Abstract
Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 spores isolated from a clean room environment are known to exhibit enhanced resistance to peroxide, desiccation, UV radiation and chemical disinfection than other spore-forming bacteria. The survival of B. pumilus SAFR-032 spores to standard clean room sterilization practices requires development of more stringent disinfection agents. Here, we report the effects of a stabilized chlorine dioxide-based biocidal agent against spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 and Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051. Viability was determined via CFU measurement after exposure. Chlorine dioxide demonstrated efficacy towards sterilization of spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 equivalent or better than exposure to hydrogen peroxide. These results indicate efficacy of chlorine dioxide delivered through a stabilized chlorine dioxide product as a means of sterilization of peroxide- and UV-resistant spores.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
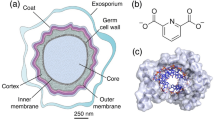
During periods of environmental stress or nutrient depletion, certain Gram-positive bacteria use sporulation to protect its DNA within a protective shell. Germination into a vegetative cell occurs when conditions improve. These processes of sporulation and germination are well understood and reviewed in relevant literature (Errington 1993; Driks 2002; Setlow 2003; Piggot and Hilbert 2004; Paredes-Sabja et al. 2011; Higgins and Dworkin 2012). While Bacillus subtilis is studied as a model organism for sporulation, other species are also relevant due to healthcare or infectious disease reasons, such as Bacillus anthracis (Schmid and Kaufmann 2002; Spotts Whitney et al. 2003), Clostridium botulinum (Chaudhry 2011), and Clostridium difficile (Roberts et al. 2008; Best et al. 2010; Peniche et al. 2013). Each layer of the spore structure protects against DNA damage. The outer layer, the coat, is laminar, serving as a permeation barrier against lysozymes and other agents (Riesenman and Nicholson 2000; Takamatsu and Watabe 2002; Driks 2004). The cortex is a cross linked peptidoglycan structure surrounding the core, implicated in heat resistance of the spore (Mallidis and Scholefield 1987; Atrih and Foster 1999); it differs from that found in vegetative cells (Warth and Strominger 1971; Warth and Strominger 1972) by converting half of its N-acetyl-muramic acids into muramic lactams, which are targets for cortex lysis during germination (Atrih et al. 1996). The spore core houses the bacterial DNA, small acid-soluble spore proteins (SASPs) (Setlow 1988; Moeller et al. 2009), and a calcium-dipicolinic acid chelate (Setlow et al. 2006; Magge et al. 2008) which serve to protect the DNA from UV damage. These features, along with a lower water content in the spore core (Setlow 2006), allow spores to survive for long periods of time.
These features facilitate bacterial spores to be highly resistant to a wide variety of potentially lethal conditions (Setlow 2006; Nicholson et al. 2000). This has led to studies analyzing the possibility of survival of spores in extraterrestrial conditions, such as Martian regolith (Schuerger et al. 2003; Kerney and Schuerger 2011; Moeller et al. 2012). In 2004, Link et al. published a study discussing UV resistance of spores of Bacillus pumilus isolated from the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, CA (Link et al. 2004). The isolates had higher UV resistance than a standard strain of B. subtilis used for dosimetry and other similarly-isolated B. pumilus strains. B. pumilus SAFR-032 was ~340 times more resistant to 254 nm UV radiation than the B. pumilus type strain, ATCC 7061, and was remarked to be “…the most highly UV-resistant spores yet to be discovered” (Link et al. 2004). B. pumilus SAFR-032 was reported as being the most resistant spore strain to UV radiation under simulated Martian environmental conditions the following year (Newcombe et al. 2005). B. pumilus SAFR-032 was also observed to have peroxide resistance (Link et al. 2004; Gioia et al. 2007). In 2012, Vaishampayan et al. noted that spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 exhibited survival rates of 10-40% on spacecraft-grade aluminum coupons exposed to space vacuum for 18 months during the EXPOSE-E mission onboard the International Space Station (ISS) (Vaishampayan et al. 2012). Additionally, limited numbers of spores were able to germinate after exposure to solar UV radiation onboard the ISS, both exposed to space vacuum and within a simulated Martian environment. Given the known ability for habitable space vehicles, including the ISS, to harbor diverse and potentially hazardous bacteria (Venkateswaran et al. 2014), the risk of contamination by bacterial spores—and thus the need for a method of inactivating them—cannot be ruled out.
Chlorine dioxide, ClO2, is an oxidant known to exhibit antimicrobial properties (Beuchat et al. 2005; Gordon and Rosenblatt 2005; Novak et al. 2008; Rastogi et al. 2010). It has been demonstrated to have effects on many biological agents, such as Bacillus anthracis (Rastogi et al. 2010; Buhr et al. 2011), Bacillus cereus and C. perfringens (Foegeding et al. 1986), and Legionella sp. (Kim et al. 2002). It is unstable as a gas and is usually generated in situ for use, either electrochemically (Foegeding et al. 1986) or by reaction of sodium chlorite + chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite + hydrogen chloride (Sharma and Sohn 2012), or sodium chlorate + peroxide and sulfuric acid (Gordon and Rosenblatt 2005). At sub-lethal concentrations, ClO2 may induce different behaviors in bacteria, with a study indicating B. subtilis formed biofilms at sub-lethal exposures to chlorine dioxide (Shemesh et al. 2010).
A 2003 paper examined the efficacy and potential mechanism of action of a stabilized chlorine dioxide solution against spores of B. subtilis compared with hypochlorite solution (Young and Setlow 2003). It was reported that there was no difference in efficacy between hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide, and that the mechanism does not damage DNA but likely damage to the internal membrane of the spore. These results were similar for a wild-type spore strain and a strain lacking the core-associated SASPs. The authors did state in their work that “…very little is known about the mechanisms of spore killing by and resistance to chlorine dioxide” (Young and Setlow 2003).
Given the known resistance of B. pumilus SAFR-032 to traditional sterilization methods, we investigated the efficacy of stabilized chlorine dioxide against spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 and B. subtilis ATCC 6051. We report that chlorine dioxide is effective at killing spores of B. subtilis ATCC 6051 in a dose-dependent fashion. Further, we report the ability of chlorine dioxide to inactivate spores of the peroxide-resistant B. pumilus SAFR-032.
Materials and methods
Spore preparation
Frozen stocks of B. pumilus SAFR-032 (provided by NASA JPL) and wild-type B. subtilis ATCC 6051 (purchased from American Type Culture Collection, Manassas VA, US) were inoculated overnight in 20 mL of lysogeny broth (LB) media, which was used to inoculate 200 mL of media at 37°C in a 1 L Erlenmeyer flask. The B. pumilus SAFR-032 was grown solely in LB media until sporulation occurred due to nutrient exhaustion, which typically occurred after three days. B. subtilis ATCC 6051 was initially grown in LB media for one day. Cells were isolated with centrifugation (10,000 X g, 20 min, 4°C) and the supernatant decanted before suspension in an equal volume (200 ml) of chemically-defined sporulation medium (CDSM) (Hageman et al. 1984); the culture sporulated in CDSM over a period of 3-10 days. The different media used were based on assessment in our lab that B. subtilis sporulated more efficiently in CDSM, while B. pumilus SAFR-032 sporulated best in LB through nutrient exhaustion. Sporulation was monitored via phase-contrast microscopy of 5-10 μL wet mounts (Olympus BX-50) at a magnification of 1000X.
Once a desired level (>80%) of free spores were observed via phase contrast microscopy, spores were purified using a modification of the protocol of Zhao et al. (Zhao et al. 2008). Cultures were centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 20 minutes at 4°C; the supernatant was decanted and the pellet then resuspended in 200 mL of sterile Milli-Q water. The pellet was washed a second time with centrifugation (10,000 X g, 20 min, 4°C); after decanting, the pellet was resuspended in 20 mL of sterile 50% (v/v) EtOH:H2O in a centrifuge tube and allowed to shake (200 rpm) at 25°C for 2 hours to kill remaining vegetative cells. The suspension was spun down (10,000 X g, 20 min, 4°C), the supernatant decanted, and the pellet resuspended in 20 mL sterile Milli-Q water. The spores were washed by repeated (3x) centrifugation (10,000 X g, 20 min, 4°C) and resuspension in sterile Milli-Q water. After the final centrifugation and resuspension, the spore suspension was stored at 4°C overnight; the following morning the suspension was spun down, resuspended in sterile Milli-Q water, filtered through 3.1/1.2 μm glass fiber syringe filters connected in series, and stored at 4°C until used. The purified spore suspensions were then diluted with Milli-Q water to attain an optical density (OD600) of 0.01 (~106 CFU mL-1), measured using a spectrophotometer (Beckman-Coulter DU 640). Spore preparations in glass test tubes were heat-shocked at 80°C for 15 min, followed by rapid cooling on ice to 4°C.
Preparation of chlorine dioxide solutions
An aqueous solution of 2% stabilized chlorine dioxide (Oxine®; Bio-Cide International, Inc., Norman, OK, USA) was used in all exposure experiments. The product was activated by citric acid addition in a ratio of 0.2 g mL-1 of stabilized ClO2 solution without stirring (30 min, room temperature), causing the formation of chlorine dioxide. Each experiment used a freshly activated ClO2 solution. The total concentration of activated chlorine dioxide (after dilution) was measured using a proprietary iodometric titration method (Bio-Cide International). The concentration of free chlorine dioxide gas, which is a fraction of the total ClO2 concentration, was determined using a Hach DR3900 spectrophotometer (Hach Co., Loveland, CO) at λ = 445 nm. The activated ClO2 solution was then diluted in water to a total concentration of 500 μg/mL, followed by subsequent dilutions to approximately total concentrations of 200 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, and 50 μg/mL for selected experiments. Experiments relying on a spray application of chlorine dioxide solution utilized 1 L of chosen dilutions in a hand-held pump-up sprayer (RL Flo-Master model 1401, Root-Lowell Manufacturing Co., Lowell, MI), which had been pressurized and flushed with at least 100 mL of the solution prior to use.
Exposure of dried spores to chlorine dioxide
To evaluate inactivation of dried spores on glass cover slips, spore cultures were mixed (200 rpm) in 1:1 EtOH:H2O for 4 hours, and after the final centrifugation, the spore suspension was diluted to an OD600 of 1.0 (~108 CFU mL-1). 100 μL of spore suspensions of both B. subtilis ATCC 6051 and B. pumilus SAFR-032 were each deposited onto three sterile microscope slide cover slips; these cover slips were allowed to dry at room temperature for 24 h in a laminar air flow chamber. After drying, the cover slips were exposed to a fine mist of stabilized chlorine dioxide solution at 47 or 187 μg/mL concentration for less than one second. The ClO2-treated samples were undisturbed for a desired duration (10 min, 60 min, or 24 h) in a laminar air flow chamber. Cover slips were transferred to a 50 mL Falcon® tube containing 10 mL 0.1 mol L-1 sodium thiosulfate to neutralize remaining active chlorine dioxide on the cover slips. The tubes containing the thiosulfate solution and cover slips were placed in an ultrasonic water bath (Ultrasonic Cleaner B-220, Branson Cleaning Equipment, Shelton, CT) for 2 minutes to dislodge the spores, followed by vigorous vortex mixing for 10 seconds (previously used in removal of B. cereus spores from metal coupons) (Tauveron et al. 2006). The resulting spore suspensions were serially diluted with sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 8 g L-1 NaCl, 0.2 g L-1KCl, 1.44 g L-1 Na2HPO4, 0.24 g L-1 KH2PO4, pH 7.4) and 100 μL portions were spread on TSA plates. Plates were incubated at 37°C to observe spore viability and the colonies counted after 48 h.
This procedure was also used with spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 on spacecraft-grade aluminum coupons that had been autoclaved prior to use. The duration of exposure to chlorine dioxide was either 60 min or 24 h before neutralization. In addition to activated ClO2, coupons with dried B. pumilus SAFR-032 spores were also exposed to inactivated ClO2 (without citric acid) and 3.5% w/v hydrogen peroxide solutions for comparison of efficacy. A control set without exposure to any agent was also prepared. Two replicates (A and B) were prepared for both exposure durations. At the end of the exposure time, coupons were neutralized, sonicated, serially diluted and plated as described above; the resulting TSA plates were incubated at 37°C with colony counting performed 24 h after neutralization.
Results
Exposure of dried spores to chlorine dioxide
The exposure results of chlorine dioxide to dried spores on glass cover slips, both B. pumilus SAFR-032 and B. subtilis ATCC 6051, are shown in Table 1. As can be seen, chlorine dioxide is effective at inactivating spores of both species. This efficacy is dependent both on ClO2 concentration and duration of exposure. Inactivation is not complete at the lower (47 μg/mL) concentration, but it does increase with longer exposure durations. At the higher concentration (187 μg/mL), inactivation is much quicker, with no colonies having been detected on TSA plates even after a ten-minute exposure.
Spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 were dried onto sterile aluminum coupons and exposed to both active and inactive chlorine dioxide. Additional data was collected for the control sample and after exposure to 3.5% w/v hydrogen peroxide, an agent for which B. pumilus SAFR-032 has resistance (Link et al. 2004; Gioia et al. 2007). Table 2 shows the results of exposure of these agents against B. pumilus SAFR-032 spores at one- and 24-hour time intervals, as determined by CFU mL-1 values. These values were calculated from the raw plate counts after 24 h growth following exposure at each time interval, as shown in Additional file: 1 Tables S1 and S2 in the supporting information.
At the shorter time interval, activated chlorine dioxide demonstrates a 4-log reduction in viability compared to the control. The presence of viable colonies after activated-ClO2 treatment is plausible given the ClO2 concentration measured (70.4 μg/mL) and detection of viable spores at a lower concentration as seen in Table 1. The activated stabilized-ClO2 clearly has sporicidal properties against B. pumilus SAFR-032; however, inactivated ClO2 has no measureable effect. Hydrogen peroxide treatment produces a one order-of-magnitude inactivation compared to the control, less effective than activated chlorine dioxide. At the longer duration of exposure, the peroxide and activated ClO2 are comparable in near-total spore kill. Inactivated chlorine dioxide still has no efficacy, being no better than the unexposed control. The almost-total lack of viable spores at the most concentrated solution shows that the efficacy of chlorine dioxide increases with longer durations, as previously seen in Table 1. Additionally, while 3.5% peroxide solution does show near-total inactivation at 24 hour exposure, the much-reduced inactivation in the one-hour exposure test indicates peroxide is slower-acting against B. pumilus SAFR-032 than chlorine dioxide.
Discussion
Efficacy of chlorine dioxide on spore inactivation, comparison with hydrogen peroxide
Stabilized chlorine dioxide could be useful for inactivation of resistant spores. As Table 1 shows, there is no appreciable loss of efficacy between B. subtilis ATCC 6051 and B. pumilus SAFR-032 inactivation at 47 μg/mL. At higher concentrations, inactivation is rapid enough that no viable colonies were found in plate counting after a 10 minute exposure.
When chlorine dioxide was compared against hydrogen peroxide, as shown in Table 2, it demonstrated a greater inactivation at the one-hour exposure time than peroxide against B. pumilus SAFR-032. Considering the known peroxide-resistance traits in this species (Link et al. 2004; Gioia et al. 2007), this data is not unexpected. The three-log difference in the CFU mL-1 value indicates that chlorine dioxide is able to circumvent the resistance properties of the spore and inactivate it in some manner. The chlorine dioxide must be activated, however; it is clear from the results that inactivated ClO2 has no measurable sporidical properties. Either inactive chlorine dioxide solution cannot permeate the spore, or chlorine dioxide is not activated within the spore environment. At the longer duration exposure of 24 hours, the chlorine dioxide and peroxide are roughly equal in sporicidal efficacy. The longer time necessary for peroxide to inactivate spores of B. pumilus SAFR-032 may result from a slow rate of penetration for peroxide, a slower rate of oxidative attack, or depletion of protective molecules in the dormant spore, such as peroxidases (Gioia et al. 2007; Checinska et al. 2012; Tirumalai et al. 2013). Another possibility arises from study of the oxidation potentials of the stabilized solution, which activated and in solution is primarily chlorine dioxide and chlorite (ClO2 -), and hydrogen peroxide. While H2O2 has higher redox potential than ClO2 or ClO2 - (1.776 V vs. 0.954 V or 0.76 V), our results indicate less inactivation from the peroxide. It is possible that the different oxychloro species in the activated solution, mainly chlorine dioxide and chlorite, have a synergistic effect to enhance the overall sporicidal properties of the solution.
Despite the resistance mechanisms of B. pumilus SAFR-032 for peroxides, the chlorine dioxide treatment demonstrated efficacy against spores of this resistant strain as noted in Tables 1 and 2. The effects of ClO2 appear equally valid for B. subtilis ATCC 6051 based on the results of Table 1. The efficacy of chlorine dioxide against B. pumilus spores in general has not, to our knowledge, been studied before, and in particular not against B. pumilus SAFR-032. This work could be of importance for inactivation and sterilization of surfaces contaminated with B. pumilus SAFR-032 in particular, and Bacillus spores in general.
Additionally, this work could form the basis for novel clinical cleaning procedures for pathogenic spore-forming bacteria in hospital environments. By showing chlorine dioxide-based sterilization of bacterial spores, including UV-resistant species such as B. pumilus SAFR-032, activated chlorine dioxide applied as a liquid could be used in a clinical setting for disinfecting and sterilization of surfaces contaminated by dormant bacterial spores, as gaseous chlorine dioxide has been shown capable of performing (Lowe et al. 2013). This treatment could also be effective against contamination with C. difficile spores; such spores are only effectively neutralized with chlorite-containing hospital cleaning agents, as alcohol-based agents have no efficacy and chlorite-containing solutions could be harmful to hospital equipment in the concentrations necessary to achieve spore inactivation (MacLeod-Glover and Sadowski 2010; Gould and McDonald 2008). Stabilized chlorine dioxide solutions applied to contaminated surfaces could serve as a useful tool in eliminating pathogenic spores from clinical settings with less negative impacts on equipment or individuals than bleach or other chlorite-based cleaning agents.
References
Atrih A, Foster SJ (1999) The role of peptidoglycan structure and structural dynamics during endospore dormancy and germination. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 75(4):299–307
Atrih A, Zollner P, Allmaier G, Foster SJ (1996) Structural analysis of Bacillus subtilis 168 endospore peptidoglycan and its role during differentiation. J Bacteriol 178(21):6173–83
Best EL, Fawley WN, Parnell P, Wilcox MH (2010) The potential for airborne dispersal of Clostridium difficile from symptomatic patients. Clin Infect Dis 50(11):1450–7, doi:10.1086/652648
Beuchat LR, Pettigrew CA, Tremblay ME, Roselle BJ, Scouten AJ (2005) Lethality of chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and a commercial fruit and vegetable sanitizer to vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus and spores of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32(7):301–8, doi:10.1007/s10295-005-0212-7
Buhr TL, Young AA, Minter ZA, Wells CM, Shegogue DA (2011) Decontamination of a hard surface contaminated with Bacillus anthracis Δ Sterne and B. anthracis Ames spores using electrochemically generated liquid-phase chlorine dioxide (eClO2). J Appl Microbiol 111(5):1057–64, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05122.x
Chaudhry R (2011) Botulism: a diagnostic challenge. Ind J Med Res 134:10–2
Checinska A, Burbank M, Paszczynski AJ (2012) Protection of Bacillus pumilus spores by catalases. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(18):6413–22, doi:10.1128/AEM. 01211-12
Driks A (2002) Overview: development in bacteria: spore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(3):389–91
Driks A (2004) The Bacillus spore coat. Phytopathology 94(11):1249–51, doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1249
Errington J (1993) Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev 57(1):1–33
Foegeding PM, Hemstapat V, Giesbrecht FG (1986) Chlorine dioxide inactivation of Bacillus and Clostridium spores. J Food Sci 51(1):197–201, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1986.tb10869.x
Gioia J, Yerrapragada S, Qin X, Jiang H, Igboeli OC, Muzny D, Dugan-Rocha S, Ding Y, Hawes A, Liu W, Perez L, Kovar C, Dinh H, Lee S, Nazareth L, Blyth P, Holder M, Buhay C, Tirumalai MR, Liu Y, Dasgupta I, Bokhetache L, Fujita M, Karouia F, Eswara Moorthy P, Siefert J, Uzman A, Buzumbo P, Verma A, Zwiya H, McWilliams BD, Olowu A, Clinkenbeard KD, Newcombe D, Golebiewski L, Petrosino JF, Nicholson WL, Fox GE, Venkateswaran K, Highlander SK, Weinstock GM (2007) Paradoxical DNA repair and peroxide resistance gene conservation in Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032. PLoS One 2(9):e928, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000928
Gordon G, Rosenblatt AA (2005) Chlorine dioxide: The current State of the art. Ozone-Sci Eng 27(3):203–7, doi:10.1080/01919510590945741
Gould CV, McDonald LC (2008) Bench-to-bedside review: Clostridium difficile colitis. Crit Care 12(1):203, doi:10.1186/cc6207
Hageman JH, Shankweiler GW, Wall PR, Franich K, McCowan GW, Cauble SM, Grajeda J, Quinones C (1984) Single, chemically defined Sporulation medium for Bacillus subtilis: growth, sporulation, and extracellular protease production. J Bacteriol 160(1):438–41
Higgins D, Dworkin J (2012) Recent progress in Bacillus subtilis sporulation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36(1):131–48, doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00310.x
Kerney KR, Schuerger AC (2011) Survival of Bacillus subtilis endospores on ultraviolet-irradiated rover wheels and Mars regolith under simulated Martian conditions. Astrobiology 11(5):477–85, doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0615
Kim BR, Anderson JE, Mueller SA, Gaines WA, Kendall AM (2002) Literature review–efficacy of various disinfectants against Legionella in water systems. Water Res 36(18):4433–44, doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00188-4
Link L, Sawyer J, Venkateswaran K, Nicholson W (2004) Extreme spore UV resistance of Bacillus pumilus isolates obtained from an ultraclean spacecraft assembly facility. Microb Ecol 47(2):159–63, doi:10.1007/s00248-003-1029-4
Lowe JJ, Gibbs SG, Iwen PC, Smith PW, Hewlett AL (2013) Impact of chlorine dioxide gas sterilization on nosocomial organism viability in a hospital room. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(6):2596–605, doi:10.3390/ijerph10062596
MacLeod-Glover N, Sadowski C (2010) Efficacy of cleaning products for C difficile: Environmental strategies to reduce the spread of Clostridium difficile–associated diarrhea in geriatric rehabilitation. Can Fam Physician 56(5):417–23
Magge A, Granger AC, Wahome PG, Setlow B, Vepachedu VR, Loshon CA, Peng L, Chen D, Yq L, Setlow P (2008) Role of dipicolinic acid in the Germination, stability, and viability of spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 190(14):4798–807, doi:10.1128/jb.00477-08
Mallidis CG, Scholefield J (1987) Relation of the heat resistance of bacterial spores to chemical composition and structure II. Relation to cortex and structure. J Appl Bacteriol 63(3):207–15
Moeller R, Setlow P, Reitz G, Nicholson WL (2009) Roles of small, acid-soluble spore proteins and core water content in survival of Bacillus subtilis spores exposed to environmental solar UV radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(16):5202–8, doi:10.1128/aem. 00789-09
Moeller R, Schuerger AC, Reitz G, Nicholson WL (2012) Protective role of spore structural components in determining Bacillus subtilis spore resistance to simulated mars surface conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(24):8849–53, doi:10.1128/AEM. 02527-12
Newcombe DA, Schuerger AC, Benardini JN, Dickinson D, Tanner R, Venkateswaran K (2005) Survival of spacecraft-associated microorganisms under simulated Martian UV irradiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8147–56, doi:10.1128/aem. 71.12.8147-8156.2005
Nicholson WL, Munakata N, Horneck G, Melosh HJ, Setlow P (2000) Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(3):548–72
Novak J, Demirci A, Han Y (2008) Novel chemical processes: ozone, supercritical CO2, electrolyzed oxidizing water, and chlorine dioxide gas. Food Sci Technol Int 14(5):437–41, doi:10.1177/1082013208098815
Paredes-Sabja D, Setlow P, Sarker MR (2011) Germination of spores of Bacillales and Clostridiales species: mechanisms and proteins involved. Trends Microbiol 19(2):85–94, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2010.10.004
Peniche AG, Savidge TC, Dann SM (2013) Recent insights into Clostridium difficile pathogenesis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 26(5):447–53, doi:10.1097/01.qco.0000433318.82618.c6
Piggot PJ, Hilbert DW (2004) Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Curr Opin Microbiol 7(6):579–86, 10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.001
Rastogi VK, Ryan SP, Wallace L, Smith LS, Shah SS, Martin GB (2010) Systematic evaluation of the efficacy of chlorine dioxide in decontamination of building interior surfaces contaminated with anthrax spores. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(10):3343–51, doi:10.1128/AEM. 02668-09
Riesenman PJ, Nicholson WL (2000) Role of the spore coat layers in Bacillus subtilis spore resistance to hydrogen peroxide, artificial UV-C, UV-B, and solar UV radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(2):620–6, doi:10.1128/aem. 66.2.620-626.2000
Roberts K, Smith CF, Snelling AM, Kerr KG, Banfield KR, Sleigh PA, Beggs CB (2008) Aerial dissemination of Clostridium difficile spores. BMC Infect Dis 8:7, doi:10.1186/1471-2334-8-7
Schmid G, Kaufmann A (2002) Anthrax in Europe: its epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and role in bioterrorism. Clin Microbiol Infect 8(8):479–88
Schuerger AC, Mancinelli RL, Kern RG, Rothschild LJ, McKay CP (2003) Survival of endospores of Bacillus subtilis on spacecraft surfaces under simulated martian environments: implications for the forward contamination of Mars. Icarus 165(2):253–76, doi:10.1016/s0019-1035(03)00200-8
Setlow P (1988) Small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus species: structure, synthesis, genetics, function, and degradation. Annu Rev Microbiol 42:319–38, doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001535
Setlow P (2003) Spore germination. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(6):550–6, doi:10.1016/j.mib.2003.10.001
Setlow P (2006) Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J Appl Microbiol 101(3):514–25, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02736.x
Setlow B, Atluri S, Kitchel R, Koziol-Dube K, Setlow P (2006) Role of dipicolinic acid in resistance and stability of spores of Bacillus subtilis with or without DNA-protective α/β-Type small acid-soluble proteins. J Bacteriol 188(11):3740–7, doi:10.1128/jb.00212-06
Sharma VK, Sohn M (2012) Reactivity of chlorine dioxide with amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Environ Chem Lett 10(3):255–64, doi:10.1007/s10311-012-0355-5
Shemesh M, Kolter R, Losick R (2010) The biocide chlorine dioxide stimulates biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis by activation of the histidine kinase KinC. J Bacteriol 192(24):6352–6, doi:10.1128/JB.01025-10
Spotts Whitney EA, Beatty ME, Taylor THJ, Weyant R, Sobel J, Arduino MJ, Ashford DA (2003) Inactivation of Bacillus anthracis spores. Emerg Infect Dis 9(6):623–7
Takamatsu H, Watabe K (2002) Assembly and genetics of spore protective structures. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(3):434–44
Tauveron G, Slomianny C, Henry C, Faille C (2006) Variability among Bacillus cereus strains in spore surface properties and influence on their ability to contaminate food surface equipment. Int J Food Microbiol 110(3):254–62, doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.04.027
Tirumalai MR, Rastogi R, Zamani N, O’Bryant Williams E, Allen S, Diouf F, Kwende S, Weinstock GM, Venkateswaran KJ, Fox GE (2013) Candidate genes that may be responsible for the unusual resistances exhibited by Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 spores. PLoS One 8(6):e66012, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066012
Vaishampayan PA, Rabbow E, Horneck G, Venkateswaran KJ (2012) Survival of Bacillus pumilus spores for a prolonged period of time in real space conditions. Astrobiology 12(5):487–97, doi:10.1089/ast.2011.0738
Venkateswaran K, Vaishampayan P, Cisneros J, Pierson D, Rogers S, Perry J (2014) International Space Station environmental microbiome — microbial inventories of ISS filter debris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(14):6453–66, doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5650-6
Warth AD, Strominger JL (1971) Structure of the peptidoglycan from vegetative cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry 10(24):4349–58
Warth AD, Strominger JL (1972) Structure of the Peptidoglycan from spores of Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry 11(8):1389–96
Young SB, Setlow P (2003) Mechanisms of killing of Bacillus subtilis spores by hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide. J Appl Microbiol 95(1):54–67
Zhao J, Krishna V, Moudgil B, Koopman B (2008) Evaluation of endospore purification methods applied to Bacillus cereus. Sep Purif Technol 61(3):341–7, doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.11.002
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Institutes of Health (1R01GM090064-01), a NASA EPSCoR Research Infrastructure Development (RID) grant NN07AL49A, and the University of Oklahoma. We also wish to express our gratitude to Dr. Kasthuri Venkateswaran, NASA JPL Biotechnology and Planetary Protection Group for sharing the B. pumilus SAFR-032 strain.
Supporting information
Tables of the raw plate counting CFUs for B. pumilus SAFR-032 exposed to stabilized chlorine dioxide solution and hydrogen peroxide are included as Additional file: 1 Tables S1 and S2, which were used to calculate the CFU mL-1 in Table 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AF, MZ, AM performed the experiments. NK, PV, CVR and AF participated in the design of the study. AF drafted the manuscript. CVR, NK, PV edited the manuscript. CVR and PV conceived the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional file
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Plate counting of B. pumilus SAFR-032 spores, one-hour exposure time. Table S2. Plate counting of B. pumilus SAFR-032 spores, 24-hour exposure time.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Friedline, A., Zachariah, M., Middaugh, A. et al. Sterilization of hydrogen peroxide resistant bacterial spores with stabilized chlorine dioxide. AMB Expr 5, 24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-015-0109-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-015-0109-4