Abstract
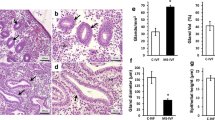
Ovulation induction therapy with clomiphene citrate can suppress endometrial receptivity. Raloxifene may be an alternative therapeutic for women with ovulatory disorders. This study aimed to compare the expression of endometrial receptivity markers, including homeobox gene 10 (HOXA10), integrin β3, and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), as well as pinopode production during the implantation window in mice stimulated with raloxifene and clomiphene citrate and natural cycles. Thirty-six 8-week-old female Kunming mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (n = 12) and administered daily raloxifene (22 mg/kg), clomiphene citrate (18 mg/kg), and normal saline (1 mL), respectively, by gavage. Two days later, mice were injected with 5 IU human chorionic gonadotropin and mated. Successfully mated female animals were identified with vaginal plugs designated gestation day 1. At day 4.5, pregnant donor mice were euthanized, and uterus samples were collected for immunohistochemistry, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, and scanning electron microscopy analyses. Homeobox gene 10, integrin β3, and LIF messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels were significantly higher in the raloxifene-treated animals compared with the clomiphene citrate group (all P < .05) but not significantly different from saline group values, except for LIF and integrin β3 mRNA levels (P < .05). Pinopodes were abundant and well developed in the raloxifene and saline groups; however, in the clomiphene citrate-treated mice, fewer and poorly developed pinopodes were obtained. In mice, raloxifene had no effect on HOXA10, integrin β3, and LIF expression as well as pinopode production, suggesting it has no adverse effects on endometrial receptivity. Raloxifene may provide a viable alternative oral ovulation induction agent to clomiphene citrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilkes S, Murdoch A. Ovulation induction with clomifene: a primary care perspective. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012; 38(1):48–52.
Brown J, Farquhar C, Beck J, Boothroyd C, Hughes E. Clomiphene and anti-oestrogens for ovulation induction in PCOS. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(4):cd002249.
Goldstein SR, Siddhanti S, Ciaccia AV, Plouffe L Jr. A pharmacological review of selective oestrogen receptor modulators. Hum Reprod Update. 2000;6(3):212–224.
Bao SH, Sheng SL, Peng YF, Lin QD. Effects of letrozole and clomiphene citrate on the expression of HOXA10 and integrin alpha v beta 3 in uterine epithelium of rats. Fertil Steril. 2009; 91(1):244–248.
Boostanfar R, Jain JK, Mishell DR Jr, Paulson RJ. A prospective randomized trial comparing clomiphene citrate with tamoxifen citrate for ovulation induction. Fertil Steril. 2001;75(5): 1024–1026.
Deligdisch L. Effects of hormone therapy on the endometrium. Mod Pathol. 1993;6(1):94–106.
Ismail SM. Pathology of endometrium treated with tamoxifen. J Clin Pathol. 1994;47(9):827–833.
Silverman S, Christiansen C. Individualizing osteoporosis therapy. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(3):797–809.
Baker VL, Draper M, Paul S, et al. Reproductive endocrine and endometrial effects of raloxifene hydrochloride, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, in women with regular menstrual cycles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83(1):6–13.
de Paula Guedes Neto E, Savaris RF, von Eye Corleta H, de Moraes GS, do Amaral Cristovam R, Lessey BA. Prospective, randomized comparison between raloxifene and clomiphene citrate for ovulation induction in polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(3):769–773.
Lessey BA, Palomino WA, Apparao KB, Young SL, Lininger RA. Estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-alpha) and defects in uterine receptivity in women. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2006;4(suppl 1):s9.
Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical physiology. A cellular and molecular approach. 2nd ed. Oxford, PA: Saunders/Elsevier; 2009.
Nikas G, Develioglu OH, Toner JP, Jones HW Jr. Endometrial pinopodes indicate a shift in the window of receptivity in IVF cycles. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(3):787–792.
Garcia-Velasco J, Simon C, Ardiles G, Neuspiller F, Remohi J, Nikas G. Assessment of endometrial response to HRT using the detection of pinopods in women with endometriosis undergoing oocyte donation. Fertil Steril. 1998;70:365.
Kolb BA, Najmabadi S, Paulson RJ. Ultrastructural characteristics of the luteal phase endometrium in patients undergoing controlled ovarian hyperstimulation. Fertil Steril. 1997;67(4): 625–630.
Quinn C, Ryan E, Claessens EA, et al. The presence of pinopodes in the human endometrium does not delineate the implantation window. Fertil Steril. 2007;87(5):1015–1021.
Pierson RA. Imaging the endometrium: are there predictors of uterine receptivity? J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2003;25(5):360–368.
Bagot CN, Kliman HJ, Taylor HS. Maternal Hoxa10 is required for pinopod formation in the development of mouse uterine receptivity to embryo implantation. Dev Dyn. 2001;222(3):538–544.
Creus M, Ordi J, Fabregues F, et al. The effect of different hormone therapies on integrin expression and pinopode formation in the human endometrium: a controlled study. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(4):683–693.
Parr MB, Parr EL. Endocytosis in the uterine epithelium of the mouse. J Reprod Fertil. 1977;50(1):151–153.
Aghajanova L, Stavreus-Evers A, Nikas Y, Hovatta O, Landgren BM. Coexpression of pinopodes and leukemia inhibitory factor, as well as its receptor, in human endometrium. Fertil Steril. 2003;79(suppl 1):808–814.
Eun Kwon H, Taylor HS. The role of HOX genes in human implantation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1034:1–18.
Benson GV, Lim H, Paria BC, Satokata I, Dey SK, Maas RL. Mechanisms of reduced fertility in Hoxa-10 mutant mice: uterine homeosis and loss of maternal Hoxa-10 expression. Development. 1996;122(9):2687–2696.
Taylor HS, Bagot C, Kardana A, Olive D, Arici A. HOX gene expression is altered in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(5):1328–1331.
Cermik D, Selam B, Taylor HS. Regulation of HOXA-10 expression by testosterone in vitro and in the endometrium of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(1):238–243.
Lindhard A, Bentin-Ley U, Ravn V, et al. Biochemical evaluation of endometrial function at the time of implantation. Fertil Steril. 2002;78(2):221–233.
Salleh N, Giribabu N. Leukemia inhibitory factor: roles in embryo implantation and in nonhormonal contraception. ScientificWorld-Journal. 2014;2014:201514.
Kaneko Y, Lecce L, Day ML, Murphy CR. beta(1) and beta(3) integrins disassemble from basal focal adhesions and beta(3) integrin is later localised to the apical plasma membrane of rat uterine luminal epithelial cells at the time of implantation. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2011;23(3):481–495.
Liu N, Zhou C, Chen Y, Zhao J. The involvement of osteopontin and beta3 integrin in implantation and endometrial receptivity in an early mouse pregnancy model. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170(1):171–176.
Zorn TM, Soto-Suazo M, Pellegrini CR, Oliveira JG, Stumpf WE. Estradiol receptor binding to the epithelium of uterine lumen and glands: region- and time-related changes during preimplantation and periimplantation periods studied by autoradiography. Histochem Cell Biol. 2003;120(1):1–12.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408.
Usadi RS, Murray MJ, Bagnell RC, et al. Temporal and morphologic characteristics of pinopod expression across the secretory phase of the endometrial cycle in normally cycling women with proven fertility. Fertil Steril. 2003;79(4):970–974.
Kuscu NK, Koyuncu FM, Var A, Lacin S, Uyanik BS, Ceylan E. Clomiphene citrate does not adversely affect endometrial leukemia inhibitory factor levels. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2002;16(2): 151–154.
Punyadeera C, Kamps R, Defrere S, et al. Effects of selective oestrogen receptor modulators on proliferation in tissue cultures of pre- and postmenopausal human endometrium. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;112(1–3):102–109.
Blauer M, Heinonen PK, Rovio P, Ylikomi T. Effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene on normal human endometrial cells in an organotypic in vitro model. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;592(1–3):13–18.
Szutu M, Morgan DJ, McLeish M, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous clomiphene isomers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989; 27(5):639–640.
Heringa M. Review on raloxifene: profile of a selective estrogen receptor modulator. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;41(8): 331–345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Yan, Q., Liu, K. et al. Endometrial Receptivity Markers in Mice Stimulated With Raloxifene Versus Clomiphene Citrate and Natural Cycles. Reprod. Sci. 23, 748–755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115616496
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115616496