Abstract
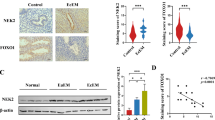
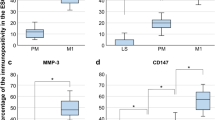
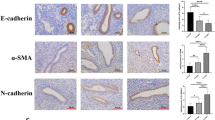
Endometriosis is a common benign gynecological disease defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity. The aim of this study was to identify the molecular mechanism underlying hypoxia-induced increases in invasive ability of human endometrial stromal cells (HESCs). Herein, we show that the expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor lα (HIF-1α) and β-catenin were greater in ectopic endometriotic tissue compared with eutopic tissue from controls. Exposure of eutopic endometrial stromal cells under hypoxic conditions or treated with desferrioxamine (DFO, chemical hypoxia) resulted in a time-dependent increase in β-catenin expression and its dephosphorylation. Hypoxia/HIF-1α also activated the β-catenin/T-cell factor (TCF) signaling pathway and the expression of target genes, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase 9, and knockdown of HIF-1α or β-catenin abrogated hypoxia-induced increases in HESC invasiveness. These results suggest that HIF-1α interacting with β-catenin/TCF signaling pathway, which is activated by hypoxia, may provide new insights into the etiology of endometriosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giudice LC, Kao LC. Endometriosis. Lancet. 2004; 364(9447):1789–1799.
Halme J, Hammond MG, Hulka JF, Raj SG, Talbert LM. Retrograde menstruation in healthy women and in patients with endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1984; 64(2):151–154.
Olive DL, Pritts EA. Treatment of endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345(4):266–275.
Figueira PG, Abrao MS, Krikun G, Taylor HS. Stem cells in endometrium and their role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1221:10–17.
Kao AP, Wang KH, Chang CC, et al. Comparative study of human eutopic and ectopic endometrial mesenchymal stem cells and the development of an in vivo endometriotic invasion model. Fertil Steril. 2011; 95(4):1308–1315.
Wu MH, Chen KF, Lin SC, Lgu CW, Tsai SJ. Aberrant expression of leptin in human endometriotic stromal cells is induced by elevated levels of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha. Am J Pathology. 2007; 170(2):590–598.
Sharkey AM, Day K, McPherson A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human endometrium is regulated by hypoxia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 85(1):402–409.
Krikun G, Schatz F, Finlay T, et al. Expression of angiopoietin-2 by human endometrial endothelial cells:regulation by hypoxia and inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 275(1):159–163.
Lu Z, Zhang W, Jiang S, Zou J, Li Y. Effect of oxygen tensions on the proliferation and angiogenesis of endometriosis heterograft in severe combined immunodeficiency mice. Fertil Steril. 2014; 101(2):568–576.
Hsiao KY, Chang N, Lin SC, Li YH, Wu MH. Inhibition of dual specificity phosphatase-2 by hypoxia promotes interleukin-8-mediated angiogenesis in endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2014; 29(12):2747–2755.
Lin SC, Wang CC, Wu MH, Yang SH, Li YH, Tsai SJ. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-20a expression increases ERK phosphorylation and angiogenic gene expression in endometriotic stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97(8):E1515–E1523.
Ulukus M, Cakmak H, Arici A. The role of endometrium in endometriosis. J Soc Gynecol Invest. 2006; 13(7):467–476.
Harada T, Kaponis A, Iwabe T, et al. Apoptosis in human endometrium and endometriosis. Hum Reprod Update. 2004; 10(1):29–38.
Bassi MA, Podgaec S, Dias Junior JA, Sobrado CW, N DAF. [Bowel endometriosis:a benign disease?]. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2009; 55(5):611–616.
Bumey RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012; 98(3):511–519.
Rogers PA, D’Hooghe TM, Fazleabas A, et al. Defining future directions for endometriosis research:workshop report from the 2011 World Congress of Endometriosis In Montpellier, France. Reprod Sci. 2013; 20(5):483–499.
Willert K, Nusse R. Beta-catenin:a key mediator of Wnt signaling. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998; 8(1):95–102.
Matsuzaki S, Darcha C. In vitro effects of a small-molecule antagonist of the Tcf/ss-catenin complex on endometrial and endometriotic cells of patients with endometriosis. PloS One. 2013; 8(4):e61690.
Matsuzaki S, Darcha C. Involvement of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in the cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis in endometriosis. PloS One. 2013; 8(10):e76808.
Matsuzaki S, Darcha C, Maleysson E, Canis M, Mage G. Impaired down-regulation of E-cadherin and beta-catenin protein expression in endometrial epithelial cells in the mid-secretory endometrium of infertile patients with endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2010; 95(7):3437–3445.
Liu L, Zhu XD, Wang WQ, et al. Activation of beta-catenin by hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to enhanced metastatic potential and poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16(10):2740–2750.
Cui XP, Xing Y, Chen JM, Dong SW, Ying DJ, Yew DT. Wnt/ beta-catenin is involved in the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells induced by hypoxia. Irish J Med Sci. 2011; 180(2):387–393.
Guillemin K, Krasnow MA. The hypoxic response:huffing and HIFing. Cell. 1997; 89(1):9–12.
Jiang QY, Wu RJ. Growth mechanisms of endometriotic cells in implanted places:a review. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012; 28(7):562–567.
Spuijbroek MD, Dunselman GA, Menheere PP, Evers JL. Early endometriosis invades the extracellular matrix. Fertil Steril. 1992; 58(5):929–833.
Bruner KL, Matrisian LM, Rodgers WH, Gorstein F, Osteen KG. Suppression of matrix metalloproteinases inhibits establishment of ectopic lesions by human endometrium in nude mice. J Clin Invest. 1997; 99(12):2851–2857.
Chung HW, Wen Y, Chun SH, Nezhat C, Woo BH, Lake Polan M. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 mRNA expression in ectopic and eutopic endometrium in women with endometriosis:a rationale for endometriotic invasiveness. Fertil Siril. 2001; 75(1):152–159.
Collette T, Maheux R, Mailloux J, Akoum A. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-8 in the eutopic endometrial tissue of women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2006; 21(12):3059–3067.
Groothuis PG, Nap AW, Winterhager E, Grummer R. Vascular development in endometriosis. Angiogenesis. 2005; 8(2):147–156.
Liang JY, Li CD, Zhang WY. [Effects of activating and inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on murine model of eutopic endometrium and endometriosis]. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi. 2012; 92(19):1352–1356.
Franke WW. Discovering the molecular components of intercellular junctions-a historical view. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 2009; 1(3):003061.
Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cad-herin pathways. Science. 2004; 303(5663):1483–1487.
Wodarz A, Nusse R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998; 14:59–88.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling:components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009; 17(1):9–26.
Mulholland DJ, Dedhar S, Coetzee GA, Nelson CC. Interaction of nuclear receptors with the Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling axis:Wnt you like to know? Endocrine Rev. 2005; 26(7):898–915.
Akiyama T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000; 11(4):273–282.
Peifer M, Polakis P. Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogen-esis-a look outside the nucleus. Science. 2000; 287(5458):1606–1609.
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell. 2010; 40(2):294–309.
Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis:1996. Fertility and Sterility. 1997; 67(5):817–821.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, W., Zhang, L., Xiong, Y. et al. Hypoxia Promotes Invasion of Endometrial Stromal Cells via Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α Upregulation-Mediated β-Catenin Activation in Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 23, 531–541 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115607999
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115607999