Abstract
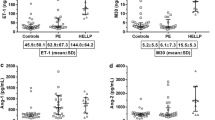
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) are proinflammatory cytokines and known to be involved in many pathological processes. However, the association between serum levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is unclear. The aim of the present study was to determine the serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6 and to investigate their potential correlation with PIH. In this study, the serum concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 in pregnant women who developed PIH and normal pregnant women were measured. We found that the serum concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 were significantly increased in the patients with PIH compared to the normal pregnant women. In addition, elevated TNF-α and IL-6 concentrations were associated with pathological complications. Moreover, in a hypoxia-induced PIH mice model, animals from the PIH group demonstrated higher TNF-a and IL-6 levels when compared to control, and serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels were positively correlated with right ventricular systolic blood pressure. Furthermore, TNF-α and IL-6 levels were decreased when the PIH mice were treated with remodulin compared to control group. In conclusion, our results suggested that high serum TNF-a and IL-6 levels are associated with PIH, and TNF-α and IL-6 might be potential predictors in the prognosis of PIH
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, JM, Yang, YC, Wang, KG Central and peripheral hemody-namics in severe preeclampsia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1996; 75(2):120–126.
Valdiviezo, C, Garovic, VD, Ouyang, P Preeclampsia and hyper-tensive disease in pregnancy: their contributions to cardiovascular risk. Clin Cardiol. 2012;35(3):160–165.
Mannisto, T, Mendola, P, Vaarasmaki, M, et al. Elevated blood pressure in pregnancy and subsequent chronic disease risk. Circulation. 2013;127(6):681–690.
Galassi, A, Reynolds, K, He, J Metabolic syndrome and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2006;119(10): 812–819.
Yadav, K, Aggarwal, S, Verma, K Serum betahCG and lipid profile in early second trimester as predictors of pregnancy-induced hypertension. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2014;64(3):169–174.
George, EM, Granger, JP Linking placental ischemia and hyper-tension in preeclampsia: role of endothelin 1. Hypertension. 2012; 60(2):507–511.
Lim, KH, Zhou, Y, Janatpour, M, et al. Human cytotrophoblast differentiation/invasion is abnormal in pre-eclampsia. Am J Pathol. 1997;151(6):1809–1818.
Redman, CW, Sacks, GP, Sargent, IL Preeclampsia: an excessive maternal inflammatory response to pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gyne-col. 1999;180(2 pt 1):499–506.
Beckmann, I, Visser, W, Struijk, PC, van Dooren, M, Glavimans, J, Wallenburg, HC Circulating bioactive tumor necrosis factor-alpha, tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors, fibronectin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inducible cell adhesion molecule VCAM-1 in uncomplicated pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177(5):1247–1252.
Zhang, Y, Gu, Y, Li, H, Lucas, MJ, Wang, Y Increased endothelial monolayer permeability is induced by serum from women with preeclampsia but not by serum from women with normal pregnancy or that are not pregnant. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2003;22(1):99–108.
Vince, GS, Starkey, PM, Austgulen, R, Kwiatkowski, D, Redman, CW Interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors in women with pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995;102(1):20–25.
Gao, X, Zhang, H, Belmadani, S, et al. Role of TNF-alpha-induced reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction during reper-fusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;295(6): H2242–H2249.
Navarro-Gonzalez, JF, Mora-Fernandez, C, Muros de Fuentes, M, García-Pérez, J Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011; 7(6):327–340.
Navarro, JF, Mora, C, Gomez, M, Muros, M, López-Aguilar, C, García, J Influence of renal involvement on peripheral blood mononuclear cell expression behaviour of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in type 2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(3):919–926.
Khong, Y, Brosens, I Defective deep placentation. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25(3):301–311.
Rajakumar, A, Doty, K, Daftary, A, Daftary, A, Harger, G, Conrad, KP Impaired oxygen-dependent reduction of HIF-1alpha and -2alpha proteins in pre-eclamptic placentae. Placenta. 2003;24(2-3): 199–208.
Gadonski, G, LaMarca, BB, Sullivan, E, Bennett, W, Chandler, D, Granger, JP Hypertension produced by reductions in uterine per-fusion in the pregnant rat: role of interleukin 6. Hypertension. 2006;48(4):711–716.
Matura, LA, Ventetuolo, CE, Palevsky, HI, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are associated with quality of life-related symptoms in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(3):370–375.
Roberts, JM, Pearson, GD, Cutler, JA, Lindheimer MD; National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Summary of the NHLBI working group on research on hypertension during pregnancy. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2003;22(2):109–127.
Liu, H, Yang, E, Lu, X, et al. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand correlate with the severity of pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015;33:39–46.
Obican, SG, Cleary, KL Pulmonary arterial hypertension in preg-nancy. Semin Perinatol. 2014;38(5):289–294.
Rosengarten, D, Kramer, R Pregnancy in a woman with pulmon-ary hypertension: favorable outcome with intravenous treprosti-nil. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2015;42(3):390–391.
Granger, JP, Alexander, BT, Bennett, WA, et al. Pathophysiology of pregnancy-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2001;14(6 pt 2):178S-185S.
LaMarca, B, Speed, J, Fournier, L, et al. Hypertension in response to chronic reductions in uterine perfusion in pregnant rats: effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade. Hypertension. 2008; 52(6):1161–1167.
Bayram, M, Taskaya, A, Bagriacik, EU, Ilhan, MN, Yaman, M The effect of maternal serum sFAS/sFASL system on etiopathogenesis of preeclampsia and severe preeclampsia[pub-lished online August 22, 2012]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012.
Drexler, H, Hornig, B Endothelial dysfunction in human disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1999;31(1):51–60.
Holvoet, P, Collen, D Thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997;8(5):320–328.
Sellati, TJ, Burns, MJ, Ficazzola, MA, Furie, MB Borrelia burgdor-feri upregulates expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells and promotes transendothelial migration of neutrophils in vitro. Infect Immun. 1995;63(11):4439–4447.
Salafia, CM, Pezzullo, JC, Lopez-Zeno, JA, Simmens, S, Minior, VK, Vintzileos, AM Placental pathologic features of preterm pre-eclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;173(4):1097–1105.
Belge, KU, Dayyani, F, Horelt, A, et al. The proinflammatory CD14+CD16+DR++ monocytes are a major source of TNF. J Immunol. 2002;168(7):3536–3542.
Conrad, KP, Benyo, DF Placental cytokines and the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1997;37(3):240–249.
Conrad, KP, Miles, TM, Benyo, DF Circulating levels of immu-noreactive cytokines in women with preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1998;40(2):102–111.
Espevik, T, Brockhaus, M, Loetscher, H, Nonstad, U, Shalaby, R Characterization of binding and biological effects of monoclonal antibodies against a human tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Exp Med. 1990;171(2):415–426.
Alexander, BT, Cockrell, KL, Massey, MB, Bennett, WA, Granger, JP Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced hypertension in pregnant rats results in decreased renal neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15(2 pt 1):170–175.
Boie, Y, Rushmore, TH, Darmon-Goodwin, A, et al. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostanoid IP receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(16):12173–12178.
Luttmann, W, Herzog, V, Matthys, H, Thierauch, KH, Virchow, JC, Kroegel, C Modulation of cytokine release from mononuclear cells by prostacyclin, IL-4 and IL-13. Cytokine. 1999;11(2): 127–133.
Meja, KK, Barnes, PJ, Giembycz, MA Characterization of the prostanoid receptor(s) on human blood monocytes at which pros-taglandin E2 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumour necrosis factor-alpha generation. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;122(1):149–157.
Raychaudhuri, B, Malur, A, Bonfield, TL, et al. The prostacyclin analogue treprostinil blocks NFkappaB nuclear translocation in human alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(36): 33344–33348.
Wang, WL, Kuo, CH, Chu, YT, et al. Prostaglandin I(2) analogues suppress TNF-alpha expression in human monocytes via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Inflamm Res. 2011;60(7): 655–663.
Zhou, W, Hashimoto, K, Goleniewska, K, et al. Prostaglandin I2 analogs inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production and T cell stimulatory function of dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2007;178(2): 702–710.
Zhou, W, Blackwell, TS, Goleniewska, K, et al. Prostaglandin I2 analogs inhibit Th1 and Th2 effector cytokine production by CD4 T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81(3):809–817.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Ding, X. et al. Serum Levels of TNF-α and IL-6 Are Associated With Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. Reprod. Sci. 23, 1402–1408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719116641760
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719116641760