Abstract
Background
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are thought to play important roles in carcinogenesis, recurrence, metastasis, and therapy-resistance. We have successfully induced cancer stem-like sphere cells (CSLCs) which possess enhanced chemoresistance and metastatic potential. To enable the development of targeted therapy against CSLCs, we identified a gene responsible for this phenotype in CSLC.
Methods
Human hepatoma cell line SK-HEP-1 was used for CSLC induction with a unique sphere inducing medium, and HuH-7 cells were used as non-sphere forming cells in the same condition. RNA-sequencing was performed followed by validation with quantitative RT-PCR and western blotting. Knockdown experiments were done by using CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing, and the rescue experiments were performed using the expressing plasmid vector. Chemoresistance and liver metastasis of the cells, was studied following the splenic injection of cells to severely immune deficient mice and evaluated using the MTS assay. Quantification of exosomes in the medium was done using ELISA.
Results
RAB3B was identified as an up-regulated gene in both CSLCs and prognostically poor hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by RNA-sequencing. RAB3B-KD cells showed altered CSLC phenotypes such as sphere formation, chemoresistance, and metastatic potentials, and those were rescued by RAB3B complementation. Increased exosome secretion was observed in CSLCs, and it was not observed in the RAB3B-KD cells. In addition, the RAB3B expression correlated with the expression of ABCG2, APOE, LEPR, LXN, and TSPAN13.
Conclusion
The up regulation of RAB3B may play an important role in the chemoresistance and metastatic potential of CSLCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the most common cancers occurring worldwide, and it has a poor prognosis owing to a high recurrence rate [1]. Most potentially curative therapies for HCC, such as surgical resection, transplantation, and ablation therapy, have limited efficacy in advanced stages, and metastatic recurrence or de novo development of HCC occurs in approximately 70% of these patients within 5 years [2,3,4,5,6]. Postoperative recurrence is the leading cause of death in these patients [7, 8] which typically occurs within 2 years of resection [9, 10]. The benefits of adjuvant therapy have not been definitively demonstrated for various types of postoperative therapies following curative treatment.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a small subset of cancer cells within the tumor bulk that are potentially responsible for malignant properties of tumors, such as tumor initiation, metastasis, recurrence, and chemoresistance [11,12,13,14]. They are produced via the accumulation of mutations in normal stem cells. In contrast, cancer cells differentiated from CSCs acquire stem cell-like properties via epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) thereby behaving like cancer stem-like cells (CSLCs) [15,16,17,18]. Owing to the plasticity of cancer, we successfully induced the formation of CSLCs from cell lines derived from human hepatoma and pancreatic cancers using a unique medium supplemented with neural survival factor-1 (NSF-1) [16, 17]. The obtained CSLC spheres exhibit increased resistance to several anticancer drugs [16], are metastatic [18], and have increased expression of the EMT-related gene set [18]. Since the sphere cells, also called spheroids, have a three-dimensional (3D) structure, their cellular environment bears a closer resemblance to in vivo tumor conditions in comparison to conventional two-dimensional (2D) cell cultures. The CSLCs generated by us exhibited CD133−/CD44high/CD24low expression unlike typical liver CSCs [16].
This study explored the genes responsible for the CSLC phenotype and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCCs) using RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) of several cell line derivatives and resected human specimens. Furthermore, we investigated the role of an interesting gene, RAB3B, in sphere formation, drug resistance, and metastatic potential of cells by performing knockdown (KD) and rescue experiments. RAB3B is one of the low-molecular-weight GTP-binding proteins (small G proteins) in the Rab family and acts as a central regulator of vesicular traffic [19]. Although the role of RAB3B in cancers is largely unknown, urinary exosomes in patients with prostate cancer reportedly contain high amounts of this protein [20]. Exosomes play an important role in the malignant transformation of cancer, including metastasis, through its contents such as microRNAs and proteins [21]. We also studied the effect of exosomes on CSLCs in this study.
Methods
Cell lines
SK-HEP-1 and HuH-7 cell lines, derived from human hepatoma, were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Rockville, MD, USA) and the Health Science Research Resources Bank (Osaka, Japan), respectively. Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Nissui Pharmaceutical, Tokyo, Japan) containing 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Kanagawa, Japan), penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and sodium bicarbonate (1.5 g/L) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 in air.
Patients
Samples were obtained with written informed consent from 14 patients who underwent curative hepatectomy for HCC between August 2002 and November 2007 in the Department of Digestive Surgery and Surgical Oncology, Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan. The study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki as reflected in a prior approval by the Institutional Review Board for Human Use at Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine. Ten samples each were used for RNA-seq and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); six samples were common to both the analyses.
Induction of sphere cells
Cells were suspended in the sphere inducing medium, which was based on a neural stem cell medium [16]. This medium, used to induce floating sphere cells, was DMEM/Nutrient Mixture F-12 Ham supplemented with 0.6% glucose, 10 mM HEPES, 2 μg/mL heparin, 0.1 mg/mL transferrin, 25 μg/mL insulin, 60 μM putrescine, 30 nM sodium selenite, 20 nM progesterone, 10 ng/mL human recombinant epidermal growth factor (all from Sigma-Aldrich Japan, Tokyo, Japan), 10 ng/mL basic fibroblast growth factor (Merck Millipore, Tokyo, Japan), 10 ng/mL leukemia inhibitory factor (Merck Millipore), 60 μg/mL N-acetyl-L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich), and 1/50 volume NSF-1 (Lonza, Tokyo, Japan).
RNA-sequencing
Total RNA was isolated with the miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Tokyo, Japan). Sequencing libraries were constructed using the TruSeq Stranded Total RNA with Ribo-Zero Gold LT Sample Prep kit (Illumina, Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing of paired-end fragments (75 bp × 2) was conducted on a NextSeq 500 sequencing platform (Illumina).
After a quality control step, the filtered short reads were mapped to the reference genome (hg38) with STAR (version 2.5.1b) [22]. Strand-specific counts of fragments from each sample were obtained using RSEM (version 1.3.3) [23] and normalized with the trimmed mean of M-values method [24] using the TCC package [25, 26]. The edgeR (version 3.28.1) [27, 28] package was used to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) based on a false discovery rate q-value threshold < 0.05.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
The mRNA expression was examined by qRT-PCR as described previously [10]. qRT-PCR was performed using a LightCycler 480 Probe Master (Roche Diagnostics, Tokyo, Japan) and Universal ProbeLibrary (Roche Diagnostics) probes or a LightCycler 480 SYBR Green I Master (Roche Diagnostics) on a LightCycler 480 System II (Roche Diagnostics). The primers and probes used are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Amplification was performed in a two-step procedure and mRNA levels were measured quantitatively using the Δ/Δ threshold cycle method. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) were used as controls. Triplicate wells were analyzed for each assay.
Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed and the proteins (10 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE on an 8% gel and transferred onto a Poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membrane (Bio-Rad, Tokyo, Japan) as described previously [29]. Membranes were blocked with 3% skim milk and treated with the primary antibodies, anti-RAB3B (ab55655; Abcam, Tokyo, Japan) and anti-VCP (anti-valosin-containing protein), (GTX113030, GeneTex, Alton Pkwy Irvine, CA, USA). The immunoreactive bands were visualized using an ECL Pro (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) and Amersham Imager (GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan), and quantified using the ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, USA). VCP was used as the loading control because its levels are more stable compared to those of other loading controls, such as GAPDH and β-actin [29].
Genome editing for RAB3B
A guide RNA (gRNA) targeting a sequence in RAB3B (5′-GTTTCACCCGCTTCTCGTGA-3′) was constructed by in vitro transcription using a GeneArt Precision gRNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Supplementary Fig. S1a). The gRNA and Cas9 mRNA (GeneArt CRISPR Nuclease mRNA, Thermo Fisher Scientific) were transfected into cells using Lipofectamine MessengerMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Genomic DNA (gDNA) from isolated monoclonal clones was subjected to Sanger sequencing (Supplementary Fig. S1b). The RAB3B-edited clone derived from SK-HEP-1 was named RAB3B-KD. The RAB3B-KD cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1(−) (Thermo Fisher Scientific) harboring full-length RAB3B cDNA, pRAB3B, using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) to generate RAB3B rescued KD/pRAB3B cells. A full-length RAB3B cDNA (NM_002867.3: position 214 to 873) with Kozak, 5′-flanking EcoRI, and 3′-flanking BamHI sequences was synthesized by FASMAC (Kanagawa, Japan) and it was inserted into the site downstream of the CMV promoter of pcDNA3.1(−).
Cell viability assay
The CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega, Tokyo, Japan), which includes a tetrazolium compound [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt; MTS] was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Cells in culture medium were incubated with one of the following anticancer drugs, 10 mM 5-fluorouracil (5-FU, Sigma-Aldrich), 250 nM docetaxel (Sigma-Aldrich), 2 μM doxorubicin (Sigma-Aldrich), 200 μM irinotecan hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich), 2.5 μM suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA, Cosmo Bio), 75 μM sorafenib tosylate (ChemScene, Monmouth Junction, NJ), 25 μM lenvatinib mesylate (Carbosynth, Berkshire, UK), 50 μM regorafenib (ChemScene), or 20 μM cabozantinib S-malate (ChemScene), 24 h at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. Cells incubated in culture medium alone were used as control. The optical density of the culture medium at 492 and 650 nm was measured by using an EnVision plate reader (PerkinElmer). The viability of cells treated with the anticancer drugs was calculated as a ratio with respect to their viability in the absence of anticancer drugs. Triplicate wells were analyzed for each assay.
Splenic injection of tumor cells
NOD-Rag1null IL2rγnull double mutant mice (NRG mice) were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA) and maintained in a HEPA-filtered environment with autoclave-sterilized cages, food, and bedding. All animal studies were conducted in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yamaguchi University and conformed to the Guide for the Care, Use of Laboratory Animals published by the United States National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA), and ARRIVE guidelines.
The ability of cells to produce tumor nodules in the liver was studied subsequent to their implantation into the spleen of 8–12-week-old NRG female mice as described previously [18]. After 8 weeks, injected mice were sacrificed and necropsied.
Quantitative analysis of exosomes
Cells were incubated for 24 h, after which the exhausted culture medium was replaced with fresh culture medium. At the same time, cell viability was measured from replicate plates using MTS assay and it was used for normalization of exosome quantification. For quantification of exosomes, the conditioned medium was collected and analyzed using a CD9/CD63 Exosome ELISA Kit, Human (Cosmo Bio) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Signals were detected using an EnVision plate reader (PerkinElmer). If necessary, GW4869 hydrochloride hydrate (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) was added as an exosome inhibitor on the next day of cell seeding. Triplicate wells were analyzed for each assay.
Statistical analysis
Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviation. Significant differences were evaluated by the Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison, paired t-test, or Fisher’s exact test, using the R version 3.6.3 software (the R project website, http://www.r-project.org/). A P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Screening of CSLC-specific mRNA expression
Using quantitative RNA-seq analysis, we compared the comprehensive mRNA levels in sphere-forming SK-HEP-1 and non-sphere-forming HuH-7 cells (Supplementary Fig. S3 left). In addition, mRNA levels in human HCC and surrounding liver tissue specimens were also compared. There were 1471 genes with significant differences in the counts between SK-HEP-1 cells in sphere inducing conditions and those in control culture (fold change > 2.0; q value < 0.05; magenta and green dots in Fig. 1a). Considering the mRNA levels in HuH-7 cells, with no sphere-forming potential [16], 755 genes were identified as specific DEGs in sphere-forming SK-HEP-1 cells (green dots in Fig. 1a).
mRNA levels of RAB3B. a and b, M-A plots generated from RNA-sequence analysis. For each gene, the log2(average expression) in the two samples (A, x axis) against the log2(fold change) between the samples (M, y axis) is plotted. a, Magenta dots represent significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in SK-HEP-1 cells. Green dots indicate sphere-specific DEGs that are not significantly changed in the experiment using non-sphere forming HuH-7 cells. b, Magenta dots represent significant DEGs in primary HCCs with/without recurrence. Green dots also represent DEGs significantly changed in HCCs compared with non-tumorous liver tissue samples. Orange diamonds are overlapping DEGs. The mRNA levels of RAB3B in cell lines (c) and clinical specimens (d) were measured using qRT-PCR and are represented as the ratio of the expression with respect to that in SK-HEP-1 cells or non-tumorous liver tissues. Recurrence-free (n = 5) and recurrence (n = 5) cases consisting of a pair of HCC and adjacent non-cancerous liver samples were used. *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test. **, P < 0.05 with pairwise t-test
To focus on clinically important genes, the DEGs were further screened with respect to recurrence after surgery (Supplementary Fig. S3 right). Two screening criteria were applied: one was the difference in expression between primary HCCs that recurred within 2 years after surgery and those without recurrence over 4 years, and the other was the difference in expression between HCCs and corresponding adjacent liver tissue. As a result, 435 genes were identified as DEGs regarding recurrence in HCC specimens (green dots in Fig. 1b).
Among the above DEGs, seven genes (ATP6V0D2, C5orf30, LOC344887, PBLD, RAB3B, STRIP2, and TKFC) were common in both the screenings with cell lines and HCC specimens (orange diamonds in Fig. 1a,b). We further focused on RAB3B because its mRNA levels were upregulated in sphere formation and were abundant in both cell lines and clinical samples (Supplementary Fig. S4). The expression of RAB3B mRNA under these conditions was validated using qRT-PCR (Fig. 1c,d).
Knockdown of the CSLC-specific RAB3B
We generated RAB3B-KD clones from SK-HEP-1 cells using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. We obtained a clone, which expressed truncated RAB3B, although this mutation was monoallelic (Supplementary Fig. S1, S2). The RAB3B-KD cells showed decreased RAB3B mRNA expression, even in the sphere inducing medium (0.3-fold, P < 0.01, Fig. 2a). Furthermore, the decreased RAB3B expression in RAB3B-KD cells was rescued by transfection with pRAB3B. Similarly, the induction of RAB3B in the sphere inducing medium diminished in the RAB3B-KD cells, and the plasmid vector rescued its expression (Fig. 2b). The antibody used for RAB3B recognized the region truncated by genome editing and therefore only RAB3B expressed from the non-mutated allele was detected in the western blot analysis.
Expression of RAB3B and sphere formation ability of SK-HEP-1 derivative cells. a, RAB3B mRNA levels in SK-HEP-1 derivative cells. RAB3B mRNA levels were quantified using qRT-PCR, and the values were subsequently normalized as the mean ratio of the value from reference cells (SK-HEP-1 cells cultured in control medium). *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test. b, Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates. The upper and lower immunoblottings were generated from the same gel, and the blots were separated around the indicated sizes and then reacted with each antibody, respectively. VCP was used as the loading control. c–e, Sphere cells derived from SK-HEP-1 (c), SK-HEP-1 harboring genome edited RAB3B (d), and the RAB3B edited SK-HEP-1 harboring a RAB3B expressing vector, pRAB3B (e)
Besides the reduced RAB3B expression, the RAB3B-KD cells showed insufficient sphere formation which was reinforced in the exogenous RAB3B-expressing RAB3B-KD cells (Fig. 2c–e). Similar to our observations in a previous study [16], SK-HEP-1 cells in the sphere inducing conditions showed a G0/G1 arrest (82.2% ± 0.4% in Supplementary Fig. S5b). In the sphere inducing conditions, RAB3B-KD cells showed a cell cycle distribution with 67.3% ± 0.5% cells in G0/G1, 3.6% ± 0.1% in S, and 29.1% ± 0.3% in G2/M phases (Supplementary Fig. S5d). This showed that an increased proportion of RAB3B-KD cells in the sphere inducing conditions were in G2/M phase compared to SK-HEP-1 cells in identical culture conditions. The cell cycle distribution of KD/pRAB3B cells in the sphere inducing condition was similar to that of SK-HEP-1 cells in identical conditions (Supplementary Fig. S5f). In control culture conditions, RAB3B-KD cells showed an increase in the S-phase population compared to SK-HEP-1 cells (Supplementary Fig. S5a,c).
Effect of RAB3B expression on the susceptibility to anticancer drugs
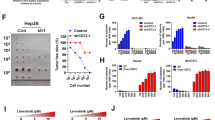
In the sphere inducing conditions, SK-HEP-1 cells showed increased viability in the presence of the tested anticancer drugs compared to those in control conditions (Fig. 3). The RAB3B-KD cells showed decreased viability in the sphere inducing conditions in the presence of any of the tested drugs compared to the parental SK-HEP-1 and RAB3B rescued KD/pRAB3B cells. In the control condition, decreased and recovered viabilities of RAB3B engineered cells were observed in the presence of 5-FU, doxorubicin, and irinotecan.
Susceptibility of SK-HEP-1 derivative cells to anticancer drugs. The viability of SK-HEP-1 (white columns), RAB3B-KD (blue columns), and KD/pRAB3B (salmon columns) cells in the presence of anticancer drugs (5-fluorouracil, docetaxel, doxorubicin, irinotecan, SAHA, sorafenib, lenvatinib, regorafenib, and cabozantinib) was evaluated using the MTS assay. For each anticancer drug, the left and right three columns represent data for cells in the control and sphere inducing cultures, respectively. *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test
Ability of RAB3B-KD cells to metastasize to the liver
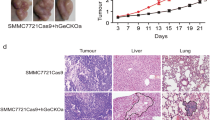
We examined the potential of RAB3B-KD cells to metastasize to the liver (Table 1, and Supplementary Fig. S6). In our previous study, injection of 1 × 103 sphere cells into the spleen of NRG mice resulted in an increased frequency in the occurrence of liver tumors compared to the injection of the same number of parental SK-HEP-1 cells (50% vs. 14%, P < 0.05). On the contrary, RAB3B-KD cells subjected to sphere induction did not exhibit increased liver metastatic potential compared to cells cultured normally (17% vs. 19%).
Quantification of exosomes released into the medium and their effect on CSLCs
We examined the amount of exosomes in the medium because certain Rab families regulate the exocytosis of vesicles [30]. For SK-HEP-1 cells, the exosome level was significantly increased (2.6-fold, P < 0.01) in the sphere inducing medium compared to that in the control medium (Fig. 4). In the RAB3B-KD cells, the number of exosomes was not increased in the sphere inducing medium. The KD/pRAB3B cells also showed increased exosome release (4.2-fold, P < 0.01), although the number of exosomes released in the control medium was similar to that in the case of SK-HEP-1 cells. The addition of an exosome inhibitor, GW4869 (final concentration, 5 μM), repressed the exosome release in all the conditions tested (Fig. 4). The sphere size of SK-HEP-1 and KD/pRAB3B cells was significantly smaller (0.6-fold each, P < 0.05) in the presence of GW4869 than that in its absence (Fig. 5).
Exosome levels released from SK-HEP-1 derivatives. Quantification of exosomes. White and gray columns represent values from the control and sphere inducing medium, respectively. If necessary, the exosome inhibitor, GW4869 hydrochloride hydrate (final concentration, 5 μM), was added. *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test
Effect of an exosome inhibitor on sphere formation of SK-HEP-1 derivative cells. a, Size of sphere cells. White and gray columns represent size of sphere cells in the absence and presence of the exosome inhibitor, GW4869 hydrochloride hydrate (final concentration, 5 μM). *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test. b–d, Representative sphere cells in the absence (upper panels) and presence (lower panels) of 5 μM GW4869
Expression profile of genes affected by RAB3B expression
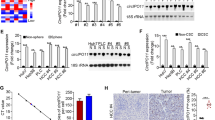
To comprehensively investigate the effect of RAB3B expression on the CSLC phenotype, we performed RNA-seq analysis using RAB3B-KD and KD/pRAB3B cells in addition to the parental SK-HEP-1 cells (Supplementary Fig. S7). The screening was performed according to the following criteria: 1. changes in expression in the sphere inducing conditions compared to that in the control condition; 2. changes in expression in constitutive RAB3B over-expressing cells compared to SK-HEP-1 cells, and 3. changes in expression in the RAB3B knocked down condition in both sphere inducing and control conditions. From the screening, we obtained 13 genes that showed specific expression under the sphere inducing conditions and their expression was associated with that of RAB3B. Among 13 genes, 5 genes (ABCG2, APOE, LEPR, LXN, and TSPAN13) passed the validation analysis using qRT-PCR (Fig. 6). ABCG2 was one of these 5 genes. The expression of ABCG2 was increased (qRT-PCR; 2.3-fold, P < 0.05, RNA-seq; 2.9-fold, q < 0.01) in SK-HEP-1 cells in the sphere inducing conditions compared to that in the control culture. In contrast, the expression of ABCG2 in RAB3B-KD cells in both sphere inducing and control conditions was lower (qRT-PCR; < 0.4-fold, P < 0.05, RNA-seq; < 0.1-folds, q < 0.01) than that in SK-HEP-1 cells. The decrease in expression was recovered in KD/pRAB3B cells. The trend of expression of LXN and TSPAN13 was similar to that of ABCG2. The expression of APOE, LEPR, and RAB3B was significantly different in sphere inducing conditions but not in control conditions.
RAB3B-affected CSLC-specific gene expression. a, The five genes (ABCG2, APOE, LEPR, LXN, and TSPAN13) were validated as the RAB3B-affected CSLC-specific genes. The mRNA expression of each gene from SK-HEP-1 (white columns), RAB3B-KD (blue columns), and KD/pRAB3B (salmon columns) cells was evaluated using quantitative RT-PCR. *P < 0.05 with Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test. b, The mRNA expressions counted by RNA-sequencing. *q < 0.05
Discussion
We performed comprehensive RNA expression profiling of HCC specimens with recurrence and a sphere-forming cell line, and detected seven significant DEGs in CSLCs (Fig. 1). Among these 7 genes, we focused on RAB3B, which was upregulated and relatively abundant in both sphere cells and HCCs with a shorter recurrence-free period (Supplementary Fig. S4). RAB3B-KD and its constitutive rescued cells were generated and used to examine the effects of RAB3B on the cancer stem-like phenotype. Interestingly, the RAB3B-KD cells exhibited a smaller sphere size and increased susceptibility to anticancer drugs compared to parental cells; these effects were reverted upon exogenous expression of RAB3B in the RAB3B-KD cells (Figs. 2, 3 and 5). With regards to the mechanism of RAB3B induction, it is known that the RAB3B is upregulated in the prostate via androgen receptor signaling [31], although our sphere inducing medium was not supplemented with androgen. In addition, several hormones other than androgen in the sphere inducing medium did not significantly affect sphere formation (data not shown). In this study, RAB3B-KD cells did not show the induction of RAB3B in the sphere inducing conditions despite the presence of the remaining wild-type allele (Fig. 2). The abovementioned regulation by androgen receptor signaling is subjected to a feed-forward regulatory loop with NKX3–1 [31]; therefore, RAB3B might also be involved in the loop regulation and its expression from monoallele may be insufficient for RAB3B induction. Interestingly, RAB3B-KD cells showed a 37% frequency of reads harboring genome-edited RAB3B by whole exome sequencing (Supplementary Fig. S2), while RNA-seq showed that the frequencies of those were only 2% in RAB3B-KD cells in both control and sphere inducing conditions (data not shown). Another possibility is that truncated RAB3B might inhibit wild-type RAB3B function. However, the mechanism of RAB3B induction remains unclear.
Interestingly, we observed that the RAB3B levels correlated with the exosome release (Fig. 4). Moreover, the effect of inhibition of the exosome release on the sphere forming ability of the cells was also observed. A well-known Rab family responsible for exosome secretion is RAB27 [30]. Exosomes play an important role in organotropic metastasis through its membrane integrins and contents [32, 33]. Indeed, no difference in the liver metastatic ability of RAB3B-KD cells prepared in control culture or under the sphere inducing condition was observed (Table 1). These observations suggest that RAB3B might be involved in the modulation of tumor microenvironment during metastasis. An exosome inhibitor, GW4869, used in this study, represses mature exosome releasing from multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) by inhibiting the inward budding of MVEs [34]. RAB27 plays a role in MVE docking at the plasma membrane to exosome secretion [30]. Similar to the role of RAB27 in exosome secretion, RAB3 is involved in synaptic vesicle exocytosis [19]. It is suggested that exosomes contain signals for cell-to-cell communication are released into the tumor microenvironment by RAB3B which might be necessary for acquiring the CSLC phenotype. However, we have not yet been able to elucidate the signals in detail in this study. A limitation of this study is that the detailed mechanism involved in RAB3B mediated acquisition of CSLC phenotype, in addition to the mechanism of RAB3B induction, have not been uncovered.
One well-known mechanism of chemoresistance is the upregulation of ABC transporters, which mediate the efflux of the anticancer drugs [35]. We previously reported that ABCG2, an ABC transporter, was upregulated in the sphere inducing conditions [16]. Herein, ABCG2 was also identified as one of the specific genes associated with sphere formation and RAB3B expression (Fig. 6). In agreement with the results of our previous study, in the sphere inducing conditions, the proportion of SK-HEP-1 cells in the G0/G1 phase were increased as compared to that in the control condition (Supplementary Fig. S5). Although the proportion of RAB3B-rescued cells increased in the G0/G1 phase was the same as that of SK-HEP-1 cells, RAB3B-KD cells showed increased population in the G2/M phase in the sphere inducting conditions.
Furthermore, we found 5 genes that were associated positively with both sphere forming conditions and RAB3B expression (Fig. 6). In addition to ABCG2, APOE and LFER reportedly play a role in cancer stem cells [36, 37]. The expression of TSPAN13 is also associated with poor prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, and bladder cancer [38]. It is consistent with our results that LXN overexpression promotes cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase in SK-HEP-1 cells, while the same study reported that LXN overexpression suppresses cell viability, colony formation, and tumorigenesis [39]. These previous findings may support the mechanism of acquisition of CSLC properties by RAB3B function in extracellular vesicle production.
Among the 7 genes that were associated with both sphere induction and poor prognosis of HCC, the expression of PBLD, STRIP2, and LOC344887 has also been correlated with poor prognosis of HCC, lung adenocarcinoma, and non-small cell lung cance [40, 41]. Moreover, these genes are associated with EMT and invasive potential of cells [40, 42, 43]. Recently, ATP6V0D2, a proton transporter, which showed the highest M value in our study (Fig. 1), was reported to be involved in oncogenic functions, such as migration, invasion, and EMT [44]. Therefore, in addition to RAB3B, these genes may also contribute to the acquisition of the CSLC phenotype.
In conclusion, RAB3B might be required for the acquisition of CSLC properties. RAB3B might be crucial in the secretion of extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, and might regulate the expression of related genes; hence, further detailed investigations on cell–cell communication would disclose key genes that can be targeted for the therapy of hepatoma.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. RNA sequencing data of this study have been deposited in the DDBJ Sequenced Read Archive repository (https://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/index.html) with accession numbers DRA012980, DRA012981, and DRA012982.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003;38:200–7.
Ban D, Ogura T, Akahoshi K, Tanabe M. Current topics in the surgical treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2018;2:137–46.
Kokudo N, Takemura N, Hasegawa K, Takayama T, Kubo S, Shimada M, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma: the Japan Society of Hepatology 2017 (4th JSH-HCC guidelines) a 2019 update. Hepatol Res. 2019;49:1109–13.
Ju MR, Yopp AC. Evolving thresholds for liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a Western experience. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2020;4:208–15.
Nakajima M, Tokumitsu Y, Shindo Y, Matsui H, Matsukuma S, Iida M, et al. The recent development of the surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Appl Sci. 2021;11:2023.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–17.
Bruix J, Llovet JM. Major achievements in hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373:614–6.
Sakon M, Umeshita K, Nagano H, Eguchi H, Kishimoto S, Miyamoto A, et al. Clinical significance of hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis by disease-free survival curves. Arch Surg. 2000;135:1456–9.
Tsunedomi R, Iizuka N, Tamesa T, Sakamoto K, Hamaguchi T, Somura H, et al. Decreased ID2 promotes metastatic potentials of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1025–31.
Visvader JE. Cells of origin in cancer. Nature. 2011;469:314–22.
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells: current status and evolving complexities. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:717–28.
Nguyen LV, Vanner R, Dirks P, Eaves CJ. Cancer stem cells: an evolving concept. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:133–43.
Tsunedomi R, Yoshimura K, Suzuki N, Hazama S, Nagano H. Clinical implications of cancer stem cells in digestive cancers: acquisition of stemness and prognostic impact. Surg Today. 2020;50:1560–77.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:704–15.
Hashimoto N, Tsunedomi R, Yoshimura K, Watanabe Y, Hazama S, Oka M. Cancer stem-like sphere cells induced from de-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cell lines possess the resistance to anti-cancer drugs. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:722.
Watanabe Y, Yoshimura K, Yoshikawa K, Tsunedomi R, Shindo Y, Matsukuma S, et al. A stem cell medium containing neural stimulating factor induces a pancreatic cancer stem-like cell-enriched population. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:1857–66.
Nishiyama M, Tsunedomi R, Yoshimura K, Hashimoto N, Matsukuma S, Ogihara H, et al. Metastatic ability and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in induced cancer stem-like hepatoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:1101–9.
Lledo PM, Vernier P, Vincent JD, Mason WT, Zorec R. Inhibition of Rab3B expression attenuates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis in rat anterior pituitary cells. Nature. 1993;364:540–4.
Wang L, Skotland T, Berge V, Sandvig K, Llorente A. Exosomal proteins as prostate cancer biomarkers in urine: from mass spectrometry discovery to immunoassay-based validation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;98:80–5.
Peinado H, Alečković M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med. 2012;18:883–91.
Wang T, Liu J, Shen L, Tonti-Filippini J, Zhu Y, Jia H, et al. STAR: an integrated solution to management and visualization of sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:3204–10.
Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:323.
Robinson M, Oshlack A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R25.
Sun J, Nishiyama T, Shimizu K, Kadota K. TCC: an R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:219.
Tang M, Sun J, Shimizu K, Kadota K. Evaluation of methods for differential expression analysis on multi-group RNA-seq count data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015;16:361.
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–40.
McCarthy DJ, Chen Y, Smyth GK. Differential expression analysis of multifactor RNA-Seq experiments with respect to biological variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:4288–97.
Fujiwara N, Usui T, Ohama T, Sato K. Regulation of beclin 1 protein phosphorylation and autophagy by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and death-associated protein kinase 3 (DAPK3). J Biol Chem. 2016;291:10858–66.
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:19–30.
Tan PY, Chang CW, Chang KR, Wansa KD, Sung WK, Cheung E. Integration of regulatory networks by NKX3-1 promotes androgen-dependent prostate cancer survival. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:399–414.
Hoshino A, Costa-Silva B, Shen TL, Rodrigues G, Hashimoto A, Mark MT, et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527:329–35.
Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49:347–60.
Essandoh K, Yang L, Wang X, Huang W, Qin D, Hao J, et al. Blockade of exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852:2362–71.
Sukowati CH, Rosso N, Crocè LS, Tiribelli C. Hepatic cancer stem cells and drug resistance: relevance in targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2010;2:114–26.
Papi A, Storci G, Guarnieri T, Carolis SD, Bertoni S, Avenia N, et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α/hypoxia inducible factor-1α interplay sustains carbonic anhydrase IX and apoliprotein E expression in breast cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54968.
Zheng Q, Banaszak L, Fracci S, Basali D, Dunlap SM, Hursting SD, et al. Leptin receptor maintains cancer stem-like properties in triple negative breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20:797–808.
Li P, Dong M, Wang Z. Downregulation of TSPAN13 by miR-369-3p inhibits cell proliferation in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19:146–54.
Ni QF, Tian Y, Kong LL, Lu YT, Ding WZ, Kong LB. Latexin exhibits tumor suppressor potential in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:1364–72.
Li A, Yan Q, Zhao X, Zhong J, Yang H, Feng Z, et al. Decreased expression of PBLD correlates with poor prognosis and functions as a tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:524–37.
Wu B, Zhang XJ, Li XG, Jiang LS, He F. Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:3808–12.
Qiu LM, Sun YH, Chen TT, Chen JJ, Ma HT. STRIP2, a member of the striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase complex, is implicated in lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and migration. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10:351–61.
Wu XC, Wang SH, Ou HH, Zhu B, Zhu Y, Zhang Q, et al. The NmrA-like family domain containing 1 pseudogene Loc344887 is amplified in gallbladder cancer and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017;90:456–63.
Qi M, Liu SM, Ji W, Wang HL. ATP6V0D2, a subunit associated with proton transport, serves an oncogenic role in esophagus cancer and is correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Esophagus. 2020;17:456–67.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers 20 K17619, 19 K09218, 16 K10574, and by a grant for the Seeds-A (A098) in the translational research program in Okayama University from Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.T., K.Y. and H.N. designed the study. R.T., Y.K., M.N., N.F., S.M., and S.K. performed the experiments. H.M., Y.S., Y.W., Y.T., S.Y., M.I, N.S., S.T., T.I. and S.H. analyzed the data. R.T. and H.N. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental protocols described in this study were approved by the Institutional Review Board for Human Use at Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine and conform to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided written informed consent. All animal studies were conducted in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Yamaguchi University and conformed to the Guide for the Care, Use of Laboratory Animals published by the United States National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA), and ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers and hydrolysis probes used in this study. Supplementary Figure S1. Genome editing of RAB3B. In each panel, upper and lower figures show Sanger sequencing data and the respective amino acid sequence it translates to. a, In the wild-type RAB3Bsequence, a protospaceradjacent motif (PAM) and guide RNA sequences are represented. b, RAB3Bsequence with heterogeneous mutation and resulting truncated amino acid sequence are represented. Supplementary Figure S2. Genome view of edited RAB3B. Genomic DNA from SK-HEP-1 (upper panel) and its derivative, RAB3B-KD cells (lower panel) were subjected to whole exome sequence using the TruSeqRapid Exome Library Prep Kit and NextSeq500 (Illumina). the filtered short reads were mapped to the reference genome (hg19) with BWA (version 0.7.12). The represented image was generated using IGV (version 2.9.4). The RAB3B-KD cells showed reads harboring insertion “T” at chromosome 1: 52,442,589 with 37% (11/30 reads) frequency. Mutation analysis using Strelka(version 0.4.10.2) showed no insertion/deletion variation by the off-target effect of the genome-editing. Supplementary Figure S3. Schematic for identification of genes specific for cancer stem-like cells and HCCs with poor prognosis. On the left, the identification was started with SK-HEP-1 cells in the sphere inducing and control conditions. On the right, the identification started from HCC specimens with/without recurrence after surgery. The represented number of starting genes showed that the number of genes with sum of a fragment-count of all samples was more than half of the sample number. DEGs, differentially expressed genes with > 2-fold change, q < 0.05, and the average count in higher group > 50. Supplementary Figure S4. mRNA levels of the identified genes determined using RNA-seqanalysis. The mRNA levels of the five identified cancer stem-like cell specific upregulated genes in SK-HEP-1 cells (a) and clinical specimens (b) are represented as transcripts per million (TPM). Supplementary Figure S5. Cell cycle analysis. Cell cycle distribution of SK-HEP-1 (aand b), RAB3B-KO (cand d), and KD/pRAB3B (eand f) cells in control (a, c, and e) and sphere inducing (b, d, and f) conditions, respectively. After cultivation, cells were dissociated with Accumax(Innovative Cell Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA). Cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry, following propidiumiodide (PI) staining. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol and then resuspendedin PI/RNase Staining Buffer (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ). The DNA content of cells was analyzed using a MACSQuantanalyzer (MiltenyiBiotec, BergischGladbach, Germany). Each panel shows a representative histogram. Supplementary Figure S6. BCAN9370Liver metastasis ability of RAB3B-KD cells. The metastatic ability of cells was evaluated by splenic injection into NOD-Rag1nullIL2rγnulldouble mutant mice. Representative images in Table 1, mice were injected with 1 x 104 tumor cells. RAB3B-KD is a RAB3B-edited clone derived from SK-HEP-1 cells. Yellow arrows indicate formed tumors. Supplementary Figure S7. Schematic for identification of RAB3B-affected cancer stem-like cell (CSLC) specific genes. With SK-HEP-1 derivative cells; parental SK-HEP-1, RAB3B-KD, and KD/pRAB3B, RAB3Baffected CSLC specific differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using RNA-seqanalysis. On the left, the DEGs in sphere-inducing conditions were identified using the same criteria as mentioned in Supplementary Fig. S3. On the right, RAB3B-affected genes in control conditions were identified as DEGs with > 1.7-fold change, q < 0.05, and average count in higher group > 30. The circled numbers are the screening criteria as shown in the text. The represented number of starting genes shows that the number of genes with sum of a fragment-count of all samples was more than half of the sample number. Supplementary Figure S8. Full-length blots used in Fig. 2. Supplementary Figure S9. Full-length blots at different exposure time used in Fig. 2.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsunedomi, R., Yoshimura, K., Kimura, Y. et al. Elevated expression of RAB3B plays important roles in chemoresistance and metastatic potential of hepatoma cells. BMC Cancer 22, 260 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09370-1