014 Reviewers manual. Joanna Briggs Institute 2014. http://joannabriggs.org/assets/docs/sumari/ReviewersManual-2014.pdf. Accessed 18 May 2017.
Smith V, Devane D, Begley CM, Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11(1):15.
Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7(1):1.
Pieper D, Mathes T, Eikermann M. Can AMSTAR also be applied to systematic reviews of non-randomized studies? BMC Res Notes. 2014;7(1):1.
Aromataris E, Riitano D. Systematic reviews: constructing a search strategy and searching for evidence. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(5):49–56.
Acknowledgements
We thank Andy Jackson, Medical Librarian at the University of Dundee, for his advice in developing the search strategy.
Funding
This study is being completed as part of a PhD by research (SJC) at the University of Dundee; there was no funding source for this review protocol.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SJC led the design of the protocol, search strategy, drafting and revision of the manuscript. RF was involved in the conception and design of the protocol and drafting and revisions to the manuscript. MPH was involved in the design of the protocol and drafting and revising of the manuscript. LA and DR were involved in the drafting and revising of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
PRISMA-P checklist for protocol CRD42016047304 (version 2.1). PRISMA-P (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analyses Protocols) 2015 checklist: recommended items to address in a systematic review protocol. (PDF 278 kb)
Additional file 2:
Search strategy—MEDLINE (Ovid). Search strategy trialled in MEDLINE using EBSCO (search date: 06.10.16). (PDF 187 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Carson, S.J., Abuhaloob, L., Richards, D. et al. The relationship between childhood body weight and dental caries experience: an umbrella systematic review protocol. Syst Rev 6, 216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0610-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0610-8