Abstract
The extracellular matrix is essential for the integrity of the lung and when disrupted can lead to the architectural changes seen in emphysema. The etiology of emphysema is believed to be due to an imbalance in the proteases and antiproteases within the lung. Studies have focused on elastolytic enzymes as the primary agents in disease pathogenesis, however, recent data suggest that collagenases may also be involved in the destruction of lung tissue in emphysema. It is hoped that this expanded understanding of the pathophysiology of emphysema will lead to improved therapy in the treatment of the disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α1-AT:
-
alpha-1-antitrypsin
- COPD:
-
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloproteinase
- MMP-1:
-
collagenase
- MMP-12:
-
metalloelastase
- MT-MMP:
-
membrane type matrix metalloproteinase.
References
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Division of Epidemiology: [http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov]
NHLBI Morbidity and Mortality Chartbook. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute,. 1998
Laurell CD, Erikson S: The electrophoretic a1-globulin pattern of serum in alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963, 15: 132-140.
Janus ED, Phillips NT, Carrell RW: Smoking, lung function, and α1-AT deficiency. Lancet. 1985, 1: 152-154. 10.1016/S0140-6736(85)91916-6.
Eidelman D, Saetta MP, Ghezzo H, Wang NS, Hoidal JR, King M, Cosio MG: Cellularity of the alveolar walls in smokers and its relation to alveolar destruction. Functional implications. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990, 141: 1547-1552.
Fujita J, Nelson NL, Daughton DM, Dobry CA, Spurzem JR, Irino S, Rennard SI: Evaluation of elastase and anti-elastase balance in patients with chronic bronchitis and pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990, 142: 57-62.
Stone PJ, Calore JD, McGowan SE, Bernardo J, Snider GL, Franzblau C: Functional alpha-1 protease inhibitor in the lower respiratory tract of cigarette smokers is not decreased. Science. 1983, 221: 1187-1189.
Campbell EJ, Campbell MA, Boukedes SS, Owen CA: Quantum proteolysis by neutophils: implications for pulmonary emphysema in α1-antitrypsin deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1999, 104: 334-337.
Liou T, Campbell E: Quantum proteolysis resulting from release of single granules by human neutrophils: a novel, nonoxidative mechanism of extracellular proteolytic activity. J Immunol. 1996, 157: 2624-2631.
Hill A, Gompertz S, Stockey R: Factors influencing airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2000, 55: 970-977. 10.1136/thorax.55.11.970.
Hautamaki RD, Kobayashi DK, Senior R, Shapiro SD: Requirement for macrophage elastase for cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. Science. 1997, 277: 2002-2004. 10.1126/science.277.5334.2002.
Finlay GA, O'Driscoll LR, Russell KJ, D'Arcy EM, Masterson JB, FitzGerald MX, O'Connor CM: Matrix metalloproteinase expression and production by alveolar macrophages in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997, 156: 240-247.
Ohnishi K, Takagi M, Kurokawa Y, Satomi S, Konttinen Y: Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated extracellular matrix protein degradation in human pulmonary emphysema. Lab Invest. 1998, 78: 1077-1087.
Gibbs DF, Warner RL, Weiss SJ, Johnson KJ, Varani J: Characterization of matrix metalloproteinases produced by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999, 20: 1136-1144.
Lang MR, Fiaux GW, Gillooly M, Stewart JA, Hulmes DJ, Lamb D: Collagen content of alveolar wall tissue in emphysematous and non-emphysematous lungs. Thorax. 1994, 49: 319-326.
Bruce M, Poncz L, Klinger J, Stern R, Tomashefski J, Dearborn D: Biochemical and pathologic evidence for proteolytic destruction of lung connective tissue in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989, 132: 529-535.
Christner P, Fein A, Goldberg S, Lippmann M, Abrams W, Winbaum G: Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985, 131: 690-695.
Micheali D, Fudenberg HH: Antibodies to collagen in patients with emphysema. Clin Immunol Immnopathol. 1974, 3: 187-192.
Pinnell SR, Krane SM, Kenzora JE, Glimcher MJ: A heritable disorder of connective tissue, hydroxylysine-deficient collagen disease. New Engl J Med. 1972, 286: 1013-1020.
Kilburn KH, Dowell AR, Pratt PC: Morphological and biochemical assessment of papain-induced emphysema. Arch Intern Med. 1971, 127: 884-890. 10.1001/archinte.127.5.884.
Yu SY, Keller NR: Synthesis of lung collagen in hamsters with elastase-induced emphysema. Exp Mol Pathol. 1978, 29: 37-43.
Riley DJ, Kramer MJ, Kerr JS, Chae CU, Yu SY, Berg RA: Damage and repair of lung connective tissue in rats exposed to toxic levels of oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987, 135: 441-447.
D'Armiento J, Dalal SS, Okada Y, Berg RA, Chada K: Collagenase expression in the lungs of transgenic mice causes pulmonary emphysema. Cell. 1992, 71: 955-961.
Cardoso W, Harmanjatinder S, Hyde D: Collagen and elastin in human pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993, 147: 975-981.
Wright JL, Churg A: Smoke-induced emphysema in guinea pigs is associated with morphometric evidence of collagen breakdown and repair. Am J Physiol. 1995, 268: L17-L20.
Selman M, Montano M, Ramos C, Vanda B, Becerril C, Delgado J, Sansores R, Barrios R, Pardo A: Tobacco smoke-induced lung emphysema in guinea pigs is associated with increased interstitial collagenase. Am J Physiol. 1996, 271: L734-L743.
Imai K, Dalal S, Chen E, Downey R, Schulman L, Ginsburg M, D'Armiento J: Human collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1) expression in the lungs of patients with emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001, 163: 786-791.
Segura-Valdez L, Pardo A, Gaxiola M, Uhal B, Becerril C, Selman M: Upregulation of gelatinase a and b, collagenases 1 and 2, and increased parenchymal cell death in COPD. Chest. 2000, 117: 684-694. 10.1378/chest.117.3.684.
Acknowledgements
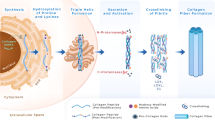
We thank K Chada, A Marks and R Cole for critical reading of the manuscript and N Kolesnikova for assistance in the preparation of Figure 1. This work is supported by a National Institutes for Health RO1 grant AG16994-0 (J D'Armiento). J D'Armiento is a recipient of a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award in the Biomedical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foronjy, R., D'Armiento, J. The role of collagenase in emphysema. Respir Res 2, 348 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1186/rr85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/rr85