Abstract
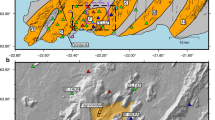
Deep low-frequency (DLF) events have often been discussed in association with fluid (magma) activity around volcanoes, in this paper, however, we will show another example of DLF activity beneath active faults. On October 6, 2000, a Mw=6.7 crustal earthquake occurred in the western Tottori, southwest Japan. Beneath the focal region of the earthquake, DLF earthquakes had been observed prior to the mainshock and the activity increased after the mainshock. The events are distributed around 30 km depth and seem to be located around the downward extension of the seismogenic fault. Three types of DLF events have been observed and their seismological features indicate fluid activity around the focal region of the DLF events. If the downward extension of the seismogenic fault in the lower crust exists, fluid activity indicated by the DLF events possibly affect the aseismic slip process of the deep portion of the fault and likely control the occurrence of the earthquakes on the seismogenic portion of the fault.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie, R. and P. Leary, Source parameters of small earthquakes recorded at 2.5 km depth, Cajon Pass, southern California: Implications for earthquake scaling, Geophys. Res. Lett., 20, 1511–1514, 1993.
Aki, K. and R. Koyanagi, Deep volcanic tremor and magma ascent mechanism under Kilauea, Hawaii, J. Geophys. Res., 86, 7095–7109, 1981.
Aki, K., M. Fehler, and S. Das, Source mechanism of volcanic tremor: Fluid-driven crack models and their application to the 1963 Kilauea eruption, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 2, 259–287, 1977.
Boatwright, J., A spectral theory for circular seismic sources: Simple estimates of source dimension, dynamic stress drops, and radiated energy, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., 70, 1–28, 1980.
Chouet, B., Excitation of a buried magmatic pipe: A seismic source model forvolcanic tremor, J. Geophys. Res., 90, 1881–1893, 1985.
Crosson, R. S. and D. A. Bame, A spherical source model for low-frequency volcanic earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res., 90, 10237–10247, 1985.
Doi, I., K. Nishigami, K. Tadokoro, and A. Shimokawa, Three dimensional structure of the S-wave reflectors in and around the source region of the 2000 Western Tottori earthquake, Monthly Chikyu, 290, 647–651, 2003.
Hasegawa, A. and A. Yamamoto, Deep, low-frequency microearthquakes in or around seismic low-velocity zones beneath active volcanoes in northeastern Japan, Tectonophys., 233, 233–252, 1994.
Iio, Y. and Y. Kobayashi, A physical understanding of large intraplate earthquakes, Earth Planets Space, 54, 1001–1004, 2002.
Kanamori, H. and D. L. Anderson, Theoretical bases for some empirical relations in seismology, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., 65, 1073–1095, 1975.
Mori, J. and A. Frankel, Source parameters for small events associated with the 1986 North Palm Springs, California, earthquake determined using empirical Green functions, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., 80, 278–295, 1990.
Mueller, C. S., Source pulse enhancement by deconvolution of an empirical Green’s function, Geophys. Res. Lett., 12, 33–36, 1985.
Obara, K., Nonvolcanic deep tremor associated with subduction in southwest Japan, Science, 296, 1679–1681, 2002.
Obara, K. and H. Hirose, Episodic deep low-frequency tremor and slow slip in southewest Japan, Abstracts, Japan Earth and Planetary Science Joint Meeting, J078–021, 2004.
Ohmi, S., Aftershock distribution of the 2000 Western Tottori earthquake by use of the station corrections as a function of hypocenter coordinates, J. Seismol. Soc. Jpn., Ser. 2, 54, 575–580, 2002.
Ohmi, S. and K. Obara, Deep low-frequency earthquakes beneath the focal region of the Mw 6.7 2000 Western Tottori earthquake, Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(16), 10.1029/2001GL014469, 2002.
Ohmi, S., K. Watanabe, T. Shibutani, N. Hirano, and S. Nakao, The 2000 Western Tottori earthquake—Seismic activity revealed by the regional seismic networks—, Earth Planets Space, 54, 819–830, 2002.
Okada, Y, Internal deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., 82, 1018–1040, 1992.
Oshiman, N., K. Aizawa, and I. Shiozaki, Deep crustal resistivity structure in and around the focal area of the 2000 Tottori-ken Seibu Earthquake, Japan, IUGG2003, JSA10/30P/D-005, 2003.
Rogers, G. and H. Dragert, Episodic tremor and slip on the Cascadia subduction zone: The chatter of silent slip, Science, 300, 1942–1943, 2003.
Sagiya, T., T. Nishimura, Y. Hatanaka, E. Fukuyama, and W. L. Ellsworth, Crustal movements associated with the 2000 western Tottori earthquake and its fault models, J. Seismol. Soc. Jpn., Ser 2, 523–534, 2002.
Tamura, Y., T. Sato, M. Ooe, and M. Ishiguro, A procedure for tidal analysis with a Bayesian information criterion, Geophys. J. Int., 104, 507–516, 1991.
Ukawa, M. and K. Obara, Low frequency earthquakes around Moho beneath the volcanic front in the Kanto district, central Japan, Bull. Volcanol. Soc. Jpn., 38, 187–197, 1993.
Umino, N., H. Ujikawa, S. Hori, and A. Hasegawa, Distinct S-wave reflectors (bright spots) detected beneath the Nagamachi-Rifu fault, NE Japan, Earth Planets Space, 54, 1021–1026, 2002.
Wessel, P. and W. H. F. Smith, New, improved version of the Generic Mapping Tools released, Eos Trans. AGU, 79, 579, 1998.
Zhao, D., H. Tani, and O. P. Mishra, Crustal heterogeneity in the 2000 Tottori earthquake region: Effect of fluids from slab dehydration, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter, 145, 161–177, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohmi, S., Hirose, I. & Mori, J.J. Deep low-frequency earthquakes near the downward extension of the seismogenic fault of the 2000 Western Tottori earthquake. Earth Planet Sp 56, 1185–1189 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03353338
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03353338