Abstract
Background
Hox genes encode master regulators of regional fate specification during early metazoan development. Much is known about the initiation and regulation of Hox gene expression in Drosophila and vertebrates, but less is known in the non-arthropod invertebrate model system, C. elegans. The C. elegans Hox gene lin-39 is required for correct fate specification in the midbody region, including the Vulval Precursor Cells (VPCs). To better understand lin-39 regulation and function, we aimed to identify transcription factors necessary for lin-39 expression in the VPCs, and in particular sought factors that initiate lin-39 expression in the embryo.
Results
We used the yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) method to screen for factors that bound to 13 fragments from the lin-39 region: twelve fragments contained sequences conserved between C. elegans and two other nematode species, while one fragment was known to drive reporter gene expression in the early embryo in cells that generate the VPCs. Sixteen transcription factors that bind to eight lin-39 genomic fragments were identified in yeast, and we characterized several factors by verifying their physical interactions in vitro, and showing that reduction of their function leads to alterations in lin-39 levels and lin-39::GFP reporter expression in vivo. Three factors, the orphan nuclear hormone receptor NHR-43, the hypodermal fate regulator LIN-26, and the GATA factor ELT-6 positively regulate lin-39 expression in the embryonic precursors to the VPCs. In particular, ELT-6 interacts with an enhancer that drives GFP expression in the early embryo, and the ELT-6 site we identified is necessary for proper embryonic expression. These three factors, along with the factors ZTF-17, BED-3 and TBX-9, also positively regulate lin-39 expression in the larval VPCs.
Conclusions
These results significantly expand the number of factors known to directly bind and regulate lin-39 expression, identify the first factors required for lin-39 expression in the embryo, and hint at a positive feedback mechanism involving GATA factors that maintains lin-39 expression in the vulval lineage. This work indicates that, as in other organisms, the regulation of Hox gene expression in C. elegans is complicated, redundant and robust.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hox genes encode evolutionarily conserved homeodomain-containing transcription factors that pattern cells and tissues along the anterior–posterior body axis during metazoan development (for review, see [1, 2]). Hox proteins perform this function by serving as master regulators of expression of batteries of genes that impart identity to a cell [3, 4], and the precise regulation of Hox protein activity is therefore vital for proper development. Due to their central and conserved role in regional identity and fate specification during metazoan development, the mechanisms underlying the initiation, maintenance and modulation of Hox gene expression have been intensively studied [5–8]. In Drosophila, an elaborate network of maternally supplied and zygotically expressed transcription factors act to initiate Hox gene expression properly in the syncytial early embryo, while in the cellularized vertebrate embryo, secreted signaling molecules and growth factors are employed to coordinate precise Hox gene expression in time and space [9, 10]. In both vertebrates and Drosophila, once Hox gene expression is initiated, it is maintained by the Trithorax and Polycomb groups of chromatin regulatory proteins [11, 12], and can be further modulated by extracellular signaling pathways, Hox protein autoregulation and cross-regulation, and other mechanisms [5, 13].
As in other metazoans, Hox genes are essential during the development of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans[14]. C. elegans has only six Hox genes, present in a dispersed cluster [15, 16]. Three Hox genes, ceh-13, nob-1, and php-3, are required for proper embryonic development [17–19]. The other three Hox genes, lin-39, mab-5, and egl-5, appear to be required only during post-embryonic development, however their expression begins in the embryo [20–22]. Very little is known about the initiation of Hox gene regulation in C. elegans in the embryo [23], although subsequent regulation of Hox gene expression in larval development by Polycomb and Trithorax-related proteins, signaling pathways, other transcription factors, microRNAs, and Hox proteins themselves, have all been noted [12, 23–40]. Elucidating the mechanisms by which Hox gene expression is initiated and regulated in nematodes will broaden our understanding of this important class of developmental regulators across a larger range of animal phyla, giving us further insight into their use during the evolution of animal diversity and their function in gene regulatory networks controlling pattern formation.
Our laboratory and others have studied the function of the Hox gene lin-39 during nematode larval development, in particular during formation of the vulva, which is part of the hermaphrodite egg-laying apparatus. Vulval development begins in the first larval stage (L1) when the twelve ventral hypodermal blast cells, P1–P12 (P cells), divide to generate posterior daughters known as Pn.p cells [41]: the central six Pn.p cells, P3.p–P8.p, become Vulval Precursor Cells (VPCs) [42]. During the third larval stage (L3) the action of Wnt, Ras and Notch extracellular signaling pathways induces the VPCs to adopt distinct cell fates in the pattern 3°-3°-2°-1°-2°-3°, where the cells P5.p - P7.p adopt 1° and 2° (vulval) fates and divide to generate 22 cells that form the vulval opening, while P3.p, P4.p and P8.p adopt the non-vulval 3° fate, which is to divide once and fuse with the surrounding syncytial hypodermis (reviewed in [43, 44]). The Hox gene lin-39 encodes a Deformed/Sex combs reduced ortholog expressed in the midbody region, including the six VPCs [20, 22]. lin-39 acts twice during vulval development. lin-39 is first required to generate the VPCs; in lin-39 null mutants, the VPCs fuse with the hypodermis during the L1 stage, causing a Vulvaless (Vul) phenotype [20, 22]. Little is known about the regulation of lin-39 expression at this time in development. lin-39 is also required at the time of VPC fate specification in the L3; loss of lin-39 activity at this time leads to defects in VPC fate specification [28, 45]. At this later time, LIN-39 acts downstream of RTK/Ras and Wnt extracellular signaling pathways [26, 28, 46, 47].
Trans-acting factors regulating lin-39 expression have been identified previously using a variety of methods including forward and reverse genetic analysis, evolutionary conservation, and transgenic reporter analysis. Trans-acting factors regulating lin-39 expression during vulval development include the RTK/Ras pathway transcriptional effectors LIN-1 and LIN-31 [28, 46–48], the Gli family member TRA-1 which acts downstream from the sex determination pathway [37], the zinc finger protein SEM-4 [49], the novel protein LIN-25 [47], several chromatin regulators [25, 32, 34, 48, 50], and LIN-39 itself [28, 47]. Direct binding to sites within the lin-39 genomic region has been established in the case of LIN-1 (and LET-418, with which it interacts), LIN-31, LIN-39 and TRA-1 [37, 46–48].
We previously undertook to identify cis-acting sites regulating lin-39 expression [47]. Due to the large size of the lin-39 genomic region (~28 kb) we inserted fragments of lin-39 genomic DNA upstream of an enhancerless GFP reporter. By that method, we identified three functional elements: a 340 bp upstream fragment (JW3.9) that directs expression in P cells in the embryo and in their larval descendants including the VPCs, a 247 bp site from the first lin-39 intron that directs expression in larval ventral cord neurons, and a 1.3 kb promoter fragment (JW5) that drives expression in P6.p at the time of vulval induction. Expression from the last element is dependent on Ras pathway function and we showed that LIN-1, LIN-31 and LIN-39 directly bind this cis-regulatory module. Using an alternative approach, Kuntz et al. used phylogenetic analysis to identify a number evolutionarily-conserved regions in the lin-39 genomic region, and showed that several of these sites also drove expression in certain cells or tissue when inserted upstream of an enhancerless GFP reporter [51]. These approaches both require that the site in question be able to mediate proper transcription activation of the reporter gene in vivo, and this requirement may lead to false negative results. To circumvent this issue, here we use the yeast one-hybrid assay, in which transcription factors that directly bind to a site of interest are identified, and then the function of these factors in gene regulation in vivo can be assayed [52].
In our previous analysis of the lin-39 genomic region, we identified a number of short DNA sequences in the lin-39 region that were strongly conserved between C. elegans and two other nematode species ([47], Supplemental material). Starting with these evolutionarily conserved elements and the 340 bp JW3.9 fragment, we used manual [53] and robotically-assisted “enhanced Y1H” (eY1H) [54] screens to identify 16 C. elegans transcription factors that bind to specific lin-39 genomic DNA fragments. Seven of these factors were characterized further to determine a role in lin-39 regulation during vulval development. We found that the orphan nuclear receptor NHR-43, the hypodermal fate regulator LIN-26 and the GATA factor ELT-6 positively regulate lin-39 expression in the embryo and may play a role in initiation of lin-39 in the vulval lineage. In the larva, NHR-43, LIN-26, ELT-6, the zinc finger proteins ZTF-17 and BED-3, and the T box factor TBX-9 positively regulate lin-39 expression in the VPCs. Interestingly, we previously showed that the adjacent GATA factor genes egl-18 and elt-6 are downstream targets of LIN-39 in the larva VPCs [55]. Combined with our current result that ELT-6 binds to and regulates lin-39 expression in the embryo, this suggests that EGL-18/ELT-6 and LIN-39 may form a positive feedback loop to initiate and maintain lin-39 gene expression during embryonic and larval life to ensure proper VPC fate specification.
Results
Identification of transcription factors that bind to lin-39genomic regions using yeast one-hybrid screens
We previously identified cis and trans-acting factors that regulate lin-39 expression in response to RTK/Ras signaling in the larval VPCs [47]. To further understand Hox gene lin-39 regulation in C. elegans, we sought to identify transcription factors that bind to and regulate lin-39 expression, with an emphasis on 1) regulation in the vulval precursor cells P3.p - P8.p (VPCs) and their descendants in the larva, and 2) expression in the precursors to the VPCs, the P cells P3 - P8, in the embryo. We used the yeast one-hybrid approach, in which DNA sequences from the gene of interest are used as ‘bait’ to screen for factors that can bind these sequences in yeast leading to activation of reporter gene expression [53]. Previously, in addition to identifying large genomic regions that drove GFP reporter expression in lin-39-expressing cells, we also identified 31 short DNA elements (<50 bp) located upstream, downstream and in introns that are conserved in lin-39 from the species C. elegans, C. briggsae and C. remanei[47] (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Reasoning that some of these evolutionarily conserved regions (ECRs) may be binding sites for transcription factors that regulate lin-39 expression, we used twelve small lin-39 genomic regions (range 150–460 bp) that each encompassed one or more ECRs in yeast one-hybrid screens (Table 1, Additional file 1: Figure S1). We also used the element JW3.9, a 340 bp fragment found 7.4 kb upstream of lin-39 that drives GFP expression in the P cells of the embryo [47], as this fragment may bind factors responsible for initiation of lin-39 expression (Additional file 1: Figure S1). These thirteen DNA fragments, which together represent ~ 13% of the genomic region between lin-39 and its neighboring genes, were used as separate ‘baits’ (Table 1).
We used two yeast one-hybrid assay procedures. One screen was performed by transformation of the thirteen bait strains with a library of 755 plasmids that each express one C. elegans transcription factor fused to the activation domain from the yeast transcription factor GAL4 [53, 56]. Two other screens were performed using a robotically-assisted mating assay in which the thirteen haploid bait strains were mated to a collection of 936 strains, each of which expresses a single C. elegans transcription factor fused to the GAL4 activation domain [54]. Factors identified as positive from the primary screens were retransformed manually and tested a second time; only factors that showed a reproducible interaction in yeast were considered true positives. In total, 18 interactions were found in yeast between 16 transcription factors and eight different fragments (site bound by each factor is shown in parenthesis): NHR-43 (YF1), ALR-1 (YF2), and ZTF-17 (YF4) were identified through the library transformation screen, while 13 factors were identified via the robotically-assisted mating screens: ODR-7, TBX-39 and TBX-40 (YF1); LIN-26 (YF4); TBX-11, TBX-39 and EGL-43 (YF7); FLH-1 and NHR-111 (YF8); TBX-9 and the protein encoded by B0238.11 (YF9); BED-3 and FLH-1 (YF10); DMD-3 and ELT-6 (JW3.9) (Additional file 2: Figure S2 and Additional file 3: Figure S3, Additional file 4: Table S2 and S3, summary in Additional file 4: Table S4).
We describe here our characterization of seven transcription regulators (Table 1) chosen because these factors had either known expression in lin-39-expressing cells or a phenotype affecting a lin-39-regulated process [57], or because our preliminary data showed an effect on lin-39 reporter expression in vivo. For each factor we carried out the following analyses. To validate the yeast interactions we expressed and purified each factor from bacteria and assayed binding to the appropriate sites in vitro (Figure 1, Additional file 5: Figure S6). To determine if these factors regulate lin-39 expression in vivo in the vulval precursor cells during larval life, we reduced function for each transcription factor and examined lin-39 expression using an integrated transcriptional lin-39::GFP reporter (deIs4) that contains 250 kb of genomic DNA around the lin-39 locus [46] (Figures 2 and 3). We also examined lin-39 expression in RNAi-treated and mutant animals at the L3 stage by qRT-PCR (Figure 4). The strain containing the integrated lin-39::GFP reporter was also used to examine the effects of reduced transcription factor activity on lin-39 expression in the embryonic P cells P5 - P8, which divide in the larva to generate lin-39-expressing vulval precursor cells and ventral cord neurons [46] (Tables 2 and 3, Figure 5). Finally, we examined the effect of reduction of factor function in a lin-39-sensitized background on the fusion of the vulval precursor cells at the L2 stage (Table 4). Below we describe our results that show that six of the factors identified in the yeast one-hybrid screens regulate lin-39 expression in the larval vulval precursor cells, while three of them also regulate lin-39 expression in the embryo.
LIN-39 regulators identified in yeast bind to lin-39 promoter regions in vitro . A - F) Gel mobility shift assays with proteins expressed and purified from E. coli. Arrowhead indicates free probe; arrow indicates protein DNA complexes. For each panel, the top line identifies the labeled probe used, the bottom line shows the amount of protein added in each lane; middle lines (panels A, B, D and F) indicate the identity and amount of competitor added. A) NHR-43 binds to YF1 (342 bp). Lanes 3–5 contain cold wild type YF1 as competitor, while lanes 6–8 contain cold YF1 with the TGAC site mutated as competitor; B) ALR-1 binds to ECR2 (40 bp); this binding is competed by wild type ECR2 but not by a scrambled oligonucleotide with the same nucleotide composition (ECR2S); C) ZTF-17 binds to YF4-2 (186 bp) and YF4-4 (110 bp); D) ZTF-17 binding to YF4-2 is competed by YF4-4 but not YF4-3; E) LIN-26 binds to YF4-3-1 (51 bp); F) LIN-26 binding to YF4-3-1 is competed by YF4-3-1 (51 bp) but not YF4-3-2 (52 b); G) Fragment YF4 with ECRs 7–10 is shown above, with smaller subfragments diagrammed below. Shading indicates fragments that were bound by ZTF-17 and/or LIN-26 in yeast one-hybrid assays and in vitro.
Seven transcription factors affect lin-39::GFP expression in the VPCs at early L3 stage. GFP expression in the VPCs P5.p - P8.p from smg-1; deIS4 (lin-39::GFP) animals treated for RNAi of individual transcription factors identified in yeast (panels B - H), or given control RNAi (empty vector; panel A). Early L3 stage animals are shown; anterior is left, ventral is down. These animals also express ajm-1::GFP, which outlines cell junctions of hypodermal cells and the pharynx (bright staining in the anterior seen in most panels). RNAi for lin-26, bed-3, and tbx-9 causes severe embryonic lethal and larva arrest phenotypes, so RNAi for these genes was performed by feeding newly-hatched L1 larvae on RNAi bacterial lawns and examining GFP expression in these same animals at the L3 stage. For all other genes, RNAi treatment was carried out on P0 animals, and their F1 progeny were examined as L3 animals. All pictures were taken under the same exposure.
Seven transcription factors affect lin-39::GFP expression in the VPCs at early L3 stage. smg-1; deIs4(lin-39::GFP) animals were treated for RNAi of individual transcription factors (panels A – G, dark bar), or control RNAi (panels A – G, light bar) as in Figure 2. Early L3 stage animals were photographed at the same exposure, and pixel counts in each VPC were determined using ImageJ (>20 animals for each strain). Bars show mean GFP pixel count in each cell with standard deviation. ‘*’ indicates P-value < 0.05. ‘**’ indicates P-value < 0.001, compared to control animals.
Regulation of lin-39 levels by transcription factors in vivo (qRT-PCR) . A) Decrease in lin-39 transcript levels in nhr-43, lin-26, tbx-9, bed-3 mutant and ztf-17(RNAi) animals. B) Decrease in lin-39 transcript levels when activity of both elt-6 and egl-18 is reduced. C) Increase in lin-39 transcript levels when either elt-6 or egl-18 was overexpressed from the heat shock promoter. All analyses were done on L3 stage animals. The mean values for each genotype were obtained from at least two independent experiments and normalized to the housekeeping gene, gpd-2, as internal standard. The data was analyzed with unpaired t-test compared to the appropriate control. ‘*’ indicates P-value < 0.05.
NHR-43, LIN-26, ELT-6 and EGL-18 are necessary for lin-39::GFP expression in the embryo. A – D) GFP expression in embryos derived from smg-1; deIs4(lin-39::GFP) animals treated for control RNAi (empty vector, panel A) or for RNAi against transcription factor genes B) nhr-43; C) lin-26 or D) elt-6. E – H) GFP expression in embryos carrying pJW3.9::GFP in a wild-type background (E) or in animals carrying mutations in elt-6 (F) or egl-18 (G and H). Embryos shown are at the ‘bean’ stage of embryogenesis (~360 minutes). All photos were taken under identical exposure settings. Note that before the individual P cells interdigitate at the ventral midline, the cells are referred to by their possible fates (i.e., P5/6 L and P5/6R), and there are two GFP-expressing cells on the left side and two on the right.
Orphan nuclear hormone receptor NHR-43 positively regulates lin-39expression in the embryo and larva
The nhr-43 gene encodes an orphan nuclear hormone receptor, and nhr-43::GFP reporter expression is present from late embryo to adult in hypodermis, excretory cells, posterior intestine cells, and two head neurons [58, 59]. In yeast, NHR-43 bound to YF1, a 342 bp fragment located 8.6 kb upstream of lin-39 (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2), and this binding was verified in vitro using NHR-43 protein purified from E. coli (Figure 1A). Some nuclear hormone receptors are known to bind sites containing the sequence TGAC [60], and there is a TGAC site in YF1. While the wild type YF1 sequence competed for NHR-43 binding in vitro, the same YF1 fragment with the TGAC site mutated no longer competed effectively (Figure 1A), suggesting that NHR-43 may bind to YF1 through this putative NHR binding site.
When RNAi was performed on worms carrying the lin-39::GFP transcriptional reporter to reduce nhr-43 function, their progeny showed a decrease in the number of animals expressing wild type levels of GFP in the vulval precursor cells at the L3 stage (Figures 2B and 3A). qRT-PCR on nhr-43(tm1381) mutant animals [57] at the L3 stage also showed a decrease in lin-39 expression compared to control animals (Figure 4A). We also found that fewer embryos derived from hermaphrodites treated with nhr-43 RNAi showed lin-39::GFP expression in P5 - 8 compared to control animals (Figure 5B, Table 2), indicating that nhr-43 positively regulates lin-39::GFP in the embryonic P cells. This embryonic defect could explain the reduction in GFP expression in the VPCs in the larva, however a decrease in lin-39::GFP expression was also observed if nhr-43 RNAi was performed on L1 worms and then the same animals were observed in the L3 stage (51% of nhr-43(L1 RNAi) animals showed wild type expression in all VPCs versus 76% of RNAi control, p < 0.001). In summary, orphan nuclear hormone receptor NHR-43 binds to a site located far upstream of the lin-39 initiation codon, and nhr-43 function is required for wild type levels of lin-39 expression in the embryo and larva in cells that will participate in vulval development.
The Aristaless homolog ALR-1 may regulate larval lin-39expression
alr-1 encodes a factor homologous to the products of the Drosophila aristaless and mouse ARX (aristaless-related) genes, and antibody staining and GFP reporter analysis have shown alr-1 expression in multiple neurons and hypodermal cells from embryo to adult [61, 62]. In yeast, ALR-1 bound to YF2, a 311 bp DNA fragment located 6.4 kb upstream of lin-39 containing the evolutionarily conserved sequence ECR2 (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2). Recently, the modENCODE project identified genomic binding sites for a number of C. elegans transcription factors, including ALR-1, using chromatin immunoprecipitation from larval animals [40, 63]. Examination of this data shows binding of ALR-1 to multiple sites in the lin-39 promoter region, including the ECR2 site. Bacterially expressed ALR-1 protein bound to a 40 bp DNA fragment encompassing ECR2 in vitro, and this binding was not competed by 100 fold excess of an oligonucleotide of the same base composition and length but scrambled sequence (Figure 1B). Therefore, ALR-1 binds a site in the upstream region of lin-39 in both in vitro and in vivo assays.
We did not observe a significant effect of alr-1 RNAi on lin-39 or lin-39::GFP expression in either the embryo or larva in the cells that will give rise to the vulva (Figures 2C, 3B, and 4A, Table 2). However, we did observe an effect of alr-1 RNAi on a lin-39 mediated process in the larval VPCs. During wild type development, the cells P3.p - P8.p are born in the L1 stage and because they express lin-39 they do not fuse with the surrounding hyp7 syncytium as more anterior and posterior Pn.p cells do [20, 22]. Later, in approximately 50% of animals, P3.p can fuse with hyp7 in the L2 stage [42]. Thus wild type animals have either five or six VPCs at the time of vulval induction in the late L2 stage. In lin-39 mutant animals, or in animals in which Wnt signaling is compromised, additional VPCs are seen to adopt this Fused fate [26, 28, 45]. To examine the role of potential lin-39 regulators in this process we used RNAi to reduce their function in a sensitized strain containing the hypodermal junction marker ajm-1::GFP and the temperature sensitive mutation lin-39(n709ts) and examined the fusion of the VPCs at the L2 stage as before [55]. We found an increased number of larva with VPC fusion defects in lin-39(ts) alr-1(RNAi) compared to lin-39(ts) control animals (Table 4). Therefore, although we were unable to detect an effect of loss of ALR-1 function on lin-39 expression in the vulval cells, we did see a weak effect on a LIN-39 dependent process, leaving open its role as an in vivo regulator of lin-39 expression.
The zinc finger protein ZTF-17 positively regulates lin-39expression
ztf-17 encodes a zinc finger transcription factor, and a ztf-17::GFP transcriptional reporter is expressed in head muscle, pharynx, and the ventral nerve cord [64]. In yeast, ZTF-17 bound to YF4, a 372 bp DNA fragment located 2 kb upstream of lin-39 that contains ECRs 7–10 (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2). To identify a smaller ZTF-17 binding region, we divided YF4 into smaller fragments, and showed by one-hybrid assays that ZTF-17 interacts with YF4-4, a 110 bp subfragment that overlaps ECR10 (Figures 1C and E, Additional file 6: Figure S4). in vitro binding and competition assays with bacterially-expressed ZTF-17 protein validated this result, showing that ZTF-17 binds to fragment YF4-4, but not the adjacent fragment YF4-3 Figure 1C and D).
ztf-17 RNAi performed on lin-39::GFP worms caused a decrease in the number of progeny animals showing wild type levels of lin-39::GFP expression in the VPCs, (Figures 2D and 3C), and qRT-PCR analysis of these ztf-17(RNAi) animals showed a statistically significant decrease in lin-39 at the L3 stage (Figure 4A). lin-39::GFP expression in the VPC parent cells, P5 - P8, was not altered in embryos derived from ztf-17(RNAi) mothers (Table 2), suggesting that ZTF-17 may be a larval regulator of lin-39 expression. In summary, in vitro and yeast one-hybrid analyses indicate that the zinc finger protein ZTF-17 binds to a 110 bp fragment located upstream of lin-39, and positively regulates lin-39 expression in the vulval precursor cells during larval life.
LIN-26, which is required for maintenance of hypodermal cell fates, may positively regulate lin-39expression in the embryo and larva
lin-26 encodes a zinc-finger protein which is expressed in all hypodermal cells based on antibody staining [65, 66]. In lin-26 mutants, cell fate transformations from hypodermal to neuronal fate occur in many cells, including the VPCs [65, 66]. LIN-26 also bound to YF4 in the yeast one-hybrid assay (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 7: Figure S5), and further analysis showed an interaction with YF4-3, a 103 bp DNA fragment that is distinct from the fragment bound by ZTF-17 (Figure 1G, Additional file 5: Figure S5). We divided fragment YF4-3 into two smaller fragments, and in vitro DNA binding and competition experiments showed that LIN-26 bound to YF4-3-1, a 51 bp DNA fragment that does not contain an evolutionarily conserved region (Figure 1E and F).
To assay lin-26 regulation of lin-39 expression in vivo, lin-26 RNAi was performed on newly hatched lin-39::GFP larvae and GFP levels in VPCs P5.p-P8.p were examined at the L3 stage in the same animals; this ‘L1 feeding’ was performed because of the embryonic lethal phenotype caused by lin-26 RNAi. lin-26 RNAi caused a weak but significant decrease in expression of lin-39::GFP in P5.p and P6.p at the L3 stage (Figures 2E and 3D), and qRT-PCR performed on lin-26(n156) mutant animals [65] also showed a small but significant decrease in lin-39 at the early L3 stage (Figure 4A). Finally, we investigated lin-26 regulation of lin-39 in the embryo, and found that fewer embryos expressed lin-39::GFP in the P cells from mothers treated with lin-26 RNAi, compared to control embryos (Figure 5C; Table 2). Consistent with effects on lin-39 expression, lin-26(RNAi) performed on newly hatched L1 larvae in a sensitized lin-39 background caused a defect in VPC fusion at the L2 (Table 4). Thus, we have identified a binding site in the lin-39 upstream region for the general hypodermal transcription factor LIN-26, and our results suggest that LIN-26 acts to positively regulate lin-39 expression in both the embryo and larva.
The T-box protein TBX-9 binds in lin-39 intron 2 and positively regulates larval lin-39expression in the VPCs
tbx-9 encodes a T-box transcription factor, and a tbx-9::GFP translational reporter is expressed in lateral and ventral hypodermal cells, intestine and muscle [67]. tbx-9 mutants have a disorganized body shape beginning in the embryo, which was attributed to defects in hypodermal cells and body wall muscles [67]. In yeast, TBX-9 bound to YF9, a 257 bp DNA fragment located in the large second intron of lin-39 that contains ECRs 21–23 (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2), and this binding was recapitulated in vitro with purified TBX-9 protein (Additional file 5: Figure S6). We divided the YF9 fragment into four smaller fragments (A-D), and found that bacterially purified TBX-9 bound best to the 79 bp subfragment C, and that this fragment could also compete for binding of TBX-9 to YF9 (Additional file 5: Figure S6).
To test TBX-9 as a regulator of lin-39 in vivo, tbx-9 RNAi was performed on L1 lin-39::GFP worms, and we observed a decrease in the number of animals with wild type levels of GFP expression in P5.p-P8.p in the same animals at the L3 stage (Figures 2F and 3E). qRT-PCR analysis on tbx-9(ok2473) mutant animals [57] also showed a decrease in lin-39 levels compared to wild type L3 stage worms (Figure 4A), and tbx-9(RNAi) performed in a sensitized lin-39 background caused a defect in VPC fusion at the L2 (Table 4). tbx-9 RNAi treatment did not effect lin-39::GFP expression in the cells P5-P8 in the embryo (Table 2). In summary, we found that TBX-9 may bind multiple sites within a 257 bp fragment from lin-39 intron 2, and TBX-9 acts as a positive regulator of lin-39 expression in the VPCs in the larva.
The Zinc-finger protein BED-3 binds to site in lin-39 intron 2 and positively regulates lin-39expression
bed-3 encodes a BED zinc-finger protein that is expressed in most hypodermal cells, including the seam cells and the progeny of the VPCs at the time of L3/L4 molt [68]. In bed-3 mutants, the granddaughters of P5.p, P6.p and P7.p often fail to divide, which suggested that BED-3 acts late during vulval induction in the terminal divisions of the induced VPCs [68]. In yeast, BED-3 bound YF10, a 319 base pair fragment from the second lin-39 intron that contains ECRs 24–26 (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2). Bacterially-expressed BED-3 protein bound to YF10 in vitro, however, we found that BED-3 protein also bound to several other unrelated DNA fragments, suggesting the purified BED-3 protein may show non-specific binding in vitro (data not shown).
Despite our inability to validate the BED-3 binding result in vitro, we observed that bed-3 RNAi caused a strong decrease in the number of animals with wild type levels of lin-39::GFP expression in P5.p-P8.p at the L3 stage (Figures 2G and 3F), and this decrease was also seen by qRT-PCR analysis on bed-3(sy702) L3 larvae (Figure 4A). Consistent with the decrease in lin-39 expression in vivo, bed-3(RNAi) caused a defect in VPC fusion at the L2 in a sensitized lin-39 background (Table 4). However lin-39::GFP expression did not change in embryos derived from mothers treated for bed-3(RNAi) (Table 2). Therefore, although we could not localize a binding site for BED-3 beyond the lin-39 intron 2 fragment used in the yeast screen, our in vivo data indicate that BED-3 is likely to function as a positive regulator of lin-39 expression in the vulval precursor cells in the larva.
The GATA factor ELT-6 binds to a lin-39enhancer that directs expression in the P cells in the embryo
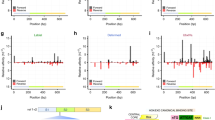
We previously described a 340 bp cis-regulatory element from lin-39 that is sufficient to drive GFP expression in the embryo in P5-P8, cells which divide to generate lin-39 expressing VPCs and neuroblasts in the ventral midbody region (construct pJW3.9, [47]). A 24 bp sequence (S1) in the pJW3.9 enhancer is conserved between C. elegans and C. briggsae, and mutation of this site abolished embryonic expression from the pJW3.9 reporter [47]. Site S1 contains the sequence TGATAA, a predicted binding site for a GATA family transcription factor, which prefer the motif WGATAR [69]. Intriguingly, we found that the transcription factor ELT-6 bound to the pJW3.9 enhancer fragment in our yeast screen (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S2). elt-6 encodes a 367 amino acid GATA transcription factor expressed in certain neurons and hypodermal cells, particularly the seam cells and VPCs [55, 70]. We performed directed yeast one-hybrid assays with eight other C. elegans GATA factors and found that ELT-6 was the only GATA factor that interacted with the pJW3.9 enhancer fragment in yeast (Additional file 4: Table S5). When the GATA site in pJW3.9 was mutated in the yeast reporters, ELT-6 no longer interacted with the DNA fragment in yeast (Figure 6A). ELT-6 protein purified from E. coli bound the S1 site in vitro, but did not bind when the GATA sequence was mutated (Figure 6B). ELT-6 binding to S1 was abolished when competed with excess wild type cold S1 probe, but when the S1 GATA site was mutated, the resulting oligonucleotide (M1) competed less well for ELT-6/S1 binding (Figure 6C). When a second GATA site at the edge of the 40 bp oligonucleotide was also mutated, the ability of the mutated oligonucleotide (M2) to compete was greatly reduced (Figure 6C).
ELT-6 interacts with pJW3.9 through a GATA binding site. A) Yeast strains containing HIS3 and lacZ reporters transformed with empty vector (Control) or ELT-6::GAL4AD plasmids (ELT-6) were diluted and replica plated to control (left), 10 mM 3aminotriazole (3AT, middle), and XGal (right) plates. Reporters had inserts of either JW3.9 (top) or JW3.9 in which GATA binding site S1 was mutated from TGATAA to GGTACC (‘Mut’ bottom). Mutation of the GATA site abolishes the interaction with ELT-6 based on lack of growth on 3AT and lack of blue color on XGal.; B) Increasing concentrations of ELT-6 interact with a 40 bp fragment around GATA site S1 (lanes 2-6). Mutation of the GATA site S1 from TGATAA to GGTACC (M1) abolishes interaction with ELT-6 (lane 8); C) 50 ng of cold wild type site S1 (W) can compete effectively for binding of ELT-6 to S1 (compare lanes 2 and 3). Mutation of GATA site S1 (M1) reduces but does not abolish the ability to compete (lane 4). Mutation of both site S1 and a second GATA site on the oligonucleotide (M2) drastically reduces the ability of the oligonucleotide to compete for ELT-6 binding (lane 5).
To examine regulation of lin-39 expression by ELT-6 in the embryo, we assayed expression of a reporter construct containing the wild type 340 bp element, pJW3.9::GFP, in elt-6(gk723) mutant animals. gk723 is an allele with 457 bp deletion covering the first intron and second exon of elt-6 and is a presumed null mutation [57]. Only 56% of embryos from elt-6(gk723) mutant animals displayed a wild type pattern of pJW3.9::GFP expression, compared to 94% of control embryos (Figure 5F, Table 3). A decrease in the penetrance of expression was also seen in the embryos derived from pJW3.9::GFP mothers treated with elt-6 RNAi (78%; Table 3). We also examined the effect of reduction of elt-6 function on embryonic expression of the large lin-39::GFP reporter that we used to assay other transcription factors. When elt-6 RNAi was performed on lin-39::GFP hermaphrodites, only 82% of embryos showed the wild type level of GFP expression in P5- P8 (Figure 5D, Table 2). Taken together, these results indicate that the GATA factor ELT-6 is necessary for proper expression of lin-39 in P5-P8 in the embryo, most likely via binding to the conserved GATA site in the pJW3.9 enhancer, which was previously shown to be necessary for enhancer driven GFP expression in the embryonic P cells [47]).
The GATA factor EGL-18 also regulates lin-39expression in the P cells in the embryo
The elt-6 open reading frame begins less than 600 bp downstream from the end of another GATA factor gene, egl-18 (see Figure 7B), and these two genes are transcribed dicistronically in some tissues [55, 70]. The DNA binding domains of EGL-18 and ELT-6 are similar, and the two genes show genetic redundancy during fate specification of the hypodermal seam cells and VPCs [55, 70, 71]. In particular, reduction of function for both elt-6 and egl-18 in the larva causes the VPCs to adopt inappropriate cell fates and fuse with the hypodermal syncytium [55], a phenotype also seen with reduction of lin-39 function [28, 45].
Direct transcriptional regulators of lin-39 in the embryo and larva. A) Horizontal lines represent 20 kb of genomic DNA surrounding the lin-39 locus. The lin-39 transcript is shown below the top line, with boxes representing exons. The next horizontal line shows evolutionarily-conserved regions (ECRs; thin vertical lines), the PCR fragments used in the yeast one hybrid assays containing the ECRs (boxes labeled 1–12), and two fragments (pJW3.9 shown, JW5 unlabeled) identified previously using an enhancerless GFP assay [47]. Transcription factors that bind the lin-39 gene are shown above the line (previously reported) or below the line (reported in this work). B) Model for positive feedback loop between egl-18/elt-6 and lin-39. EGL-18 and ELT-6 act via the GATA site in enhancer pJW3.9 to facilitate initiation of lin-39 expression in the embryo, and then LIN-39 acts to positively regulate egl-18/elt-6 expression via the Hox/Pbx binding site in the intron of egl-18[55].
Although EGL-18 did not bind to the 340 bp pJW3.9 fragment in yeast assays (Additional file 4: Table S5), the known functional redundancy of elt-6 and egl-18 and their dicistronic expression in hypodermal cells led us to test for a role for egl-18 in the regulation of lin-39 expression. When the pJW3.9::GFP reporter was moved into two different egl-18 mutant strains, egl-18(ga97) and egl-18(n162)[55], we found that GFP expression in P5 - P8 in the embryo decreased from 94% for control animals to 60% in egl-18(ga97) and 68% in egl-18(n162) (Figure 5G and H, Table 3). These results suggest that EGL-18 is also required for proper lin-39 expression in the embryo. To test for redundant function in lin-39 regulation, we performed RNAi for one gene in the background of a mutant for the other (because the genes are adjacent, we were unable to build egl-18; elt-6 double mutant animals). In neither case was there a significant decrease in the number of embryos showing pJW3.9::GFP expression compared to the egl-18 or elt-6 mutant strain treated with control vector (Table 3). Thus we did not obtain evidence for functional redundancy of elt-6 and egl-18 in regulating pJW3.9::GFP expression in the embryo, even though reduction of function for either gene alone affects embryonic GFP expression.
ELT-6 and EGL-18 also regulate lin-39expression post-embryonically
We also examined whether elt-6 affects lin-39 expression post-embryonically. elt-6 RNAi was performed on lin-39::GFP L1 larvae and we observed GFP expression in the VPCs in the same animals at the L3 stage. A statistically significant decrease in the number of VPCs (P5.p - P8.p) showing a wild type level of lin-39::GFP expression in the VPCs at the L3 stage was seen for elt-6(L1 RNAi) animals (Figures 2H and 3G), indicating that elt-6 also positively regulates lin-39 in the larval VPCs. EGL-18 is also likely to regulate lin-39 expression postembryonically, since qRT-PCR on animals in which both egl-18 and elt-6 function is compromised had lower expression of lin-39 than elt-6(gk723) mutant animals alone (Figure 4B).
To test the hypothesis that lin-39 is a downstream target of ELT-6 and/or EGL-18 in the larva, we asked if overexpression of the GATA factors could increase lin-39 levels. We overexpressed egl-18 and elt-6 using the heat shock promoter and assayed lin-39 levels by qRT-PCR for lin-39 one hour after a single heat shock at the L2/L3 molt. We found that lin-39 levels went up 1.8 fold when ELT-6 was over-expressed, 1.6 fold when EGL-18 was over-expressed, and 1.7 fold when both ELT-6 and EGL-18 were over expressed (Figure 4C), supporting the hypothesis that lin-39 is a downstream target of both ELT-6 and EGL-18 in the larval VPCs.
Discussion
The C. elegans Hox gene lin-39 functions in the midbody region of the developing C. elegans larva, where it is expressed in the P cells and their descendants, including the hermaphrodite vulval precursor cells (VPCs) [14]. During vulval development, lin-39 expression is regulated by Wnt and Ras signaling pathways to facilitate VPC fate specification [26, 28, 45, 46]. To further understand the function of lin-39 in hermaphrodite vulval development, we wish to identify cis-acting sites and trans-acting factors required for initiation, maintenance and regulated expression of lin-39 in the P cells and VPCs. Previously, using an enhancerless GFP reporter assay, we identified a lin-39 enhancer fragment (JW5) that directs expression in the VPC P6.p at the time of vulval induction, which responds to Ras pathway activity, and which is bound by the Ras pathway effectors LIN-1 and LIN-31, as well as by LIN-39 itself [47]. We also identified a lin-39 enhancer (JW3.9) that directs expression in the P cells in the embryo and in their larval descendants (the VPCs and ventral cord neurons), and showed that expression in the embryo depended on an evolutionarily conserved site that contains within it a putative GATA transcription factor binding site.
Here we took a complementary approach to identify additional factors that may regulate lin-39 expression during vulval development. We concentrated on 27 short, evolutionarily conserved regions (ECRs) that we previously identified in the lin-39 gene in C. elegans, C. briggsae and C. remanei[47], on the assumption that some may represent binding sites for phylogenetically conserved transcriptional regulators. We used the yeast one-hybrid technique to identify transcription factors that could bind to DNA fragments containing one or more of these ECRs, circumventing the requirement that the DNA site be sufficient to direct in vivo reporter expression [53]. Having found multiple transcription factors that interact with lin-39 DNA fragments, we looked for effects on endogenous lin-39 transcript levels and on expression from a lin-39::GFP reporter in vivo when the function of these proteins was reduced. Using this approach we identified six transcription factors that bind lin-39 promoter sequences in yeast and in vitro and regulate lin-39 expression and/or function in vivo (Figure 7A, Table 1). Three factors, the orphan nuclear receptor NHR-43, the hypodermal cell fate regulator LIN-26 and the GATA factor ELT-6 positively regulate lin-39 expression in the embryo. In addition to those three factors, we identified the zinc finger proteins ZTF-17 and BED-3 and the T box factor TBX-9 as positive regulators of lin-39 expression in the larval VPCs. Before this work, only four transcription factors were known to directly bind at the lin-39 gene and regulate its expression; LIN-1, LIN-31, LIN-39 and TRA-1, all of which act during larval life (Figure 6B) [37, 47]. Therefore, by this approach combining phylogenetic conservation and yeast one-hybrid screening, we have more than doubled the number of factors known to directly bind to and regulate lin-39, and for the first time we have identified factors that regulate expression of this Hox gene in the embryo.
We believe these factors regulate lin-39 in vivo because we observed a reproducible change in expression of the full length lin-39::GFP reporter and/or a decrease in endogenous lin-39 transcript levels when the function of each of these factors was reduced, and in several cases we observed a phenotype in a LIN-39 regulated process (prevention of VPC fusion). Given their binding to sites from the lin-39 genomic region, the simplest model would be that these factors directly regulate lin-39 expression in the cells we examined (Figure 7A). However, in the current work we did not pursue in vivo binding studies for any of these factors; although published results from the modENCODE project show binding of ALR-1 to the evolutionarily conserved site we identified at the relevant time in development [40, 63]. Additionally, while existing GFP reporters for four of these proteins (TBX-9, NHR-43, ALR-1 and ZTF-17) are turned on in some lin-39-expressing cells, expression in the P cells or VPCs has not been directly observed [57, 59, 61, 64, 67]. GFP reporters suffer from the caveat that all the elements required to recapitulate endogenous expression may not be present, or the expression may be weak or dynamic. However, until we can verify expression of each transcription factor in the embryonic P cells or larval VPCs, and show evidence of binding to the sites we identified in vivo, it remains possible that some of these factors regulate lin-39 indirectly via another transcription regulator, or even act non cell-autonomously on lin-39 expression. The strongest case for direct regulation can be made for BED-3, which regulates lin-39 expression during larval life, and for LIN-26 and ELT-6, which regulate lin-39 expression in the embryonic P cells.
BED-3
bed-3 encodes a 599 amino acid zinc finger protein with a BED DNA binding domain, and bed-3 mutants show an Egl- laying (Egl) defective phenotype and defects in the terminal cell divisions of the descendants of the VPCs [68]. An intronic enhancer element from bed-3 directs GFP expression in VPC descendants, leading to the hypothesis that BED-3 functions in the terminal cell divisions of vulval cells during vulval induction [68]. We found that bed-3 (RNAi) showed the strongest effect on full length lin-39::GFP expression in the VPCs; in wild type animals the VPCs P5.p - P8.p showed lin-39::GFP expression 89% of the time (averaged over all four cells), while in bed-3 (RNAi) animals these cells showed GFP expression only 37% of the time. This suggests that BED-3 could be acting at an earlier stage in vulval development. Consistent with this, we observed that the bed-3 enhancer::GFP reporter does show expression in the VPCs before they divide (Additional file 8: Figure S7), which would be consistent with BED-3 acting upstream of lin-39 in the VPCs themselves. Therefore, although we could not verify BED-3 binding to the YF10 site in vitro with purified protein, we believe BED-3 is likely to be a positive regulator of lin-39 in the larval VPCs before vulval induction, as well as functioning in the subsequent cell division of their progeny, as previously reported [68].
LIN-26
LIN-26 is a 438 amino acid zinc finger transcription factor that shows continuous expression in all embryonic and larval hypodermal cells after their birth [65]. Loss of lin-26 causes hypodermal cells to adopt incorrect cell fates or degenerate after their birth, resulting in embryonic lethality [65, 66]. Ectopic expression of LIN-26 in the early embryo can induce cells to adopt hypodermal-like fates [72]. These results suggest that LIN-26 is required to specify and/or maintain the hypodermal cell fate [65]. lin-26 itself is positively regulated by the GATA factor ELT-1, which is another global regulator of hypodermal cell fate [73]. We found that lin-26 RNAi caused a weak but significant decrease in the expression of the full length lin-39::GFP reporter in the P cells in the embryo; 100% of wild type embryos show GFP expression, compared to 86% of lin-26(RNAi) animals. LIN-26 binds in vitro to a 51 bp sequence located approximately 2 kb upstream of the lin-39 start codon (Figure 6B). Recent data recording reporter gene expression from live developing embryos shows that a lin-26::mCherry transcriptional reporter shows expression in the mothers of the P cells shortly before they divide, at the same time as these cells also begin to show expression of a lin-39::mCherry reporter [74] (Additional file 9: Figure S8). Based on these results, and the known function of LIN-26 in hypodermal cell fate, we propose that LIN-26 positively regulates lin-39 expression in the embryonic P cells, and that the function of this regulation is to aid in initial P cell fate specification and/or to maintain the P cell identity once established.
ELT-6
elt-6 encodes a 367 amino acid GATA family transcription factor. The elt-6 gene is immediately downstream from another GATA factor gene, egl-18 (Figure 7B), and reporter gene experiments suggest elt-6 may be expressed on its own and as part of a dicistronic message with egl-18[70]. These genes are expressed in many cells in the embryo, including the descendants of the MS and AB blastomeres (which give rise to the P cells). In the larva, they are expressed strongly in the lateral hypodermal seam cells and weakly in the VPCs [55, 70]. These two GATA factors share 76% identity in their DNA-binding domains, and have been shown to act redundantly in seam cell development in both the embryo and larva [70, 71]. We previously showed that a 340 bp lin-39 enhancer (JW3.9) directs GFP expression in the embryonic P cells, and a conserved GATA site in the enhancer was necessary for expression [47]. Here we identify the GATA factor ELT-6 as binding to this lin-39 enhancer in yeast and in vitro, and show that binding was dependent on the GATA sequence. elt-6 RNAi showed a decrease in expression of the full length lin-39::GFP reporter in embryonic P cells, and this result was recapitulated with the pJW3.9 reporter in elt-6(gk723) mutant and elt-6(RNAi) embryos. These data suggest that ELT-6 is required for proper expression of the Hox gene lin-39 in the embryonic P cells. Consistent with this, recent data from live recordings of developing embryos shows that elt-6 expression in the mothers of P3 - P8 begins before lin-39 expression is first seen ([74]; Additional file 8: Figure S7). This is the first example to our knowledge of a phenotype caused by reduction of elt-6 function alone. elt-6 RNAi treatment of newly hatched L1 larvae also led to a weak reduction in lin-39::GFP expression in the L3 VPCs, and overexpression of ELT-6 or EGL-18 increased endogenous lin-39 expression in larvae. These results suggest that ELT-6 and/or EGL-18 may continue to positively regulate lin-39 expression in larval life in the VPCs.
Given these results, it is interesting that we previously showed, in collaboration with the Rothmann laboratory, that the egl-18/elt-6 locus was likely to be a downstream target of LIN-39 in the larval VPCs [55]. In that work an 800 bp enhancer element was identified in intron 2 of the egl-18 gene that directs GFP expression in the VPCs and their descendants starting in the L2 stage. This enhancer contains two Hox protein-binding sites that are bound in vitro by LIN-39 and its binding partner CEH-20, and mutation of one site eliminated enhancer-driven GFP expression. Finally, overexpression of egl-18 from the heat shock promoter was able to partially rescue vulval defects in lin-39(RNAi) animals. These data led to the model that egl-18/elt-6 is a downstream target of LIN-39 during vulval development.
Combining these previous data with our current results, our working model suggests LIN-26 and ELT-6 are involved in the initiation of expression of the Hox gene lin-39 in the P cells in the embryo (Figure 7A). lin-39 may also be regulated by EGL-18 at this time, since egl-18 mutants had reduced enhancer-driven GFP expression in the P cells, and EGL-18 protein bound to the pJW3.9 GATA site in vitro (W. Liu and D. Eisenmann, unpublished results). Once the fate of these cells is established, a positive feedback loop is established between ELT-6, acting via the upstream lin-39 enhancer pJW3.9, and LIN-39, acting via the intronic enhancer in egl-18[55]. We propose that this positive feedback loop helps maintain expression of these genes and the fate of these cells and their descendants, the VPCs, during subsequent embryonic and larval development (Figure 7B). Interestingly, we have seen another example of lin-39 feedback regulation. The zinc finger protein SEM-4 was previously shown to positively regulate lin-39 expression in VPCs [49]. We have found that in animals overexpressing either LIN-39 or LIN-39 and CEH-20, sem-4 expression is decreased, suggesting that feedback mechanisms to decrease lin-39 levels when they are elevated may also exist (J. Siegel and D. Eisenmann, unpublished results). Recent chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments from larvae verify binding of tagged LIN-39 protein upstream and in introns of both the egl-18 and sem-4 genes [40, 63].
Conclusion
While much is known about the initiation and regulation of Hox gene expression in Drosophila and vertebrates, less is known outside of these well-studied groups. Our laboratory and others have been studying the expression and function of the Hox gene lin-39 during vulval development in the nematode C. elegans. We used the yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) method to identify 16 transcription factors that interact with specific regions of the lin-39 gene, and further characterized several factors (ALR-1, BED-3, ELT-6, LIN-26, NHR-43, TBX-9 and ZTF-17) showing that their function is required for proper expression of lin-39::GFP reporters and endogenous lin-39 in vivo. This work greatly expands the number of factors known to directly regulate lin-39 expression. Given the known caveats of the yeast one-hybrid technique (absence of specific posttranslational modifications, lack of heterodimeric binding factors), and our emphasis on characterization of factors with known expression or phenotypes in the vulval cells, it is likely that there are additional factors that regulate lin-39 in the embryo and larva that we did not identify in our screens. Given the important role of Hox genes in patterning the developing metazoan body, it is not surprising that Hox gene expression is found to be complicated in those species where it has been examined closely. Our results suggest that expression of the C. elegans Hox gene lin-39 in the P cells and VPCs during vulval development may be regulated by a large number of transcription factors, each making a small contribution to overall lin-39 expression on its own. This is consistent with in vivo data from C. elegans showing that the average worm gene is bound by several transcription factors at one time in larval development [40, 63]. Such a mechanism may ensure a robustness of expression for important developmental regulators like Hox genes. Transcription factors behaving in this manner would also not be identified in genetic screens, since each makes a small overall contribution to lin-39 expression, and feedback mechanisms may exist to compensate for reductions in lin-39 transcript levels. Finally, for the first time, we have identified factors required for lin-39 expression in the embryo (NHR-43, LIN-26 and ELT-6), and our results with EGL-18 and ELT-6, combined with our earlier work on LIN-39 regulation of egl-18/elt-6, hint at a positive feedback mechanism to maintain lin-39 expression in the vulval lineages. The identification of LIN-26, ELT-6, and NHR-43 will help us further characterize the mechanisms for the initiation of Hox gene expression in the nematode, allowing us to make comparisons across metazoan phyla about the mechanisms utilized to regulate this essential class of developmental regulators.
Methods
Yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) assays
Y1H assays were performed using two methodologies: a traditional library ‘transformation’ screen, and a robotically-assisted ‘mating’ screen (“enhanced” Y1H, eY1H). Briefly, each DNA fragment of interest (YF1 - YF12, pJW3.9; see Additional file 1: Figure S1) was cloned into reporter vectors pMW#2 (HIS3) and pMW#3 (LacZ) and the resulting constructs were sequentially integrated into the genome of yeast strains BY5444 and YM4271 to generate thirteen “DNA bait” strains. BY5444 and YM4271 are isogenic for multiple marker genes (MATa ura3-52 his3-200 ade2-101 lys2-801 leu2-3,112 trp1-901 tyr1-501 gal4-Δ512 gal80-Δ538 ade5::hisG) but BY5444 does not mate efficiently with the Yalpha1867 strain used in eY1H assays.
The ‘transformation’ screen was performed as described [53]. Each of the thirteen bait strains (BY5444 background) was transformed with DNA from a commercially-available, C. elegans transcription factor library containing 755 plasmids that each express one C. elegans transcription factor fused in frame with the yeast GAL4 activation domain (Open Biosystems; [75]). Potential interactions were identified as those colonies that turned blue on plates containing X-Gal, and which grew on plates containing a higher concentration of 3-aminotriazole than the control strain grew on. The eY1H screens were performed as described [54]. Each of the thirteen bait strains (both BY5444 and YM4271 backgrounds) was mated with a collection of 936 Y1Halpha1867 strains of the opposite mating type, each of which expresses a single C. elegans transcription factor fused to the GAL4 activation domain. Matings were done in quadruplicate. Potential interactions were identified as those for which at least two of the four colonies exhibited higher expression of both reporters than control yeast, as assayed by blue color and growth on SC-His + 5 mM 3-aminotriazole + X-Gal. For both methods, plasmids were recovered from positive yeast, sequenced to identify the C. elegans gene, and then retransformed back into the appropriate yeast strain to confirm the interaction. From both screens, only those interactions that repeated after retransformation were considered true positives. For the haploid transformation screen, while most baits gave many 3-aminotriazole resistant colonies, only RF1, RF2, RF4 and RF6 gave double positive colonies, and only interactions with NHR-43, ALR-1 and ZTF-17 repeated (all three factors were identified multiple times). For the robotically assisted mating screens, the results are presented in Additional file 4: Table S2-S4.
Genetic methods, alleles and strains
Methods for culture and genetic manipulation of C. elegans were performed as described [76]. Bristol variety (strain N2) of C. elegans was used as wild-type. Experiments were performed at 20°C unless noted. Genes and alleles used in this work are described in [77] and Wormbase [57].
LGII: rrf-3(pk1426), lin-26(n56)
LGIII: tbx-9(ok2473), tbx-9(ms31), unc-119(ed3), pha-1(e2123), lin-39(n709ts)
LGIV: nhr-43(tm1381), bed-3(sy702), bed-3(sy705), elt-6(gk723), egl-18(ga97), egl-18(n162), egl-18(ok290)
LGX: alr-1(ok545)
Strains used:
lin-39::GFP: smg-1(e1228); him-5(e1490); deIs4[lin-39TN::GFP; dpy-20(+); ajm- 1::GFP][46]
nhr-43::gfp: unc-119(ed3); Ex[C29E6.5::gfp; unc-119 (+)][64]
bed-3::GFP: unc-119(ed3); syEx962[pTI06.29; unc-119(+); pBSKSII(+)][68]
pJW3.9::GFP: pha-1(e2123); deEx105[pJW3.9::gfp; pha-1(+); ajm-1::GFP][47]
Strains created for this work:
hs::control: unc-119(ed3); deEx106[pPD49.78; unc-119(+); ajm-1::GFP]
hs::elt-6: unc-119(ed3); deEx107[pLG1; unc-119(+), ajm-1::GFP]
hs::egl-18: unc-119(ed3); deEx108[pPK8; pPK9; unc-119(+); ajm-1::GFP]
hs::egl-18+ hs::elt-6: unc-119(ed3); deEx109 [pLG01; pKK8; pKK9 unc-119 (+); ajm-1::GFP]
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) was performed using the bacterial ‘feeding’ method in which dsRNA for the gene of interest is produced in E. coli strain HT115 and ingested by worms [78]. For feeding of L1 larvae, eggs from strains to be tested were placed on plates without E. coli for at least 18 hours at 20°C, then semi-synchronized L1 larvae were washed off, placed onto plates with the desired HT115 RNAi strain and grown at 20°C to the appropriate stage for scoring. For feeding of P0 animals, L1 stage P0 larvae were put onto the desired RNAi plates, grown to adulthood and their F1 progeny were analyzed at the appropriate stage.
Reporter gene analysis
Worms carrying GFP reporter constructs were analyzed using fluorescence microscopy on a Zeiss Axioplan 2 at the desired developmental time. GFP expression in live animals was captured using a Nikon DXM 1200 digital camera and the ACT-1 program (version 2.12). For deIs4 [lin-39::GFP] and pJW3.9::GFP reporter analysis, the percentage of animals showing an intensity of expression similar to wild-type was determined. For embryonic expression in the cells P5 - P8 the number of embryos showing wild type expression in all four cells was recorded. For larval expression in the cells P5.p - P8.p the intensity of GFP expression in the individual cells at the L3 stage was analyzed using ImageJ [79] and pixel counts for each cell were recorded (after subtraction of background). For each RNAi treatment, at least 20 animals at the L3 stage were photographed, under identical conditions. Expression data was statistically analyzed using an unpaired t-test and both P values and SD were gathered. All deIs4 experiments were carried out in a smg-1 mutant background, in which nonsense-mediated decay is abrogated, leading to more robust reporter expression [46].
Creation of strains expressing EGL-18 and ELT-6 from the heat shock promoter
For heat-shock induced expression of EGL-18, we used the previously described constructs pKK8 and pKK9 in which the entire coding region of egl-18 is inserted into the heat shock promoter vectors pPD49.78 and pPD49.83 respectively [55]. A similar heat shock expression construct, pLG1 (gift of L. Gorrepati), was made by cloning elt-6 genomic DNA from the start to stop codon into vector pPD49.78 (available at [80]; gift of A. Fire, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA). To create transgenic strains, DNA for these constructs was co-injected at 25 ng/ul with unc-119 (+) (100 ng/ul) and ajm-1::gfp DNA (50 ng/ul) [81] into unc-119(ed3) hermaphrodites. For the hs::control strain, the empty heat-shock vector pPD49.78 was used. For the hs::elt-6 + hs::egl-18 strain, pLG1, pKK8 and pKK9 were injected together. Several lines rescued for the Unc phenotype were recovered for each injection and the ones with the highest percentage transmission to progeny were analysed.
Heat shock protocol
Embryos from transgenic animals containing the arrays hs::control, hs::elt-6, hs::egl-18, and hs::elt-6 + hs::egl-18 were collected from hypochlorite-treated gravid animals and hatched on NGM plates without food for at least 18 hours at 20°C, allowing for early L1 stage arrest. Synchronized L1 animals were fed with OP50, grown to the early L3 stage (25 hours post feeding at 20°C), heat shocked at 33°C for 30 minutes, then transferred back to 20°C and collected 30 minutes later for RNA isolation.
RNA isolation
For genes with existing mutant strains, animals were synchronized and grown to early L3 stage (26 hours after feeding at 20°C) to be collected. For genes without existing mutant strains, RNAi was performed on wild type worms. For heat shocked worms, animals were treated with the heat shock program described above. Three biological replicates were performed for each strain and RNA was extracted using the RNAeasy mini kit (Qiagen).
qRT-PCR
The mRNA fraction of extracted total RNA pools was reverse transcribed to cDNA using iScript™ cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad) and used in triplicate qRT-PCR reactions run on an iCycleriQ real-time PCR machine (BioRad). Relative expression ratios were calculated from observed Ct values using the ΔΔCt method [fold change = (Etarget) targetΔCt (control-sample)/ (Eref) RefΔCt (control-sample)[82]] with the house keeping gene gpd-2 as a reference [83]. For mutant strains, N2 animals were the control. For RNAi-treated worms, N2 animals treated with the empty RNAi ‘feeding vector’ (L4440) (available at [80]; gift of A. Fire, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA) were the control. For heat shocked strains, hs::control animals which underwent the heat shock treatment were the control. Three biological replicates were used for each sample. The data was statistically analyzed using unpaired t-test and both P values and SD were gathered with Graphpad software. Primers for gpd-2 and lin-39 were gpd-2FW (CCTCTGGAGCCGACTATGTC), gpd-2RV (TGGCATGATCGTACTTCTCG), lin-39FW (CGGAGATCAGTCACTATGCT) and lin-39RV (CCGCGTGAACCTCCTGTAGT).
Site direct mutagenesis
Site directed mutagenesis was performed using the Quick Change site directed technique following manufacturer’s instructions with the high fidelity DNA polymerase Pfu Turbo (Stratagene). Plasmid DNA was extracted and sequenced to confirm the presence of mutations.
Protein purification
Full length cDNAs for nhr-43, alr-1, ztf-17, lin-26, bed-3, tbx-9, and elt-6 were obtained by PCR amplification from plasmids obtained from the Open Biosystems Y1H library [75] and cloned individually into the plasmid pQE-80 L (Qiagen), which introduces a 6His tag at the N terminus. Plasmids were transformed into E. coli strain BL21, grown to an OD of 0.7 and induced with 1 mM IPTG for 4 hours. For purification of NHR-43, ALR-1, LIN-26, BED-3, TBX-9, and ELT-6, cells were centrifuged, resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mM, NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0 plus protease inhibitors [Sigma]), sonicated for 3 minutes on a Branson Sonifier 450, and centrifuged. The supernatant were collected and loaded on a Ni2+-NTA agarose column (Qiagen), washed five times with wash buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, pH 8.0) and eluted with elution buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, pH 8.0). For purification of ZTF-17, cells were centrifuged, resuspended in sonication buffer (20 mM Tris 7.9, 500 mM NaCl), sonicated and centrifuged. The pellet was resuspended in solubilizing buffer (6 M Guanidine, 20 mM Tris 7.9, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM Imidazole, 5% glycerol plus protease inhibitors [Sigma]). Insoluble material was pelleted by centrifugation and the supernatant was loaded onto a Ni2+-NTA agarose column, washed five times with buffer and eluted with elution buffer 2(6 M Guanidine, 300 mM NaCl, 300 mM Imidazole, 40% glycerol, 20 mM HEPES pH7.5). Protein was diluted to 0.5 mg/ml with elution buffer, dialyzed at 4°C overnight against dialysis buffer (20 mM HEPES pH7.5, 300 mM NaCl, 40% glycerol) and concentrated to 500 ng/ul using a Centricon-10.
The primers for cDNA amplification were:
NHR-43: FW:GCGCGGATCCATTAGCGGCCCATTTCTTCAC/RV: GCGCGCAAGCTTTTAGATTGAGTACAAGTAGGC
ALR-1: FW: GCGCGCATGCCCCGAGTTGAAGAAAGAAGA/RV: GCGCGCAAGCTTTCATGAACTTTCTTCTTTTG
ZTF-17: FW: GCGCGCATGCCTGCGCTACCAGGCGTCCGTG/RV:CGCCCCGGGCTATTTTACTCTAAGAAATA
LIN-26: FW: GCGCGCATGCCTTTCTAAATTTGTGGTAGTC/RV: CGCCCCGGGCTACACCAATGGTTGAGCCAT
TBX-9: FW: GCGCGAGCTCTCCAAAGTCAAAGTATCA/RV: CGCCCCGGGTCAACCAACAATATCAAT
BED-3: FW: GCGCGCATGCCAGACCCAAAGTCCATTT/RV: CGCCCCGGGTCAAACAAGTTGATCAAT
ELT-6: FW: GCGCGCATGCACGTCGTCGAAGGAGGAGATG/RV: CGCCCCGGGTCAGGGAGACTTGCGCTGCTC
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays
For DNA probes larger than 100 bp, DNA fragments were produced by PCR, and 5 pmole was labeled with 32P using T4 polynucleotide kinase (NEB). For DNA probes less than 100 bp, one oligonucleotide was labeled with 32P, then annealed with the complementary oligonucleotide. The labeled double stranded DNA probes were purified using Centri-Spin-20 columns (Princeton Separation), and their activity was measured using a standard scintillation counter. The oligonucleotides used to make EMSA probes are listed in Additional file 5: Figure S6.
DNA binding reaction were set up at 4°C in a volume of 20 ul in final buffer conditions of 50 mM KCl, 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.9, 0.2 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM DTT, 3 mM MgCl2, 1 μg poly(dI–dC), 0.5 μg/ul BSA, 5000 cpm 32P-labeled DNA probe and 0–800 ng of protein. Reactions were incubated 20 minutes on ice, then loaded onto 4.5% (probe size smaller than 100 bp) or 6% (probe size larger than 100 bp) polyacrylamide gels. Gels were run in 0.5xTBE buffer at 150 V for 2.5 hours (4.5% gel), or 220 V for 2 hours (6% gel), dried and analyzed using a Storm 860 phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics). For competitive binding experiments, the indicated concentration of cold competitor was added to the reaction before the protein.
VPC fusion assay in lin-39 sensitized background
For nhr-43, alr-1, ztf-17, tbx-9, elt-6 and control RNAi, P0 lin-39(n709ts); wIs79(ajm-1::GFP) larvae were grown to adulthood at 25°C on the desired RNAi plates, then semi-synchronized F1 progeny were grown to the late L2 stage, when ajm-1::GFP expression in the vulval precursor cells was examined (17 hours post feeding). For bed-3 and lin-26 RNAi, lin-39(n709ts); wIs79(ajm-1::GFP) eggs were hatched in M9 overnight at 20°C, then semi-synchronized L1 larvae were washed off, placed onto plates with the desired HT115 RNAi strain and grown at 25°C to the late L2 stage and scored. At least 25 animals were scored for each RNAi treatment using fluorescence microscopy on a Zeiss Axioplan 2. Wild type animals have either 5 or 6 VPCS with ajm-1::GFP expression at this time (due to fusion of P3.p with hyp7). The percentage of animals lacking ajm-1 :: GFP expression in P4.p - P8.p was determined. The data was statistically analyzed using Fisher’s exact test. 2X2 contingency tables were analyzed using Fisher’s exact test and P values were gathered.
References
Hueber SD, Lohmann I: Shaping segments: Hox gene function in the genomic age. Bioessays. 2008, 30 (10): 965-979. 10.1002/bies.20823.
McGinnis W, Krumlauf R: Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992, 68 (2): 283-302. 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-N.
Foronda D, de Navas LF, Garaulet DL, Sanchez-Herrero E: Function and specificity of Hox genes. Int J Dev Biol. 2009, 53 (8–10): 1404-1419.
Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W: Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat Rev Genet. 2005, 6 (12): 893-904. 10.1038/nrg1726.
Deutsch J: Hox Genes: Studies from the 20th to the 21st Century. Advance in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Volume 689. Edited by: Deutsch J. 2010, Austin, Texas USA: Landes Bioscience
Gellon G, McGinnis W: Shaping animal body plans in development and evolution by modulation of Hox expression patterns. Bioessays. 1998, 20 (2): 116-125. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199802)20:2<116::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-R.
Kmita M, Duboule D: Organizing axes in time and space; 25 years of colinear tinkering. Science. 2003, 301 (5631): 331-333. 10.1126/science.1085753.
Tschopp P, Duboule D: A genetic approach to the transcriptional regulation of Hox gene clusters. Annu Rev Genet. 2011, 45: 145-166. 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163429.
Akam M: The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987, 101 (1): 1-22.
Deschamps J, van den Akker E, Forlani S, De Graaff W, Oosterveen T, Roelen B, Roelfsema J: Initiation, establishment and maintenance of Hox gene expression patterns in the mouse. Int J Dev Biol. 1999, 43 (7): 635-650.
Brock HW, Fisher CL: Maintenance of gene expression patterns. Dev Dyn. 2005, 232 (3): 633-655. 10.1002/dvdy.20298.
Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort M, Leblanc B, Cavalli G: Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007, 128 (4): 735-745. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.009.
Carroll S, Grenier JK, Weatherbee SD: From DNA to Diversity: Molecular Genetics and the Evolution of Animal Design. 2001, Malden, MA: Blackwell Science
Kenyon CJ, Austin J, Costa M, Cowing DW, Harris JM, Honigberg L, Hunter CP, Maloof JN, Muller-Immerglück MM, Salser SJ, Waring DA, Wang BB, Wrischnik LA: The dance of the Hox genes: patterning the anteroposterior body axis of Caenorhabditis elegans. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1997, 62: 293-305.
Aboobaker A, Blaxter M: Hox gene evolution in nematodes: novelty conserved. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003, 13 (6): 593-598. 10.1016/j.gde.2003.10.009.
Aboobaker AA, Blaxter ML: Hox Gene Loss during Dynamic Evolution of the Nematode Cluster. Curr Biol. 2003, 13 (1): 37-40. 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01399-4.
Brunschwig K, Wittmann C, Schnabel R, Bürglin T, Tobler H, Müller F: Anterior organization of the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo by the labial-like Hox gene ceh-13. Development. 1999, 126 (7): 1537-1546.
Van Auken K, Weaver DC, Edgar LG, Wood WB: Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic axial patterning requires two recently discovered posterior-group Hox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000, 97 (9): 4499-4503. 10.1073/pnas.97.9.4499.
Wittmann C, Bossinger O, Goldstein B, Fleischmann M, Kohler R, Brunschwig K, Tobler H, Müller F: The expression of the C. elegans labial-like Hox gene ceh-13 during early embryogenesis relies on cell fate and on anteroposterior cell polarity. Development. 1997, 124 (21): 4193-4200.
Clark SG, Chisholm AD, Horvitz HR: Control of cell fates in the central body region of C. elegans by the homeobox gene lin-39. Cell. 1993, 74 (1): 43-55. 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90293-Y.
Ferreira H, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Emmons S: Patterning of Caenorhabditis elegans posterior structures by the Abdominal-B homolog, egl-5. Dev Biol. 1999, 207 (1): 215-228. 10.1006/dbio.1998.9124.
Wang BB, Muller-Immergluck MM, Austin J, Robinson NT, Chisholm A, Kenyon C: A homeotic gene cluster patterns the anteroposterior body axis of C. elegans. Cell. 1993, 74 (1): 29-42. 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90292-X.
Streit A, Kohler R, Marty T, Belfiore M, Takacs-Vellai K, Vigano M, Schnabel R, Affolter M, Müller F: Conserved regulation of the Caenorhabditis elegans labial/Hox1 gene ceh-13. Dev Biol. 2002, 242 (2): 96-108. 10.1006/dbio.2001.0544.
Salser S, Loer C, Kenyon C: Multiple HOM-C gene interactions specify cell fates in the nematode central nervous system. Genes Dev. 1993, 7 (9): 1714-1724. 10.1101/gad.7.9.1714.
Ch’ng Q, Kenyon C: egl-27 generates anteroposterior patterns of cell fusion in C. elegans by regulating Hox gene expression and Hox protein function. Development. 1999, 126 (15): 3303-3312.
Eisenmann DM, Maloof JN, Simske JS, Kenyon C, Kim SK: The beta-catenin homolog BAR-1 and LET-60 Ras coordinately regulate the Hox gene lin-39 during Caenorhabditis elegans vulval development. Development. 1998, 125 (18): 3667-3680.
Jiang LI, Sternberg PW: Interactions of EGF, Wnt and HOM-C genes specify the P12 neuroectoblast fate in C. elegans. Development. 1998, 125 (12): 2337-2347.
Maloof JN, Kenyon C: The Hox gene lin-39 is required during C. elegans vulval induction to select the outcome of Ras signaling. Development. 1998, 125 (2): 181-190.
Maloof JN, Whangbo J, Harris JM, Jongeward GD, Kenyon C: A Wnt signaling pathway controls hox gene expression and neuroblast migration in C. elegans. Development. 1999, 126 (1): 37-49.
Alper S, Kenyon C: REF-1, a protein with two bHLH domains, alters the pattern of cell fusion in C. elegans by regulating Hox protein activity. Development. 2001, 128 (10): 1793-1804.
Chamberlin HM, Thomas JH: The bromodomain protein LIN-49 and trithorax-related protein LIN-59 affect development and gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 2000, 127 (4): 713-723.
Chen Z, Han M: C. elegans Rb, NuRD, and Ras regulate lin-39-mediated cell fusion during vulval fate specification. Curr Biol. 2001, 11 (23): 1874-1879. 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00596-6.
Ross JM, Zarkower D: Polycomb group regulation of Hox gene expression in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2003, 4 (6): 891-901. 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00135-7.
Zhang H, Emmons SW: The novel C. elegans gene sop-3 modulates Wnt signaling to regulate Hox gene expression. Development. 2001, 128 (5): 767-777.
Li X, Kulkarni RP, Hill RJ, Chamberlin HM: HOM-C genes,Wnt signaling and axial patterning in the C. elegans posterior ventral epidermis. Dev Biol. 2009, 332 (1): 156-165. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.05.567.
Studencka M, Wesolowski R, Opitz L, Salinas-Riester G, Wisniewski JR, Jedrusik-Bode M: Transcriptional repression of Hox genes by C. elegans HP1/HPL and H1/HIS-24. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8 (9): e1002940-10.1371/journal.pgen.1002940.
Szabo E, Hargitai B, Regos A, Tihanyi B, Barna J, Borsos E, Takacs-Vellai K, Vellai T: TRA-1/GLI controls the expression of the Hox gene lin-39 during C. elegans vulval development. Dev Biol. 2009, 330 (2): 339-348. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.04.005.
Yu H, Seah A, Herman MA, Ferguson EL, Horvitz HR, Sternberg PW: Wnt and EGF pathways act together to induce C. elegans male hook development. Dev Biol. 2009, 327 (2): 419-432. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.12.023.
Zhao Z, Boyle TJ, Liu Z, Murray JI, Wood WB, Waterston RH: A negative regulatory loop between microRNA and Hox gene controls posterior identities in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6 (9): e1001089-10.1371/journal.pgen.1001089.
Niu W, Lu ZJ, Zhong M, Sarov M, Murray JI, Brdlik CM, Janette J, Chen C, Alves P, Preston E, Slightham C, Jiang L, Hyman AA, Kim SK, Waterston RH, Gerstein M, Snyder M, Reinke V, Snyder M, Reinke V: Diverse transcription factor binding features revealed by genome-wide ChIP-seq in C. elegans. Genome Res. 2011, 21 (2): 245-254. 10.1101/gr.114587.110.
Sulston JE, Horvitz HR: Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode. Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1977, 56 (1): 110-156. 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90158-0.
Sternberg PW, Horvitz HR: Pattern formation during vulval development in C. elegans. Cell. 1986, 44 (5): 761-772. 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90842-1.
Greenwald I: Development of the Vulva. C elegans II. Edited by: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR. 1997, Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2
Sternberg PW: Vulval development. 2005, WormBook, 1-28.
Clandinin TR, Katz WS, Sternberg PW: Caenorhabditis elegans HOM-C genes regulate the response of vulval precursor cells to inductive signal. Dev Biol. 1997, 182 (1): 150-161. 10.1006/dbio.1996.8471.
Wagmaister JA, Gleason JE, Eisenmann DM: Transcriptional upregulation of the C. elegans Hox gene lin-39 during vulval cell fate specification. Mech Dev. 2006, 123 (2): 135-150. 10.1016/j.mod.2005.11.003.
Wagmaister JA, Miley GR, Morris CA, Gleason JE, Miller LM, Kornfeld K, Eisenmann DM: Identification of cis-regulatory elements from the C. elegans Hox gene lin-39 required for embryonic expression and for regulation by the transcription factors LIN-1, LIN-31 and LIN-39. Dev Biol. 2006, 297 (2): 550-565. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.05.008.
Guerry F, Marti C, Zhang Y, Moroni P, Jaquiéry E, Müller F: The Mi-2 nucleosome-remodeling protein LET-418 is targeted via LIN-1/ETS to the promoter of lin-39/Hox during vulval development in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2007, 306 (2): 469-479. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.03.026.
Grant K, Hanna-Rose W, Han M: sem-4 promotes vulval cell-fate determination in Caenorhabditis elegans through regulation of lin-39 Hox. Dev Biol. 2000, 224 (2): 496-506. 10.1006/dbio.2000.9774.
Chen Z, Han M: Role of C. elegans lin-40 MTA in vulval fate specification and morphogenesis. Development. 2001, 128 (23): 4911-4921.
Kuntz SG, Schwarz EM, DeModena JA, De Buysscher T, Trout D, Shizuya H, Sternberg PW, Wold BJ: Multigenome DNA sequence conservation identifies Hox cis-regulatory elements. Genome Res. 2008, 18 (12): 1955-1968. 10.1101/gr.085472.108.
Reece-Hoyes JS, Walhout AJ: Gene-centered yeast one-hybrid assays. Methods Mol Biol. 2012, 812: 189-208. 10.1007/978-1-61779-455-1_11.
Deplancke B, Dupuy D, Vidal M, Walhout A: A gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid system. Genome Res. 2004, 14 (10B): 2093-2101. 10.1101/gr.2445504.
Reece-Hoyes JS, Diallo A, Lajoie B, Kent A, Shrestha S, Kadreppa S, Pesyna C, Dekker J, Myers CL, Walhout AJ: Enhanced yeast one-hybrid assays for high-throughput gene-centered regulatory network mapping. Nat Methods. 2011, 8 (12): 1059-1064. 10.1038/nmeth.1748.
Koh K, Peyrot SM, Wood CG, Wagmaister JA, Maduro MF, Eisenmann DM, Rothman JH: Cell fates and fusion in the C. elegans vulval primordium are regulated by the EGL-18 and ELT-6 GATA factors – apparent direct targets of the LIN-39 Hox protein. Development. 2002, 129 (22): 5171-5180.
Walhout AJ, Temple GF, Brasch MA, Hartley JL, Lorson MA, van den Heuvel S, Vidal M: GATEWAY recombinational cloning: application to the cloning of large numbers of open reading frames or ORFeomes. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 328: 575-592.
Yook K, Harris TW, Bieri T, Cabunoc A, Chan J, Chen WJ, Davis P, de la Cruz N, Duong A, Fang R, Ganesan U, Grove C, Howe K, Kadam S, Kishore R, Lee R, Li Y, Muller HM, Nakamura C, Nash B, Ozersky P, Paulini M, Raciti D, Rangarajan A, Schindelman G, Shi X, Schwarz EM, Ann Tuli M, Van Auken K, Wang D, et al: WormBase 2012: more genomes, more data, new website. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40 (Database issue): D735-D741.
Sluder AE, Mathews SW, Hough D, Yin VP, Maina CV: The nuclear receptor superfamily has undergone extensive proliferation and diversification in nematodes. Genome Res. 1999, 9 (2): 103-120.
Deplancke B, Mukhopadhyay A, Ao W, Elewa A, Grove C, Martinez N, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Reece-Hoyes J, Hope I, Tissenbaum HA, Mango SE, Walhout AJ: A gene-centered C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network. Cell. 2006, 125 (6): 1193-1205. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.038.
Zilliacus J, Carlstedt-Duke J, Gustafsson J, Wright A: Evolution of distinct DNA-binding specificities within the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994, 91 (10): 4175-4179. 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4175.
Tucker M, Sieber M, Morphew M, Han M: The Caenorhabditis elegans aristaless orthologue, alr-1, is required for maintaining the functional and structural integrity of the amphid sensory organs. Mol Biol Cell. 2005, 16 (10): 4695-4704. 10.1091/mbc.E05-03-0205.
Melkman T, Sengupta P: Regulation of chemosensory and GABAergic motor neuron development by the C. elegans Aristaless/Arx homolog alr-1. Development. 2005, 132 (8): 1935-1949. 10.1242/dev.01788.
Gerstein MB, Lu ZJ, Van Nostrand EL, Cheng C, Arshinoff BI, Liu T, Yip KY, Robilotto R, Rechtsteiner A, Ikegami K, Alves P, Chateigner A, Perry M, Morris M, Auerbach RK, Feng X, Leng J, Vielle A, Niu W, Rhrissorrakrai K, Agarwal A, Alexander RP, Barber G, Brdlik CM, Brennan J, Brouillet JJ, Carr A, Cheung MS, Clawson H, Contrino S, et al: Integrative analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome by the modENCODE project. Science. 2010, 330 (6012): 1775-1787. 10.1126/science.1196914.
Reece-Hoyes J, Shingles J, Dupuy D, Grove C, Walhout A, Vidal M, Hope I: Insight into transcription factor gene duplication from Caenorhabditis elegans Promoterome-driven expression patterns. BMC Genomics. 2007, 8: 27-10.1186/1471-2164-8-27.
Labouesse M, Hartwieg E, Horvitz HR: The Caenorhabditis elegans LIN-26 protein is required to specify and/or maintain all non-neuronal ectodermal cell fates. Development. 1996, 122 (9): 2579-2588.
Labouesse M, Sookhareea S, Horvitz H: The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-26 is required to specify the fates of hypodermal cells and encodes a presumptive zinc-finger transcription factor. Development. 1994, 120 (9): 2359-2368.
Andachi Y: Caenorhabditis elegans T-box genes tbx-9 and tbx-8 are required for formation of hypodermis and body-wall muscle in embryogenesis. Genes Cells. 2004, 9 (4): 331-344. 10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00725.x.
Inoue T, Sternberg P: C. elegans BED domain transcription factor BED-3 controls lineage-specific cell proliferation during organogenesis. Dev Biol. 2010, 338 (2): 226-236. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.005.
Ko LJ, Engel JD: DNA-binding specificities of the GATA transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1993, 13 (7): 4011-4022.
Koh K, Rothman J: ELT-5 and ELT-6 are required continuously to regulate epidermal seam cell differentiation and cell fusion in C. elegans. Development. 2001, 128 (15): 2867-2880.
Gorrepati L, Thompson KW, Eisenmann DM: C. elegans GATA factors EGL-18 and ELT-6 function downstream of Wnt signaling to maintain the progenitor fate during larval asymmetric divisions of the seam cells. Development. 2013, 140 (10): 2093-2102. 10.1242/dev.091124.
Quintin S, Michaux G, McMahon L, Gansmuller A, Labouesse M: The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-26 can trigger epithelial differentiation without conferring tissue specificity. Dev Biol. 2001, 235 (2): 410-421. 10.1006/dbio.2001.0294.
Landmann F, Quintin S, Labouesse M: Multiple regulatory elements with spatially and temporally distinct activities control the expression of the epithelial differentiation gene lin-26 in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2004, 265 (2): 478-490. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.009.
Murray JI, Boyle TJ, Preston E, Vafeados D, Mericle B, Weisdepp P, Zhao Z, Bao Z, Boeck ME, Waterston R: Multidimensional regulation of gene expression in the C. elegans embryo. Genome Res. 2012, 22: 1282-1294. 10.1101/gr.131920.111.
Open Biosystems. [http://www.thermoscientificbio.com/openbiosystems]
Brenner S: The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974, 77 (1): 71-94.
Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR: C. elegans II. 1997, Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Timmons L, Fire A: Specific interference by ingested dsRNA. Nature. 1998, 395 (6705): 854-10.1038/27579.
Image J. [http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/]
Addgene. [http://www.addgene.org]
Mohler WA, Simske JS, Williams-Masson EM, Hardin JD, White JG: Dynamics and ultrastructure of developmental cell fusions in the Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermis. Curr Biol. 1998, 8 (19): 1087-1090. 10.1016/S0960-9822(98)70447-6.
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29 (9): e45-10.1093/nar/29.9.e45.
Hoogewijs D, Houthoofd K, Matthijssens F, Vandesompele J, Vanfleteren JR: Selection and validation of a set of reliable reference genes for quantitative sod gene expression analysis in C. elegans. BMC Mol Biol. 2008, 9: 9-10.1186/1471-2199-9-9.
Expression Patterns in Caenorhabditis. [http://epic.gs.washington.edu]
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Hamza, T. Inoue, K. Koh, J. Rothman, and P. Sternberg for sharing reagents, strains and unpublished information, and members of the Bieberich lab (UMBC) for helpful assistance. We thank Wormbase. Some nematode and yeast strains used in this work were provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center which is funded by the NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440), and by the National BioResource Project of Japan. This work was supported by NIH grants GM65424 to DME and GM082971 to AJMW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Authors’ contributions
JRH carried out all robotically-assisted yeast one hybrid screens. WJL performed all other work. WJL and DME wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12861_2013_773_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Figure S1: lin-39 genomic region and fragments used in yeast one-hybrid screens. The top line shows 26 kb around the lin-39 locus with base locations on chromosome II shown. Two lin-39 transcripts and the upstream microRNA gene mir-231 are diagrammed below. JW1-10 (bottom) are lin-39 genomic regions previously used in reporter gene analysis; those in green drove GFP expression in vivo in lin-39 expressing cells [47]. pJW3.9 (orange box) is a 340 bp subfragment that drove GFP expression in P5 – P8 in the embryo [47]. Thirty-one evolutionarily-conserved regions (ECRs) with >75% identity in the lin-39 gene from three Caenorhabditis species were previously identified [47]. ECRs are shown on the middle line as unlabeled, vertical black lines. Twenty-seven ECRS were grouped into 12 PCR fragments (numbered 1–12; red boxes). The twelve fragments (YF1-12) and pJW3.9 were used as ‘baits’ in Y1H screens. (PDF 99 KB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2: Figure S2: Fourteen transcription factors interact with lin-39 genomic fragments in yeast one-hybrid assays (strain BY5444). Thirteen strains in background BY5444 containing fragments (YF1 - 12, pJW3.9) from the lin-39 genomic region were screened for interactions with C. elegans transcription factors by both the haploid library transformation method, and the robotically-assisted mating method (see Methods). Any positive interactions from primary screens were retested by retransformation of the rescued interacting plasmid back into the appropriate ‘bait’ strain (see Additional file 4: Table S2). Shown here are three-fold serial dilutions of each strain grown on SC–His-Ura-Trp plates with no 3AT (control plates), SC–His-Ura-Trp with 10 mM 3AT, and plates with X-gal. Bait strains transformed with the pDEST-AD empty vector were the ‘Control’. Positive interactions were considered those showing more growth on 3AT and/or more blue color on XGal than the control. Note that the YF8 strain shows considerable self-activation on 3AT, but positive interactions for NHR-111 and FLH-1 are observable on the XGal plates. (PDF 5 MB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Additional file 3: Figure S3: Four transcription factors interact with lin-39 genomic fragments in yeast one-hybrid assays (strain YM4271). Thirteen strains in background YM4271 containing fragments (YF1 - 12, pJW3.9) from the lin-39 genomic region were screened for interactions with C. elegans transcription factors by the robotically-assisted mating method (see Methods). Positive interactions from the primary screen were retested by retransformation of the rescued interacting plasmid back into the appropriate ‘bait’ strain (see Additional file 4: Table S3). Shown here are three-fold serial dilutions of each strain grown on SC–His-Ura-Trp plates with no 3AT (control plates), SC–His-Ura-Trp with 10 mM 3AT, and plates with X-gal. Bait strains transformed with the pDEST-AD empty vector were the ‘Control’. Positive interactions were considered those showing more growth on 3AT and/or more blue color on XGal than the control. (PDF 2 MB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM4_ESM.docx
Additional file 4: Table S1: Sequences of 12 YFs and pJW3.9. Table S2. Yeast one-hybrid screen with strain BY5444 (screen YM2). Table S3. Yeast one-hybrid screen with strain YM4271 (screen YM2). Table S4. Summary of yeast one-hybrid screen results. Table S5. Only GATA factor ELT-6 binds pJW3.9 in yeast. elegans GATA factors. Table S6. Oligonucleotides for EMSA probes. (DOCX 33 KB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM5_ESM.pdf
Additional file 5: Figure S6: TBX-9 binds a 79 bp region in fragment YF9. A) The top line shows fragment YF9 and the location of ECRs 21 – 23. Subfragments A – D are diagrammed below. Shading indicates the fragment bound by TBX-9 in vitro; B) Gel mobility shift assay with TBX-9 protein purified from E. coli and labeled fragment YF9 (lane 2) and competition with subfragments A – D (lanes 3–6). Arrowhead indicates free probe; arrow indicates the protein DNA complex that can be competed by fragment C. Two other bands appear with added TBX-9 protein: the upper band is competed away by all four competing fragments, while the lower band is competed by none of the fragments. The nature of these complexes is unknown, although they are likely to represent non-specific binding by TBX-9 or another protein. C) Gel mobility shift assay with TBX-9 protein and labeled fragment subfragments A – D. The bracket indicates the migration locations of free probes (which differ in size, see panel A). Arrow indicates a complex with TBX-9 and subfragment C. (PDF 110 KB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM6_ESM.pdf
Additional file 6: Figure S4: ZTF-17 binds to fragment YF4-4 in yeast. BY5444 ‘bait’ strains containing subfragments of YF1 (YF4-1 to YF4-4; see Figure 1) were made and transformed with the plasmid encoding ZTF-17::Gal4AD or with the pDEST-AD empty vector as control. Three-fold serial dilutions of each strain grown on SC–His-Ura-Trp plates with no 3AT (control plates), SC–His-Ura-Trp with 10 mM 3AT, and plates with X-gal are shown. Fragment YF4-1 shows strong self-activation on 3AT. Only fragment YF4-4 shows a strong interaction with ZTF-17 on both 3AT and XGal plates. (PDF 2 MB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM7_ESM.pdf
Additional file 7: Figure S5: LIN-26 binds to fragment YF4-3 using yeast. BY5444 ‘bait’ strains containing subfragments of YF1 (YF4-1 to YF4-4; see Figure 1) were made and transformed with the plasmid encoding LIN-26::Gal4AD or with the pDEST-AD empty vector as control. Three-fold serial dilutions of each strain grown on SC–His-Ura-Trp plates with no 3AT (control plates), SC–His-Ura-Trp with 10 mM 3AT, and plates with X-gal are shown. Fragment YF4-1 shows strong self-activation on 3AT. Only fragment YF4-3 shows a strong interaction with LIN-26 on both 3AT and XGal plates. (PDF 2 MB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM8_ESM.pdf
Additional file 8: Figure S7: bed-3::GFP expression in the larval VPCs. Expression from strains carrying syEx962 which contains the bed-3::GFP reporter pTI06.29 [68]. GFP expression is seen in the Pn.p cells in the L1 stage (A) and L2 stage (B), including the VPCs P3.p - P8.p (indicated by white bars). (PDF 152 KB)
12861_2013_773_MOESM9_ESM.pdf
Additional file 9: Figure S8: Expression of transcription factor genes elt-1, elt-3, lin-26 and lin-39 in the ABpra lineage in developing embryos. The images shown are taken directly from the Expression Patterns in Caenorhabditis web site [84]. As described [74], live images were recorded from developing embryos that expressed a histone:mCherry fusion protein driven from the upstream promoter sequences for each of the indicated genes. Expression levels in individual embryonic cells were characterized and diagrammed on the cell lineage chart. An expression scale for all experiments is shown at the top and shows the fluorescence intensity of the reporter construct in the individual cells; time (in minutes) for each experiment is shown along the left. The data shown are from the following experiments: 20080128_elt-1_3.html, 20070817_elt-6_5.html, 20080805_lin-26_5_L1.html and 20071015_lin-39_9. (PDF 158 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WJ., Reece-Hoyes, J.S., Walhout, A.J. et al. Multiple transcription factors directly regulate Hox gene lin-39 expression in ventral hypodermal cells of the C. elegans embryo and larva, including the hypodermal fate regulators LIN-26 and ELT-6. BMC Dev Biol 14, 17 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-14-17
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-14-17