Abstract
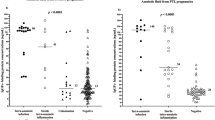
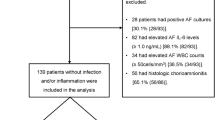
To determine the clinical significance of an increase in various fragmented forms of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) in amniotic fluid (AF), a retrospective cohort study was conducted in 103 consecutive patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Amniotic fluid samples were cultured for aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and mycoplasmas, and then assayed for matrix metalloproteinase-8. Fragmented-to-intact IGFBP-1 ratios were evaluated by densitometric analysis of Western blot assays. Intact IGFBP-1 (30 kDa) and 21, 17, and 12 kDa fragments were detected in AF. Median ratios of fragmented-to-intact IGFBP-1 were higher in patients whose neonates had significant morbidity than in those whose neonates did not (P < .05), in patients spontaneously delivered within 2 and 7 days from amniocentesis than in those delivered after 2 and 7 days (P < .05), and in patients with intra-amniotic infection/inflammation than in those without (P < .001). Collectively, fragmented IGFBP-1 in AF may be indicators for adverse perinatal outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomez R, Ghezzi F, Romero R, Munoz H, Tolosa JE, Rojas I. Premature labor and intra-amniotic infection. Clinical aspects and role of the cytokines in diagnosis and pathophysiology. Clin Perinatal. 1995;22(2):28–342.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Moon JB, et al. Clinical significance of intra-amniotic inflammation in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185(5): 1130–1136.
Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(20):1500–1507.
Romero R, Espinoza J, Kusanovic JP, et al. The preterm parturition syndrome. BJOG. 2006;113(suppl 3):17–42.
Eschenbach DA. Intrauterine infection and premature membrane rupture. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 1989;1(1):23–26.
Hillier SL, Witkin SS, Krohn MA, Watts DH, Kiviat NB, Eschenbach DA. The relationship of amniotic fluid cytokines and preterm delivery, amniotic fluid infection, histologic chorioamnionitis, and chorioamnion infection. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;81(6): 941–948.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Kim CJ, et al. Amniotic fluid interleukin-6: a sensitive test for antenatal diagnosis of acute inflammatory lesions of preterm placenta and prediction of perinatal morbidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172(3):960–970.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Jun JK, et al. Amniotic fluid cytokines (interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-8) and the risk for the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177(4):825–830.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Kim CJ, et al. High expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in periventricular leukomalacia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177(2):406–411.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Park JS, et al. Fetal exposure to an intraamniotic inflammation and the development of cerebral palsy at the age of three years. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182(3): 675–681.
Hagberg H, Mallard C, Jacobsson B. Role of cytokines in preterm labour and brain injury. BJOG. 2005;112(suppl 1):16–18.
Ramsey PS, Lieman JM, Brumfield CG, Carlo W. Chorioamnionitis increases neonatal morbidity in pregnancies complicated by preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(4):1162–1166.
Normann E, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Eaton F, Schwendimann L, Gressens P, Thebaud B. A novel mouse model of Ureaplasmainduced perinatal inflammation: effects on lung and brain injury. Pediatr Res. 2009;65(4):430–436.
Romero R, Yoon BH, Mazor M, et al. The diagnostic and prognostic value of amniotic fluid white blood cell count, glucose, interleukin-6, and gram stain in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993; 169(4):805–816.
Vaisbuch E, Romero R, Erez O, et al. Total hemoglobin concentration in amniotic fluid is increased in intraamniotic infection/ inflammation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199(4):426 e1–e7.
Puchner T, Egarter C, Wimmer C, Lederhilger F, Weichselbraun I. Amniotic fluid interleukin-8 as a marker for intraamniotic infection. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 1993;253(1):9–14.
Greig PC, Herbert WN, Robinette BL, Teot LA. Amniotic fluid interleukin-10 concentrations increase through pregnancy and are elevated in patients with preterm labor associated with intrauterine infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;173(4):1223–1227.
Kara M, Ozden S, Arioglu P, Cetin A. The significance of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 levels in preterm labour. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998;38(4):403–406.
Hsu CD, Meaddough E, Aversa K, et al. Elevated amniotic fluid levels of leukemia inhibitory factor, interleukin 6, and interleukin 8 in intra-amniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179(5): 1267–1270.
Nhan-Chang CL, Romero R, Kusanovic JP, et al. A role for CXCL13 (BCA-1) in pregnancy and intra-amniotic infection/ inflammation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;21(11): 763–775.
Romero R, Quintero R, Emamian M, et al. Arachidonate lipoxygenase metabolites in amniotic fluid of women with intra-amniotic infection and preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;157(6):1454–1460.
Locksmith GJ, Clark P, Duff P, Schultz GS. Amniotic fluid matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels in women with preterm labor and suspected intra-amniotic infection. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;94(1):1–6.
Angus SR, Segel SY, Hsu CD, et al. Amniotic fluid matrix metalloproteinase-8 indicates intra-amniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185(5):1232–1238.
Harirah H, Donia SE, Hsu CD. Amniotic fluid matrix metalloproteinase-9 and interleukin-6 in predicting intraamniotic infection. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99(1):80–84.
Gravett MG, Novy MJ, Rosenfeld RG, et al. Diagnosis of intraamniotic infection by proteomic profiling and identification of novel biomarkers. JAMA. 2004;292(4):462–469.
Bujold E, Romero R, Kusanovic JP, et al. Proteomic profiling of amniotic fluid in preterm labor using two-dimensional liquid separation and mass spectrometry. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;21(10):697–713.
Fowler DJ, Nicolaides KH, Miell JP. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1): a multifunctional role in the human female reproductive tract. Hum Reprod Update. 2000;6(5): 495–504.
Gicquel C, Le Bouc Y. Hormonal regulation of fetal growth. Horm Res. 2006;65(suppl 3):28–33.
Koistinen R, Kalkkinen N, Huhtala ML, Seppala M, Bohn H, Rutanen EM. Placental protein 12 is a decidual protein that binds somatomedin and has an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence with somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Endocrinology. 1986;118(4):1375–1378.
Bell SC, Patel SR, Jackson JA, Waites GT. Major secretory protein of human decidualized endometrium in pregnancy is an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. J Endocrinol. 1988;118(2):317–328.
Martina NA, Kim E, Chitkara U, Wathen NC, Chard T, Giudice LC. Gestational age-dependent expression of insulinlike growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) phosphoisoforms in human extraembryonic cavities, maternal serum, and decidua suggests decidua as the primary source of IGFBP-1 in these fluids during early pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(6): 1894–1898.
Shim SS, Romero R, Hong JS, et al. Clinical significance of intraamniotic inflammation in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191(4):1339–1345.
Park JS, Romero R, Yoon BH, et al. The relationship between amniotic fluid matrix metalloproteinase-8 and funisitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185(5):1156–1161.
Lee SE, Han BD, Park IS, Romero R, Yoon BH. Evidence supporting proteolytic cleavage of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) protein in amniotic fluid. J Perinat Med. 2008;36(4):316–323.
Wang H, Chen B, Chow SC. Sample size determination based on rank tests in clinical trials. J Biopharm Stat. 2003;13(4):735–751.
Bunn RC, Fowlkes JL. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein proteolysis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003;14(4):176–181.
Nakamura M, Miyamoto S, Maeda H, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 degrades all insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and facilitates insulin-like growth factor bioavailability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333(3): 1011–1016.
Coppock HA, White A, Aplin JD, Westwood M. Matrix metalloprotease-3 and -9 proteolyze insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. Biol Reprod. 2004;71(2):438–443.
Bischof P, Meisser A, Campana A, Tseng L. Effects of decidua-conditioned medium and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 on trophoblastic matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Placenta. 1998;19(7):457–464.
Romero R, Yoon BH, Mazor M, et al. A comparative study of the diagnostic performance of amniotic fluid glucose, white blood cell count, interleukin-6, and gram stain in the detection of microbial invasion in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169(4): 839–851.
Jacobsson B, Mattsby-Baltzer I, Andersch B, et al. Microbial invasion and cytokine response in amniotic fluid in a Swedish population of women in preterm labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2003;82(2):120–128.
Yoon BH, Romero R, Lim JH, et al. The clinical significance of detecting Ureaplasma urealyticum by the polymerase chain reaction in the amniotic fluid of patients with preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189(4):919–924.
Tisi DK, Liu XJ, Wykes LJ, Skinner CD, Koski KG. Insulin-like growth factor II and binding proteins 1 and 3 from second trimester human amniotic fluid are associated with infant birth weight. J Nutr. 2005;135(7):1667–1672.
Chard T. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in normal and abnormal human fetal growth. Growth Regul. 1994;4(3):91–100.
Verhaeghe J, Van Herck E, Billen J, Moerman P, Van Assche FA, Giudice LC. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 concentrations in preterm fetuses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 188(2):485–491.
Chevallier B, Lagarde A, Degrelle H, Belaisch-Allart J, Giraudet P, Gallet JP. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 level in amniotic fluid: correlation with birth weight. Biol Neonate. 1998;73(6):404–406.
Hakala-Ala-Pietila TH, Koistinen RA, Salonen RK, Seppala MT. Elevated second-trimester amniotic fluid concentration of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in fetal growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169(1): 35–39.
Crossey PA, Pillai CC, Miell JP. Altered placental development and intrauterine growth restriction in IGF binding protein-1 transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(3):411–418.
Ning Y, Williams MA, Vadachkoria S, Muy-Rivera M, Frederick IO, Luthy DA. Maternal plasma concentrations of insulinlike growth factor-1 and insulinlike growth factor-binding protein-1 in early pregnancy and subsequent risk of preeclampsia. Clin Biochem. 2004;37(11):968–973.
Vatten LJ, Nilsen TI, Juul A, Jeansson S, Jenum PA, Eskild A. Changes in circulating level of IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-1 from the first to second trimester as predictors of preeclampsia. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158(1):101–105.
Hansen-Pupp I, Hellstrom-Westas L, Cilio CM, Andersson S, Fellman V, Ley D. Inflammation at birth and the insulin-like growth factor system in very preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96(6):830–836.
Marchini G, Hagenas L, Kocoska-Maras L, Berggren V, Hansson LO. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 and interleukin-6 are markers of fetal stress during parturition at term gestation. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005;18(8):777–783.
Fowlkes JL. Insulinlike growth factor-binding protein proteolysis an emerging paradigm in insulinlike growth factor physiology. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997;8(8):299–306.
Rechler MM, Clemmons DR. Regulatory actions of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1998;9(5):176–183.
Gibson JM, Aplin JD, White A, Westwood M. Regulation of IGF bioavailability in pregnancy. Mol Hum Reprod. 2001;7(1):79–87.
Diamandi A, Mistry J, Krishna RG, Khosravi J. Immunoassay of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3): new means to quantifying IGFBP-3 proteolysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(6):2327–2333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Lee, S.M., Oh, K. et al. Fragmented Forms of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 in Amniotic Fluid of Patients With Preterm Labor and Intact Membranes. Reprod. Sci. 18, 842–849 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719111399927
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719111399927