Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia are associated with increased susceptibility to bacterial infections and poor treatment outcomes. This post hoc evaluation of the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) and complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) aimed to evaluate baseline characteristics, efficacy, and safety in patients with and without diabetes treated with ceftolozane/tazobactam and comparators. Ceftolozane/tazobactam is an antibacterial with potent activity against Gram-negative pathogens and is approved for the treatment of cIAI (with metronidazole) and cUTI (including pyelonephritis).
Methods
Patients from the phase 3 ASPECT studies with (n = 245) and without (n = 1802) diabetes were compared to evaluate the baseline characteristics, efficacy, and safety of ceftolozane/tazobactam and active comparators.
Results
Significantly more patients with than without diabetes were 65 years of age or older; patients with diabetes were also more likely to weigh ≥75 kg at baseline (57.1% vs 44.5%), to have renal impairment (48.5% vs 30.2%), or to have APACHE II scores ≥10 (33.8% vs 17.0%). More patients with diabetes had comorbidities and an increased incidence of complicating factors in both cIAI and cUTI. Clinical cIAI and composite cure cUTI rates across study treatments were lower in patients with than without diabetes (cIAI, 75.4% vs 86.1%, P = 0.0196; cUTI, 62.4% vs 74.7%, P = 0.1299) but were generally similar between the ceftolozane/tazobactam and active comparator treatment groups. However, significantly higher composite cure rates were reported with ceftolozane/tazobactam than with levofloxacin in patients without diabetes with cUTI (79.5% vs 69.9%; P = 0.0048). Significantly higher rates of adverse events observed in patients with diabetes were likely due to comorbidities because treatment-related adverse events were similar between groups.
Conclusions
In this post hoc analysis, patients with diabetes in general were older, heavier, and had a greater number of complicating comorbidities. Patients with diabetes had lower cure rates and a significantly higher frequency of adverse events than patients without diabetes, likely because of the higher rates of medical complications in this subgroup. Ceftolozane/tazobactam was shown to be at least as effective as comparators in treating cUTI and cIAI in this population.
Trial registration
cIAI, NCT01445665 and NCT01445678 (both trials registered prospectively on September 26, 2011); cUTI, NCT01345929 and NCT01345955 (both trials registered prospectively on April 28, 2011).
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In recent decades, the incidence and prevalence of diabetes have increased rapidly [1], with recent studies estimating that 422 million people worldwide are affected [2]. In addition to the burden directly imposed by the condition, patients with diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia have been shown to have increased susceptibility to bacterial infections and poor outcomes, including increased risk for hospitalization, reduced cure rates, and increased mortality due to infection [3, 4]. Furthermore, patients with diabetes commonly have comorbidities that may further affect their response to treatment; for example, both cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease appear to be predictors of lengthened hospital stay and infection-related mortality [5,6,7].
Ceftolozane/tazobactam, an antibacterial with potent activity against Gram-negative pathogens [8, 9], is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of patients with complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) when used in combination with metronidazole and for the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis [10, 11]. Ceftolozane/tazobactam was studied in a large phase 3 clinical trial program (Assessment of the Safety Profile and Efficacy of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam [ASPECT]) in patients with cIAI or cUTI. In ASPECT-cIAI (NCT01445665 and NCT01445678), ceftolozane/tazobactam plus metronidazole was noninferior to meropenem in patients with cIAI [12]. In ASPECT-cUTI (NCT01345929 and NCT01345955), ceftolozane/tazobactam demonstrated efficacy superior to that of high-dose levofloxacin in patients with cUTI [13].
Herein we present a post hoc investigation of baseline characteristics, efficacy, and safety from patients with or without a reported medical history of diabetes in the phase 3 ASPECT trials. The aims of this evaluation were to examine the baseline characteristics of patients with and without diabetes who were enrolled in the ASPECT trials and to assess whether ceftolozane/tazobactam was safe and effective in treating cIAI and cUTI in patients with diabetes.
Methods
Study design
Two multicenter, multinational, randomized (1:1 ratio), double-blind, noninferiority trials were conducted from 2011 to 2013 (Merck protocols: CXA-cIAI-10-08, CXA-cIAI-10-09, CXA-cUTI-10-04, and CXA-cUTI-10-05). Studies were conducted in accordance with the principles of Good Clinical Practice and were approved by the appropriate institutional review boards and regulatory agencies [12, 13]. In ASPECT-cIAI, adults with cIAI in need of surgical intervention were assigned to receive intravenous (IV) ceftolozane/tazobactam 1.5 g plus metronidazole 500 mg every 8 h (q8h) or IV meropenem 1 g plus placebo q8h for 4 to 14 days. In ASPECT-cUTI, adults with cUTI (including pyelonephritis) were assigned to receive IV ceftolozane/tazobactam 1.5 g q8h or IV levofloxacin 750 mg/day for 7 days.
Patients
Patients enrolled in the trials were classified into subgroups with and without diabetes, based on their reported medical history, and all analyses were evaluated between these two subgroups. Baseline demographics and characteristics were recorded descriptively. Between-group differences were determined, and statistical significance was calculated using the Miettinen and Nurminen method [14].
Efficacy assessments
In ASPECT-cIAI, clinical cure, defined as complete resolution or significant improvement in signs and symptoms of index infection with no additional antibiotics or surgical intervention, was assessed at the test-of-cure (TOC) visit (24–32 days after study drug start). In ASPECT-cUTI, composite cure, defined as both clinical cure (complete resolution or significant improvement in all signs and symptoms) and microbiologic eradication (reduction in all baseline uropathogens to <104 CFU/mL in urine culture) was assessed at the TOC visit (5–9 days after the end of therapy). For this analysis, clinical cure and composite cure rates were compared between patients with and without diabetes, with indeterminate responses imputed as clinical failures, and Wilson score intervals were used to calculate confidence intervals.
Safety assessments
Safety and tolerability were assessed by recording adverse events (AEs). AEs were categorized by the investigator as treatment related (possibly, probably, or definitely) or not treatment related. Data were recorded descriptively. Between-group differences were determined, and statistical significance was calculated using the Miettinen and Nurminen method [14].
Analysis populations
The cIAI microbiologic intention-to-treat population included all randomly assigned patients with cIAI with ≥1 baseline intra-abdominal pathogen regardless of receipt of, or susceptibility to, study drug. The cUTI microbiologic modified intention-to-treat population included all randomly assigned patients with cUTI with ≥1 dose of study drug and ≥1 uropathogen at baseline, regardless of susceptibility to study drug. The integrated safety population included all patients with cIAI or cUTI who received any amount of study drug.
Results
Patient population and disposition
The pooled analysis population comprised 979 patients from ASPECT-cIAI and 1068 patients from ASPECT-cUTI [12, 13], including 245 patients with diabetes and 1802 without diabetes. Patient disposition is shown in Table 1. Patient groups (with diabetes and without diabetes) had similar rates of study completion and study drug completion and similar reasons for discontinuation. In ASPECT-cUTI, negative/contaminated urine culture (12.1% and 18.8%, respectively) was the most common reason for early discontinuation of study drug, which was required per protocol.
Baseline characteristics
Baseline demographics and disease characteristics are reported in Table 2. In the subgroups with and without diabetes, most patients were white, and slightly more women than men were included. Patients were evenly distributed between treatment arms in the subgroups with and without diabetes (data not shown).
Notable differences between patients with and without diabetes included age, weight, race, and comorbidities (Table 2). Significantly more patients with than without diabetes were 65 years of age or older; patients with diabetes were also significantly more likely (57.1%) to weigh ≥75 kg at baseline than those without diabetes (44.5%). In addition, there was a significantly higher proportion of Asian patients in the subgroup with diabetes than in the subgroup without diabetes. As expected, renal impairment was more common in the subgroup with diabetes (48.5%) than in the subgroup without it (30.2%); 15.7% of patients with diabetes had moderate renal impairment compared with 4.5% of patients without diabetes. In cIAI, a significantly higher percentage of patients with diabetes had Acute Physiologic Assessment and Chronic Health Evaluation II scores ≥10 (33.8% vs 17.0% in patients without diabetes), potentially driven by older age and decreased renal function. Additionally, cholecystitis was significantly more common in patients with diabetes; appendiceal infections were significantly more common in patients without diabetes.
A summary of medical history ongoing at baseline is shown in Table 3. As expected, cardiac, endocrine, and eye disorders were reported at significantly higher incidences in the subgroup with diabetes. For cardiac disorders, the major driver of the difference between patients with and without diabetes was coronary artery disorders (17.2% vs 7.6%); for eye disorders, the major driver was diabetic retinopathy (4.5% vs 0%).
Significantly higher incidences of renal diseases and complications were also associated with diabetes, particularly chronic kidney disease (8.6% in patients with diabetes vs 1.3% in patients without diabetes) and diabetic nephropathy (6.1% vs 0%). The significantly higher incidence of vascular disorders in patients with diabetes (70.7% vs 27.7% in patients without diabetes) was largely driven by the incidence of hypertension (66.2% vs 24.3%). Patients with diabetes also had significantly more ongoing infections and more hepatic, nervous system, and respiratory disorders.
Bacteriology findings across subgroups with and without diabetes were generally similar within each indication (cUTI and cIAI; Table 4). Escherichia coli was the most common pathogen in both indications and subpopulations.
Efficacy
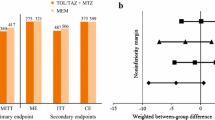
In general, patients with diabetes had lower cure rates than patients without diabetes (cIAI, 75.4% vs 86.1%, P = 0.0196; cUTI, 62.4% vs 74.7%, P = 0.1299 [Fig. 1a]). However, cure rates were similar between treatment arms in both indications (Fig. 1b, c), with the exception of significantly higher composite cure rates for ceftolozane/tazobactam than for levofloxacin (79.5% vs 69.9%, P = 0.0048) in patients with cUTI but without diabetes (Fig. 1c).
Clinical cure (cIAI) and composite cure (cUTI) in patients with and without diabetes at test-of-cure in cIAI (MITT population) and cUTI (mMITT population) (a). Clinical cure at test-of-cure in cIAI (MITT population) (b). Composite cure at test-of-cure in cUTI (mMITT population) (c). Values above brackets indicate treatment difference (95% confidence intervals)
Safety
Patients with diabetes had significantly higher rates of AEs (49.0% vs 37.3%) and serious AEs (10.6% vs 4.6%) than patients without diabetes (Table 5). However, rates of treatment-related AEs were similar between patients with and without diabetes (8.2% vs 10.1%, respectively), suggesting comorbidities were responsible for differences in AE rates. Types of AEs were generally similar between patient subpopulations, but the incidences of infections and vascular disorders were significantly higher in patients with diabetes.
Discussion
In this post hoc analysis of patients with or without a reported medical history of diabetes in the phase 3 ASPECT trials, we have shown that older age, increased weight, and renal impairment are more common in patients with diabetes than in patients without diabetes. In addition, more patients with diabetes had comorbidities and an increased incidence of complicating factors in both cUTI and cIAI, with cardiac, endocrine, and eye disorders reported at significantly higher incidences in the subgroup with diabetes. It has been reported that patients with diabetes are more susceptible to infections and associated complications because of a variety of factors, including but not limited to lower production of interleukins in response to infection and increased virulence of some pathogens in hyperglycemic environments [15].
In our analysis, clinical and composite cure rates were shown to be lower in patients with diabetes but were generally similar between treatment groups, with the exception of significantly higher composite cure rates in ASPECT-cUTI for ceftolozane/tazobactam than for levofloxacin in patients without diabetes. Rates of AEs were also significantly higher in patients with diabetes but were comparable between treatment groups. Overall, the results of this subgroup analysis confirm previous findings in the published literature demonstrating that diabetes increases the risk for poor clinical outcomes and mortality from infectious disease [3, 16,17,18,19]. We can postulate that the high levels of complications (including renal and cardiac disorders and additional ongoing infections) in the patient subgroup with diabetes are likely to have had a negative impact on treatment outcomes and that higher rates of AEs in patients with diabetes were also likely due to comorbidities.
This analysis has several limitations, including the post hoc nature of the calculations, which prohibited any statistical significance surrounding the conclusions. Given that the population with diabetes was not prespecified but was defined post hoc based on medical history, the results are contingent on the accuracy of the data reporting and could be confounded by overestimation or underestimation of this patient subgroup. Furthermore, the patient population in the ASPECT studies may not be reflective of the variety of patients seen in clinical practice. Finally, it must be noted that the correlations seen between AE rates, complicating factors, and poorer outcomes among patients with diabetes may be confounded by other unmeasured factors.
Conclusions
In this post hoc analysis of two phase 3 studies in patients with cIAI and cUTI, baseline factors associated with diabetes included older age, increased weight, and complicating medical factors. Diabetes was associated with lower cure rates and significantly higher AE rates, likely because of the presence of comorbidities. Despite this, ceftolozane/tazobactam was as effective as comparators in treating cUTI and cIAI in patients with diabetes—a population at increased risk for infections and poor clinical outcomes.
Abbreviations
- AE:
-
Adverse event
- ASPECT:
-
Assessment of the Safety Profile and Efficacy of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam
- cIAI:
-
Complicated intra-abdominal infections
- cUTI:
-
Complicated urinary tract infections
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- q8d:
-
every 8 h
- TOC:
-
Test-of-cure
References
Geiss LS, Wang J, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ, Barker L, Li Y, et al. Prevalence and incidence trends for diagnosed diabetes among adults aged 20 to 79 years, United States, 1980-2012. JAMA. 2014;312:1218–26.
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4·4 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387:1513–30.
Benfield T, Jensen JS, Nordestgaard BG. Influence of diabetes and hyperglycaemia on infectious disease hospitalisation and outcome. Diabetologia. 2007;50:549–54.
Shah BR, Hux JE. Quantifying the risk of infectious diseases for people with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:510–3.
Bertoni AG, Saydah S, Brancati FL. Diabetes and the risk of infection-related mortality in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1044–9.
Dalrymple LS, Go AS. Epidemiology of acute infections among patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1487–93.
Wang HE, Gamboa C, Warnock DG, Muntner P. Chronic kidney disease and risk of death from infection. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34:330–6.
Zhanel GG, Chung P, Adam H, Zelenitsky S, Denisuik A, Schweizer F, et al. Ceftolozane/tazobactam: a novel cephalosporin/β-lactamase inhibitor combination with activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli. Drugs. 2014;74:31–51.
Wooley M, Miller B, Krishna G, Hershberger E, Chandorkar G. Impact of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and safety of ceftolozane-tazobactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:2249–55.
Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) [prescribing information]. Whitehouse Station; Merck Sharpe & Dohme Corp.; 2015.
Zerbaxa (ceftolozane and tazobactam) [summary of product characteristics]. Hoddesdon, Hertforshire; Merck Sharpe & Dohme Ltd.; 2016.
Solomkin J, Hershberger E, Miller B, Popejoy M, Friedland I, Steenbergen J, et al. Ceftolozane/tazobactam plus metronidazole for complicated intra-abdominal infections in an era of multidrug resistance: results from a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial (ASPECT-cIAI). Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60:1462–71.
Wagenlehner FM, Umeh O, Steenbergen J, Yuan G, Darouiche RO. Ceftolozane-tazobactam compared with levofloxacin in the treatment of complicated urinary-tract infections, including pyelonephritis: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial (ASPECT-cUTI). Lancet. 2015;385:1949–56.
Miettinen O, Nurminen M. Comparative analysis of two rates. Stat Med. 1985;4:213–26.
Casqueiro J, Casqueiro J, Alves C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: a review of pathogenesis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012;16(suppl 1):S27–36.
Grabe M, Bjerklund-Johansen TE, Botto H, Wullt B, Çek M, Naber KG, et al. Guidelines on urological infections. 2012. http://uroweb.org/wp-content/uploads/19-Urological-infections_LR2.pdf. Accessed 1 May 2017.
Tsai C-C, Lee J-J, Liu TP, Ko W-C, Wu C-J, Pan C-F, et al. Effects of age and diabetes mellitus on clinical outcomes in patients with peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013;14:540–6.
Thomsen RW, Hundborg HH, Lervang H-H, Johnsen SP, Schønheyder HC, Sørensen HT. Diabetes mellitus as a risk and prognostic factor for community-acquired bacteremia due to enterobacteria: a 10-year, population-based study among adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:628–31.
Pertel PE, Haverstock D. Risk factors for a poor outcome after therapy for acute pyelonephritis. BJU Int. 2006;98:141–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sally Mitchell, PhD, and Sarah Utley, PhD, of ApotheCom, Yardley, PA, USA, who provided medical writing and editorial services on behalf of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA.
Funding
This work was supported by Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA.
Employees of the study sponsor, in collaboration with the authors, were involved in the design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors’ contributions
MWP made substantial contributions to acquisition and analysis of the data, interpretation of the results, and drafting and revising the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the manuscript for submission. JL made substantial contributions to the study conception and design, acquisition and analysis of the data, interpretation of the results, and revising the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the manuscript for submission. JAH made substantial contributions to the analysis of the data, interpretation of the results, and revising the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the manuscript for submission. All authors had full access to all the data and take responsibility for the integrity of the work and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Competing interests
All authors are employees of Merck, Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. JAH also reports holding stocks in Merck & Co., Inc.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The studies were conducted in accordance with principles of Good Clinical Practice and were approved by the appropriate institutional review boards and regulatory agencies. All patients provided written informed consent before participation in the studies.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Popejoy, M.W., Long, J. & Huntington, J.A. Analysis of patients with diabetes and complicated intra-abdominal infection or complicated urinary tract infection in phase 3 trials of ceftolozane/tazobactam. BMC Infect Dis 17, 316 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2414-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2414-9