Abstract
Background
The novel chiral phosphorus-1,1-dithiolates [4-CH3OC6H4P(S)(OR)S]-[H3NC(CH3)3]+ were synthesized by the reaction of [RPS2)]2 (R = 4-MeOC6H4) or P2S5 and the respective alcohol ROH (R = myrtanyl, 2-naphthylethyl, myrtenyl, borneol) in toluene. The reaction of phosphorus-1,1-dithiolates 1–4 and Au(tht)Cl, AuClPPh3 or AgNO3 and PPh3 gave rise to gold(I)- and silver(I)-complexes in THF. All compounds have been characterised by elemental analyses, IR, NMR (1H-, 13C- and 31P-) spectroscopy as well as MS measurements. Optical rotation values confirmed the chirality of the compounds. The Compound 4 has been characterized structurally by X-ray crystallography.
Results
Phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolate compounds were formed as liquids and were treated with suitable amine in order to convert them to their salts 1–4 . They have been successfully characterized spectroscopically (IR, 1H, 13C, 31P NMR) as well as mass spectra. The compound 4 has been also structurally by X-ray crystallography. The compound 4 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) with Z = 4. Compounds containing phosphorus and sulfur donor atoms are excellent ligands due to offering many metal complexes especially group 11–12 metals. The synthesis of gold(I) and silver(I) complexes with chiral phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolate and triphenylphosphine have been described and investigated.
Conclusions
In the present work, we report the synthesis, charactreization of the chiral phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate ligands and preparing the gold(I) and silver(I) phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate or S-donor with phosphine complexes. The molecular structure of the Compound 4 was determined by X-ray diffraction. Due to an easy synthesis method of phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate compounds and a good complexion reagent, it is possible the improvement of the collecting metallic gold or silver from the minerals. When the more ionic salt of phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate compounds were prepared in this way, the water can be used as a cheap solvent. As a result, it can be an alternatively method for the collecting metallic gold or silver from the minerals in future.

Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Phosphorus-1,1’-dithiolate ligands are an important class in organophophorus chemistry [1, 2]. To date, many phosphorus-1,1’-dithiolate have been synthesized and widely utilised in agricultural, medicinal and technological fields[1–4]. Since the discovery of Lawesson reagent’s and its anologue, they have been used a thionation reagent in organic chemistry and also considerable number of dithiophosphonates and their metal complexes have been synthesized [5–29]. For example, dithiophosphonates which are derivatives of phosphorus-1,1’-dithiolate ligands are not commercially available but they can be easily synthesized by the reaction of Lawesson’s reagent or Ferrocenyl Lawesson’s reagent and the respective alcohols or amines due to a ring opening reaction by nucleophilic attack. The application of metal complexes in the field of medicinal, bioinorganic and bioorganic chemistry has become important in recent decades. For example, some complexes of gold(I), such as Auranofin and some related complexes have been used in the treatment of severe rheumathoidal arthritis [30]. Although there are many gold(I), silver(I) and copper(I) complexes of dithiophosphonates [8–12, 22, 24], chiral dithiophosphonates and their metal complexes are rare. Recently, a few gold(I) complexes with chiral dithiophosphonates have been reported in our laboratory [5, 6].
In the present work, we report mono and dinuclear metal complexes with chiral dithiophosphonates and also triphenylphosphine complexes. All compounds were characterized by elemental analyses, IR, NMR (1H-, 13C-, 31P-) spectroscopy as well as MS measurements.
Results and discussion
Chiral phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate ligands have been synthesized from Lawesson’s reagent and chiral hydroxyl compounds (Scheme 1).
O-dithiophosphonic acid derivatives of phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolate were formed as liquids and were treated with suitable amine in order to convert them to their salts 1–4. The 31P NMR spectra of the ligands 1–4 were measured in [D6]DMSO and showed one signal as expected. The synthesis and X-ray determination of the compound 2 was reported by Solak et. al. [7] but the spectral studies of the compound 2 were not. All ligands 1–4 and gold(I) complexes reported here have been characterised by elemental analysis, IR, NMR and mass spectrocopies. An analogue (triethyl ammonium -O,O’-diborneildithiophosphate) of the compound 4 was sythesized by Ohta et. al.[31]. In this study, a single crytal structural and full spectroscopically studies of the compound 4, tert-butylammonium -O,O’-diborneildithiophosphate, also performed here.
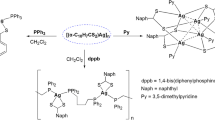
The synthesis of gold(I) and silver(I) complexes with chiral phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolate and triphenylphosphine have been described and also characterized by elemental analyses, IR, NMR and MS spectroscopies (Additional file 1). The synthesis mononuclear and dinuclear gold(I) complexes were summarized in the Scheme 2. The ligands 1, 2 and 3 were reacted with AuCl(PPh3) in order to obtain gold(I)-phosphin complexes with phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolate (Scheme 2). The 31P NMR spectrum of 1a exhibits two signal at 100.33 ppm (PS2) and 37.30 ppm (PPh3). The complexes 2a and 3a also showed two signals in the 31P NMR spectrum as expected and other spectroscopic data confirm their structure (Additional file 1). The reaction of the ligands 1 and 4 with Au(tht)Cl gave rise to dinuclear gold(I) complex 1b and 4a. The spectra of the complexes 1b and 4a were suitable and agree with reported similar structures by Van Zyl et. al. [8–10, 22]. To obtain dinuclear gold(I) complexes with amido derivatives of phosphoro-1,1-dithilato, all attempts were unsuccessful. The complex 1b displayed two signals as expexted in its 31P NMR spectrum. One signal is assigned to the trans isomer and the other is assigned to cis isomer. Both signals in the 31P NMR spectrum for dinuclear and mononuclear gold(I) complexes are slightly upfield when compared to the free ligands.
In the case of dinuclear silver(I) complexes, the ligands were reacted with AgNO3 in acetone-water(1:1) at room temperature (Scheme 3). The 31P NMR spectra of the dinuclear silver(I) complexes are similar to the dinuclear gold(I) complexes. The expected cis and trans isomer were observed at 107.35 and 105.49 ppm ( for 1c) and 107.2 and 105.8 ppm (for 2b) (Additional file 1).
The IR spectrum of the ligands and their complexes showed two characteristic bands at around 692–642 cm-1 and 582 – 515 cm -1 which are assigned to νas(PS2) and νs(PS2), respectively (Additional file 1). The molecular ion peak of the ligands 2 and 4, the complexes 1b and 2a were observed at m/z = 430 (for [M + 1]+), 476 [for M]+, 832 (for [M]+), 1104 (for [M]+), respectively, in their mass spectra whereas the other ligands and the complexes exhibited m/z-values for identifiable certain fragments (Additional file 1). Specific rotations of all compounds showed that only one optical isomer was formed.
Molecular structure of 4
Single crystals of 4 suitable for X-ray diffraction studies were obtained from acetone/n-hexane. Compound 4 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) with Z = 4. The molecular structure of 4 is depicted in Figure 1. Selected bond lengths and angles are given Table 1 and Crystal and structure-refinement data in Table 2. The P1-S1 and P1-S2 bond lengths are 197.56(5) and 198.13(5) pm, respectively. Those values are very close to each other due to a delocalized PS2 fragments. Bond lengths and angles are in a good agreement with those of related previously reported compounds [7, 9]. Figure 1 shows that the phosphorus atom has a tetrahedral coordination environment with [O1-P1-S1 113.30(4)°, O2-P1-S1 110.12(4)°, O(1)-P(1)-S(2) 105.02(4)°, O2-P1-S2 110.05(4)°] and the O1-P1-O2 [99.61(6)°] having a deviation from the ideal value (109.5°).
Experimental
Materials
When necessary, the reactions were carried out under an atmosphere of nitrogen using standard Schlenk techniques. All other chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used directly without further purification.
Measurements
Elemental analyses were determined with a GmbH varioMICRO CHNS apparatus. Melting points were determined by using Electrotermal apparatus. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AVANCE DRX 400 NMR spectrometer and Jeol GSX 270 in CDCl3 and d6-DMSO. IR spectra was measured on a Perkin-Elmer 2000 FTIR spectrophotometer (4000 – 400 cm-1). Mass spectra were recorded with an AGILENT 1100 MSD and Waters machines. Optical rotation values were determined with an automatic digital ADP 440+ polarimeter.
X- ray crystallograpy
Data were collected on an Xcalibur-S diffractometer (Agilent Technologies) using Mo-Kα radiation (λ = 71.073 pm) and ω-scan rotation (see Table 2). Data reduction was performed with CrysAlis Pro [32] including the program SCALE3 ABSPACK for empirical absorption correction. The structure was solved by direct methods and the refinement of all non-hydrogen atoms was performed with SHELX97 [33]. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic thermal parameters. With the exception of one borneol molecule (C(11) to C(20)) all hydrogen atoms were located on difference Fourier maps calculated at the final stage of the structure refinement. The structure figure was generated with DIAMOND-3 [34]. Crystallographic details are given in the Additional file 2. CCDC (4) 921954 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. The data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
Synthesis of compounds
Synthesis of t-butyl ammonium salt of (1S,2S,5S)-(−)-myrtanyl −4- methoxyphenyl dithiophoshonate 1
2,4-Bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,2,4-dithiadiphosphetane-2,4-disulfide (Lawesson’s reagent: LR) ( 0.50 g, 1.23 mmol) was reacted with 1S,2S,5S)-(−)-myrtanol (0.39g, 2.4693 mmol) in toluene (20 mL). The mixture was refluxed until all solids had dissolved. The colourless solution was cooled to rt, filtered and treated with excess tert-butyl amine. The product precipitated at −18°C from toluene as a white solid, which was isolated by filtration, washed with toluene and n-hexane and then dried in air. Yield: 0.76 g (72%), m.p.: 161-163°C. [α]58925 = 57.14 (c = 0.105 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C21H36NO2PS2 (429.63 g.mol-1):C, 58.71; H, 8.45; N, 3.26; S, 14.93, Found: C, 59.18; H, 8.51; N, 3.18; S, 14.69. IR(cm-1): 670 (νasym PS2) and 556(νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 8.07 (dd, 2H, 3JP,H = 13.65 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.80 Hz), 6.9 (dd, 2H, 4JP.H =2.57 Hz, 3JH.H =8.75 Hz), 3.85 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.48 ( m. 2H, OCH2), 1.88 (m, 7H, myrtanyl), 1.37 (s, 9H.3×CH3), 1.17 (d, 3H, CH3), 0.79(d, 3H, CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ =161.32 (d, 4JP,C =2.91 Hz), 133.16(d, 1JP,C =109.49 Hz), 132.32 (d, 2JP,C =13.43 Hz), 112.91(d, 3JP,C =14.83 Hz), 68.78(d, 2JP,C =8.55), 55.36, 54.00, 35.45(d, 3JP,C = 8.40 Hz) 28.22, 42.10, 40.86, 39.02, 26.63, 24.09, 23.36, 20.12, 18.12 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = 105.24 ppm. MS: m/z = 430[M + 1]+. 357[M-NH2C(CH3)3]+.
Triethyl ammonium salt of (S)-(−)-O-(2-naphthyl)ethyl-4-methoxyphenyl dithiophosphonate 2
Compound 2 was prepared as described in the literature [7]. [α]58925 = −37.74 (c = 0.053 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C25H34NO2PS2 (475.66 g.mol-1): C, 63.13; H, 7.21;. N, 2.95; S, 13.48 %, Found: C, 63.59; H, 7.32; N, 2.92; S, 12.74 %. IR(cm-1): 667 (νasym PS2) and 569 (νsym PS2). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 9.89 (br, H, HN), 8.1 (dd, 2H, 3JP,H = 13.58 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.81 Hz), 7.21 (m. 4H.), 7.53 (dd, 1H), 7.40 (m. 2H), 6.7 (dd, 2H. 4JP,H =2.62 Hz, 3JH,H =8.87 Hz), 5.7 (m. 1H, OCH, 3JP,H = 13.07, 2JH,H = 6.53 Hz), 3.69 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.07 (q, 6H, 3xNCH2), 1.56 (d, 3H, CH3), 1.18 (t, 9H, 3×CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 160.75(d, 4JP,C =3.03 Hz), 141.64(d, 3JP,C = 4.32 Hz), 135.54(d, 1JP,C =111.36 Hz), 133.11, 132.10, 132.03(d, 2JP,C =13.48 Hz), 127.97, 127.50, 125.70, 125.45, 124.99(d, 4JP,C =5.01 Hz.), 112.52(d, 3JP,C =14.88 Hz), 73.84(d, 2JP,C =7.41), 55.23, 45.90, 24.66(d, 3JP,C =4 .19 Hz), 8.48 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = 105.35 ppm.
Synthesis of t-Butyl ammonium salt of (1R)-(−)-O-myrtenyl-4- methoxyphenyl dithiophoshonate 3
Compound 3 was prepared in the same way as compound 1, from LR (0.50 g, 1.23 mmol) and (1R)-(−)-myrtenol (0.38 mL. 2.4693 mmol ) in toluene (20 mL). Yield: 0.73 g (69%), m.p.: 110-113°C. [α]58925 = 159.1 (c = 0.044 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C21H34NO2PS2 (427.61 g.mol-1): C, 58.99; H, 8.01; N, 3.28; S, 15.00; Found: C, 59.18; H, 8.51; N, 3.18; S, 14.69. IR(cm-1): 669 (νasym PS2) and 556 (νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 8.07 (dd, 3JP,H = 13.59 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.83 Hz), 6.9 (dd, 2H, 4JP,H =2.66 Hz, 3JH,H =8.88 Hz), 4.1 (m, 2H, OCH2), 5.46 (t, H, CH), 3.84 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.2 (m, 5H, myrtenyl ), 1.38 (s, 9H, 3×CH3), 1.27 (d, 3H, CH3) 1.09 (d, 1H, CH) 0.74 (d, 3H, CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ =161.33(d, 4JP,C =3.03 Hz), 144.20(d, 3JP,C =9.68 Hz), 133.25 (d, 1JP,C =109.67 Hz), 132.29 (d, 2JP,C =13.50 Hz), 119.69, 112.92 (d, 3JP,C =14.91 Hz), 67.70 (d, 2JP,C = 7.62), 55.36, 53.17, 43.25, 40.76, 37.98, 31.35, 28.19, 26.16, 20.97 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ =104.88 ppm.
Synthesis of t-Butyl ammonium salt of O,O’-dibornyl-4-methoxyphenyl dithiophosphonate (4)
P4S10 (1g, 2.25 mmol) was reacted with (−) borneol (2.77 g, 9 mmol) in a 1:4 ratio in 50 mL hot toluene to give the crude dithiophosphoric acid. The reactions were refluxed until all solids dissolved and the yellow solutions were obtained. The solution was filtered and then was treated with excess tert-butyl amine at r.t. The tert-butyl ammonium salt of O,O’-dibornyl-dithiophosphoric acids resulted in as a precipitated white solid product. The product was filtrated, washed with pentane several times, dried under vacuum and recrystallized from acetone/hexane. Yield: 3.89g (91%), m.p.: 188°C. Elemental analysis calculated for C24H46NOPS2(475.73 g/mol): C, 60.79; H, 9.26; N, 2.89; S, 13.18; Found: C, 60.59; H, 9.74; N, 2.94; S 13.48. IR(cm-1): 665 (νasym PS2) and 560 (νsym PS2). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.64 (t, 2H), 2.28 (br, 4H), 2.00 (br, 2H), 1.71-179(br, m, 4H), 1.23(br, m, 4H), 0.91(s, 6H, 2×CH3), 0.86(s, 6H, 2×CH3), 0.85(s, 6H, 2×CH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 53.83, 49.52(d, 2JP,C = 6.74 Hz), 47.31, 44.93, 37.44, 28.30, 27.00, 19.94, 18.69, 13.67. 31P-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 106.53(d). MS (FAB): m/z 476 [M]+.
Synthesis of complexes
[Au(PPh 3 )(R 1 PS 2 (OR 2 )] (R 1 : 4-methoxyphenyl and R 2 : ((1S,2S,5S)-(−)-myrtanyl) 1a
A solution of the compound 1 (0.044 g. 0.102 mmol ) in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of AuClPPh3 (0.05 g, 0.102 mmol) in THF (10 mL) and stirred at r.t. for 2 h. A colourless solution was observed and then a solid, t-butylammonium chloride, was immediately precipitated. The reaction mixture was filtered and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The reaction mixture was filtered and 10 mL of n-hexane was added to the solution. The solvent was removed at room temperature and a white crystalline product was isolated. The white crystalline product was dried in air. Yield: 0.042 g (51%), m.p.: 72–74°C. [α]58925 = 37.97 (c = 0.079 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C35H39O2SP2Au (814.78 g.mol-1); calcd: C, 51.60; H, 4.82; S, 7.87; Found: C, 49.78; H, 4.52; S, 10.61. IR(cm-1): 668(νasym PS2) and 536(νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 7.89(dd, 2H, 3JP,H = 13.77 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.61 Hz), 7.50(m, 15H,), 6.77 (dd, 2H, 3JH.H = 8.31 Hz, 3JP,H = 2.18 Hz), 3.95 (q, H, OCH2), 3.73 (s, 3H, OCH3) 1.80 - 0.78 (br, 15H, myrtanyl) ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = 100.33 (PS2), 37.31(PPh3) ppm.
[Au{R 1 PS 2 (OR 2 )}] 2 (R 1 : 4-methoxyphenyl and R 2 : (1S,2S,5S)-(−)-myrtanyl) 1b
A solution of 1 (0.15 g, 0.35 mmol) in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of Au(tht)Cl (tht = tetrahydrothiophene) ( 0.11 g, 0.35 mmol) in THF (10 mL) and stirred for 2 h. A solid, t-butylammonium chloride, was immediately observed. The reaction mixture was filtered and 10 mL of n-hexane was added to the mixture. The solvent was removed at room temperature and orange crystals were isolated. Yield: 0.097 g (50%), m.p.: 123–125°C. [α]58925 = 29.85 (c = 0.067 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C34H48O4S4P2Au2 (1104.90 g.mol-1): C, 36.96; H, 4.38; S, 11.61; Found: C, 36.76; H, 4.51; S, 11.75. IR(cm-1): 640(νasym PS2) and 542(νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 7.91 (br, 4H ), 6.90 (dd, 4H, 3JH,H = 8.63 Hz, 3JP,H = 2.41 Hz), 4.40 (br, 4H, OCH2), 3.79 (s, 6H, OCH3), 1.81-1.29 (m, 18H. myrtenyl), 1.17 (s, 6H, 2×CH3), 0.79 (s, 6H, 2xCH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 163.06(d, 4JP,C = 3.12 Hz), 133.87 (d, 1JP,C =118.49 Hz), 132.46 (d, 2JP,C = 13.25 Hz), 113.95 (d, 3JP,C =15.43 Hz), 71.31(d, 2JP,C =5.33), 55.51, 35.68 (d, 3JP,C = 7.70 Hz), 42.23, 40.84, 39.36, 28.20, 26.71, 24.03, 23.75, 20.28, 18.09 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): (cis, trans isomer) δ = 104.12, 100.95. MS(ESI): m/z = 1104[M]+, 907[M-Au]+.
[Ag{R1PS 2 (OR2)}] 2 (R1: 4-methoxyphenyl and R2: (1S,2S,5S)-(−)-myrtanyl) 1c
The compound 1 (0.20 g, 0.41 mmol) was dissolved in acetone (10 mL). A solution of AgNO3 (0.08 g, 0.41 mmol) in a mixture (10 mL) of acetone-water (1:1) was added dropwise to the solution and stirred for 2 h. A white powder solid was obtained, filtered and recrytallized in CHCl3. The solvent was removed at room temperature and white powder were isolated.Yield: 0.14g (73%), m.p.: 124–126°C. [α]58925 = 27.39 (c = 0.073 in CHCl3). Elemental analysis calculated for C34H48O4S4P2Ag2 (926.70 g.mol-1): C, 44.07; H, 5.22; S, 13.84; Found: C, 43.62; H, 5.32; S, 13.37. IR(cm-1): 656 (νasym PS2) and 543 (νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 7.90 (dd, 4H, 3JP,H = 13.15 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.54 Hz), 6.84 (br, 4H), 3.76 (s, 6H, 2×OCH3), 1.9 (m, 18H, myrtanyl), 1.11 (d, 6H, CH3) 0.73 (d, 6H, CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 162.24, 132.50 (d, 2JP,C = 13.24 Hz), 129.83 (d, 1JP.C = 119.83 Hz), 113.54 (d, 3JP,C = 15.06 Hz), 70.25 (d, 2JP,C = 7.03), 55.42, 35.57 (d, 3JP,C = 8.40 Hz), 42.19, 40.87, 39.22, 26.69, 24.11, 23.66, 20.54, 18.14 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3) (cis, trans isomer) δ = 107.35 and 105.49 ppm.
[Au(PPh 3 )(R 1 PS 2 (OR 2 )] (R 1 : 4-methoxyphenyl, R 2 : ((S)-(−)-O-(2-naphthyl)ethyl) 2a
2a was prepared in a similar manner to 1a using AuClPPh3 (0.049 g. 0.10 mmol) and t-butyl ammonium ((S)-(−)-O-(2-naphthyl)ethyl −4-methoxyphenydithiophosphonate 2 (0.049 g. 0.10 mmol ). Yield: 0.04g (48%), m.p.: 62–64 °C. [α]58925 = 51.94 (c = 0.077 in THF). Elemental analysis calculated for C37H33O2S2P2Au (832.72 g.mol-1): C, 53.37; H, 3.99; S, 7.70; Found: C, 52.50; H, 4.12; S, 7.12 %. IR(cm-1): 674 (νasym PS2) and 537 (νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 8.09(dd, 2H, 3JP,H = 13.94 Hz, 3JH,H = 8.86 Hz), 7.5(br, 15H), 6.79 (dd, 2H, 3JH.H = 8.86, 3JP,H = 3.06 Hz), 6.10(q, H, OCH), 3.78 (s, 3H, OCH3), 1.78 (m, 3H, CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 161.52 (d, 4JP,C =4.42 Hz), 135.21(d, 1JP.C =134.60 Hz), 134.23(d, 2JP,C =13.94 Hz), 132.07, 131.93, 131.70, 129.15, 128.14, 127.88, 127.56, 127.45, 125.84, 125.66, 125.01, 124.77, 124.66, 113.14 (d, 3JP,C =15.63 Hz), 74.66(d, 2JP.C = 6.61 Hz), 55.30, 24.82(d) ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = 100.43 (PS2), 37.20 (PPh3). MS(ESI) = m/z: 832[M]+.
[Ag{R 1 PS 2 (OR 2 )}] 2 (R 1 : 4-methoxyphenyl and R 2 : (2-naphthyl)ethyl) 2b
2b was prepared in a similar manner to 1b using AgNO3 (0.07 g, 0.41 mmol) and triethyl ammonium(S)-(−)-O-(2-naphthyl)ethyl-4-methoxyphenyl dithiophosphonate, (0.20 g, 0.41 mmol). Yield: 0.13 g (64%), m.p.: 114–115°C. [α]58925 = −36.14 (c = 0.083 in CHCl3). Elemental analysis calculated for C38H3604P2S4Ag2 (962.65 g.mol-1): C, 47.41; H, 3.77; S, 13.32; Found: C, 46.15; H, 3.99; S, 12.29. IR(cm-1): 655 (νasym PS2) and 569 (νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 7.60 (br, 18H), 6.55 (br, 4H), 5.62 (br, 2H, OCH), 3.55 (s, 6H, OCH3), 1.50 (d, 6H, CH3) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 162.06 (d, 4JP,C = 2.26 Hz), 139.78 (d, 4JP,C = 4.27 Hz), 133.01 (d, 2JP,C = 11.68 Hz), 129.94 (d, 1JP,C =117.92 Hz), 128.26, 128.16, 127.03, 125.89, 124.69. 124.99 (d, 4JP,C = 5.01 Hz.), 113.22 (d, 3JP,C = 12.57 Hz), 55.27, 24.66 (d) ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3) (cis, trans isomer): δ = 107.21, 105.84 ppm. MS (ESI) = m/z: 855[M-Ag]+.
2.3.6. [Au(PPh 3 )(R 1 PS 2 (OR 2 )] (R 1 : 4-methoxyphenyl and R 2 : (1R-(−)-myrtenyl) 3a
3a was prepared in a similar manner to 1a using AuClPPh3 (0.05 g. 0.10 mmol) and t-butyl ammonium-(1R)-(−)-myrtenyl-4-methoxyphenyldittiophosphonate 3 (0.048 g, 0.10 mmol). Yield: 0.036 g. (43%), m.p.: 76–78°C. [α]58925 = 30.76 (c = 0.065 in THF). C35H37O2SP2Au (812.73 g.mol-1); calcd: C, 51.72; H, 4.59; S, 7.89%, found: C, 51.01; H, 5.22; S, 6.69%. IR(cm-1): 691 (νasym PS2) and 565 (νsym PS2). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δ = 7.99 (dd, 2H, 3JP.H = 13.84 Hz, 3JH.H = 8.76 Hz), 7.41-7.19(br, 15H, ), 6.75 (dd, 2H, 3JH,H = 8.79 Hz, 3JP,H = 2.96 Hz), 5.49 (t, H, CH), 4.52 (q, H, OCH2), 3.71 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.25 - 078 (br, 12H, myrtenyl) ppm. 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ = 161.56 (s, 4JP,C = 3.32 Hz), 144.22 (d, 3JP,C = 9.87 Hz), 134.37(d, 1JP.C = 121.39 Hz), 132.29 (d, 2JP,C =13.50 Hz), 131.75, 129.52, 128.94, 120.26, 113.25 (d, 3JP.C = 15.47 Hz), 66.96 (d, 2JP,C = 6.27 Hz), 55.34, 43.32, 40.86, 38.10, 31.20, 26.19, 21.20 ppm. 31P NMR (CDCl3): δ = 100.60 (PS2), 37.29 (PPh3) ppm.
Synthesis of [O,O’-(Bornyl) 2 PS 2 ]Au 2 4a
Compound 4a was prepared in a similar manner to 1b using 4 (0.075 g, 0.155 mmol) and Au(tht)Cl (tht = tetrahydrothiophene) (0.05 g, 0.155 mmol) in THF(20 mL). Yield: 0.065 g (% 70), m.p. 212°C. Elemental analysis calculated for C40H68O4P2S4Au2(1197.10 g/mol): C, 40.67; H, 5.68; S, 10.68; Found C, 40.13; H, 5.72; S, 10.71. IR(cm-1): 644(νasym PS2) and 543(νsym PS2). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 4.95 (br, t, 2H), 2.43 (br, t, 2H), 1.79(br, s, 4H), 1.44(t, 4H, 3JH,H = Hz), 1.30(br, t, 4H), 0.99(s, 6H, 2xCH3), 0.93(s, 6H, 2×CH3), 0.89(s, 6H, 2xCH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 49.94, 47.55, 47.95, 37.35, 30.05, 27.96, 26.86, 19.91, 18.93, 13.71. 31P-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 102.19(s). MS (ESI): m/z 999.5 [M-Au]+, 967.5[M-AuS]+.
Conclusion
The new chiral phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate ligands were synthesized and were then utilised in the preparation of gold(I) and silver(I) phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate or S-donor with phosphine complexes. If the phosphorus-1,1-dithiolate ligands carefully utilised in the preparation of gold(I) complexes, those type compounds can be improvement of the collecting metallic gold or silver from the minerals. We hope that this study will extend the unexplored area in phosphoro-1,1-dithiolate chemistry.
Authors’ information
Part of M.Sc. of S. Solak.
References
Burn AJ, Gosney I, Warrens CP, Wastle JP: Phosphorus-31 NMR investigation of the heterogeneous hydrolytic decomposition of zinc(II) bis(O, O-dialkyl dithiophosphate) lubricant additives. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1995, 2: 265-
Contarini S, Tripaldi G, Ponti G, Lizzit S, Baraldi A, Paolucci G: Surface investigation of lubricant-metal interactions by synchrotron photoemission spectroscopy. Appl Surf Sci. 1997, 108: 359-10.1016/S0169-4332(96)00678-2.
Fuller M, Yin Z, Kasrai M, Bancroft GM, Yamaguchi ES, Ryason PR, Willermet PA, Tan KH: Chemical characterization of tribochemical and thermal films generated from neutral and basic ZDDPs using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Tribol Int. 1997, 30: 305-10.1016/S0301-679X(96)00059-X.
Ma Q, Wang X-Y, Chen Q, Leung WH, Zhang QF: Dinuclear ruthenium complexes containing tripodal dithiophosphonate ligands. Inorg Chimica Acta. 2011, 378: 148-10.1016/j.ica.2011.08.044.
Karakus M: Synthesis and Characterization of Chiral Gold (I) Phosphine Complexes with New Dithiophosphorus Ligands. Phosphorus Sulfur. 2011, 186: 1523-10.1080/10426507.2010.521214.
Karakus M, Lonnecke P, Hildebrand M, Hey-Hawkins E: Heterobimetallic Nickel(II) Complexes of Ferrocenyldithiophosphonates. Molecular Structures of [{FcP(OR)S2}2Ni] [Fc = Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5), R = Et, Pri, Bus, Bui]. Z Anorg Allg Chem. 2011, 637 (7–8): 983-
Solak S, Karakus M, Tercan B, Hökelek T: Triethylammonium (S)-(−)-O-[1-(2- naphthyl)ethyl] (4-methoxyphenyl)- dithiophosphonate. Acta Crystall Sec E-Structure Reports Online. 2011, 67: o1260-10.1107/S1600536811015820.
Van Zyl WE: Dithiophosphonates and related P/S-type ligands of group 11 metals. Comments on Inorganic Chem. 2010, 31: 13-10.1080/02603590903510474.
Van Zyl WE, Lopez-de-Luzuriaga JM, Mohamed AA, Staples RJ, Fackler JP: Dinuclear gold(I) dithiophosphonate complexes: Synthesis, luminescent properties, and X-ray crystal structures of [AuS2PR(OR')]2(R = Ph, R' = C5H5; R = 4-C6H4OMe, R' = (1S, 5R, 2S)-(−)-menthyl; R = Fc, R' = (CH2)2O(CH2)2OMe). Inorg Chem. 2002, 11 (17): 4579-
Van Zyl WE, Staples RJ, Fackler JP: Dinuclear gold(I) dithiophosphonate complexes: formation, structure and reactivity. Inorg Chem Commun. 1998, I: 51-
Pollnitz A, Silvestru A, Gimeno MC, Laguna A: New gold(I) and silver(I) complexes with organophosphorus ligands with SPNSO skeleton. Crystal and molecular structures of monomeric [Au{(SPPh2)(O2SR)N}(PPh3)] (R = Me, C6H4Me-4) and dimeric [Ag{(SPPh2)(O2SPh)N}(PPh3)]2 · 2CH2Cl2]. Inorg Chimica Acta. 2010, 363: 346-10.1016/j.ica.2009.10.022.
Liu SL, Wang XY, Duan T, Leung WH, Zhang QF: Hydrolysis and coordination behavior of ferrocenyl-phosphonodithiolate: Synthesis and structure of Cu4[FcP(OCH3)(μ-S)(μ3- S)]4 [Fc = Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5)]. J Mol Struct. 2010, 964: 78-10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.11.014.
Alphia RG, Safin DA, Gimadiev TR, Pinus MV: Complexes of podand-containing bis(dithiophosphonate)ligands with cobalt(II), nickel(II) and cadmium(II):recognation of CH2Cl2. Transititon Met Chem. 2008, 33: 921-10.1007/s11243-008-9133-4.
Arsanious MHN, Maigali SS, Boulos LS: Scope and limitation f the reaction of benzocycloalkanone oximes with Lawesson’s reagents. Phosphorus Sulfur. 2010, 185: 57-10.1080/10426500802713242.
Muniz J, Sansores LE, Martinez A, Salcedo R: Electronic structure and luminescence of [AuS2PPh(OCH2CH = CH2)](2) complex. Theochem. 2007, 820: 141-10.1016/j.theochem.2007.06.019.
del Herna´ndez-Galindo MC, Jancik V, Moya-Cabrera MM, Toscano RA, Cea-Olivares R: 2D hydrogen bond networks in the crystals of [(NH4 center dot H2O)(2)][(RO)(Fc)P(S)(2)](2) (R = 3-(BzO)-Bz, 4-(n-Bu)-Bz, Bz = benzyl). J Organomet Chem. 2007, 692: 5295-10.1016/j.jorganchem.2007.08.014.
Karakus M: Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Organothiophosphorus Compounds: X-ray Crystal Structure of H3COC6H4P(OC2H4S)(S) Synthesized by a New Method. Z Anorg Allgs Chem. 2006, 632 (8–9): 1549-
Foreman RSTJ, Slawin AMZ, Woollins JD: 2,4-Diferrocenyl-1,3,dithiadiphosphetane 2,4-disulfide; structure and reactions with catechols and [PtCl2(PR3)2] (R = Et or Bu). J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. 1996, 3653-
Foreman MRSJ, Slawin AMZ, Woollins JD: The reaction of dithiadiphosphetane disulfides with dienes, alkenesand thioaldehydes. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. 1999, 1175-
Gray IP, Milton HL, Slawin AMZ, Woollins JD: Synthesis and Structure of [Fc(RO)PS2]- Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2003, 3450-
Gray IP, Milton HL, Slawin AMZ, Woollins JD: Synthesis and Structure of [An(RO)PS2]- Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2004, 2477-
Maspero A, Kani I, Mohammed AA, Omary MA, Fackler RJ: Syntheses and Structures of Dinuclear Gold(I) Dithiophosphonate Complexes and the Reaction of the Dithiophosphonate Complexes with Phosphines: Diverse Coordination Types. Inorg Chem. 2003, 42: 5311-10.1021/ic034114y.
Karakus M, Aydogdu Y, Celik O, Kuzucu V, Ide S, Hey-Hawkins E: Synthesis, Molecular Structure, Optical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Zwitterionic Ferrocenyldithiophosphonates. Z Anorg Allg Chem. 2007, 633: 405-10.1002/zaac.200600319.
Haiduc I, Mezei G, Micu–Semeniuc R, Edelman FT, Fisher A: Differing Coordination Modes of (O-Alkyl)-p-Ethoxyphenyldithiophosphonato Ligands in Copper(I), Silver(I) and Gold(I) Triphenylphosphine Complexes. Z Anorg Allg Chem. 2006, 632: 295-10.1002/zaac.200500356.
Albano VG, Aragoni MC, Arca M, Castellari C, Demartin F, Isaia F, Lippolis V, Loddo L, Verani G: An unprecendented example of a cis –phosphonodithioato nickel(II) complex built by an extensive hydrogen bonding supramolecular network. 2002, Commun: Chem, 1170-
Santana MD, Garcia G, Navarro CM, Lozano AA, Perez J, Garcia L, Lopez G: Dithiophosphate and dithiophosphonate complexes of pentacoordinate nickel(II) containing the macrocycle 2,4,4-trimethyl-1,5,9-triazacyclododec-1-ene ([12]aneN(3)-mc1) or its 9- methyl derivative ([12]aneN(3)-mc2). Crystal structures of [Ni([12]aneN(3)- mc1){S2P(OEt)(2)}][PF6] and [Ni([12]aneN(3)-mc1){S2P(p-CH3OPh)((OPr)-Pr-i)}][PF6]. Polyhedron. 2002, 21: 1935-10.1016/S0277-5387(02)01080-X.
Karakus M, Alpoguz HK, Kaya A, Acar N, Gorgulu AO, Arslan M: A Kinetic Study of Mercury(II) Transport Through A Membrane Assisted by New Transport Reagent. Chem Cent J. 2011, 5: 45-10.1186/1752-153X-5-45.
Aragoni MC, Arca M, Devillanova FA, Ferraro JR, Isaia F, Lelj F, Lippolis V, Verani G: An experimental and theoretical approach to phosphonodithioato complexes: molecular orbital analysis by hybrid-DFT and EHT calculations on trans-bis[O-alkyl-phenylphosphonodithioato]NiII, and vibrational assignments. Can J Chem. 2001, 79: 1483-10.1139/v01-163.
Karakus M, Lönnecke P, Hey-Hawkins E: Zwitterionic ferrocenyldithiophosphonates: the molecular structure of [FcP(S)S(OCH2CH2NH2Me)] [Fc = Fe(η5-C5H4)(η5-C5H5)]. Polyhedron. 2004, 23: 2281-10.1016/j.poly.2004.07.003.
Baker MV, Barnard PJ, Berners-Price SJ, Brayshaw SK, Hickey JL, Skelton BW, White AH: Synthesis and structural characterisation of linear Au(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: New analogues of the Au(I) phosphine drug Auranofin. J Organomet Chem. 2005, 690: 5625-10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.07.013.
Ohta H, Kita M, Kanno H, Kojima M: Optically-active tris(O, O′-dialkyl dithiophosphato-S, S′)Chromium(III) complexes. Isolation ofdiastereoisomers and isomerization reactions. Inorg Chim Acta. 2000, 311: 75-10.1016/S0020-1693(00)00307-8.
CrysAlis Pro: Data collection and data reduction package, Agilent Technologies including the program SCALE3 ABSPACK for empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics. 2006, : Varian, Inc
Sheldrick GM: SHELX includes SHELX-97, SHELXS-97. Acta Cryst. 2008, A6 (4): 112-
Brandenburg K: DIAMOND 3. Bonn, Germany: Crystal Impact Gbr
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Turkish Council of Research and Technology, TUBITAK (Grant no: 107T817) and Pamukkale University (Grant nos: 2009FBE020 and 2010FBE043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MK has coordinated the experimental work, characterized the structure of the all compounds and wrote the manuscript. SS synthesized the compounds and measured the IR spectra. CA synthesized and obtained the single crystals of the compound 4. PL carried out X-ray studies. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Solak, S., Aydemir, C., Karakus, M. et al. Novel Gold(I) and Silver(I) Complexes of Phosphorus-1,1,-dithiolates and Molecular Structure of [O,O’-(Bornyl)2PS2]H3NC(CH3)3. Chemistry Central Journal 7, 89 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-7-89
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-7-89