Abstract
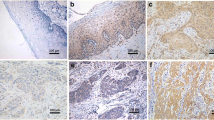
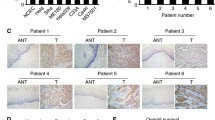
To investigate the novel role of lipocalin 2 and its concernment with human nonmetastatic clone 23 type 1 (nm23-H1) and p53 in cervical carcinogenesis, SiHa cervical cancer cells were knocked down for nm23-H and lipocalin 2 or overexpressed by lipocalin 2 genes. We found that the overexpression of lipocalin 2 or knockdown of nm23-H1 genes increased the proliferation of SiHa cancer cells, while knocking down of lipocalin 2 decreased the proliferation of SiHa. Furthermore, knockdown of nm23-H1 or overexpression of lipocalin 2 was associated with reduced expression of p53 and its downstream gene p21. Using tissue microarrays, lipocalin 2 immunoreactivity was significantly elevated in cancer tissues as compared with it in high- or low-grade dysplasia or normal tissues. Serum secreted form lipocalin 2 from patients with cervical cancer increased in comparison with normal controls. Conclusively, secreted form lipocalin 2 reflects its implication in cervical cancer tissues and may be utilized as an adjuvant biomarker.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosengard AM, Krutzsch HC, Shearn A, et al. Reduced Nm23/Awd protein in tumour metastasis and aberrant Drosophila development. Nature. 1989;342(6246):177–180.
Wallet V, Mutzel R, Troll H, et al. Dictyostelium nucleoside diphosphate kinase highly homologous to Nm23 and Awd proteins involved in mammalian tumor metastasis and Drosophila development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1889;82(14):1199–1202.
Kimura N, Shimada N, Nomura K, Watanabe K. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding rat nucleoside diphosphate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(26):15744–15749.
Lacombe ML, Milon L, Munier A, Mehus JG, Lambeth DO. The human Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2000;32(3):247–258.
Ouatas T, Salerno M, Palmieri D, Steeg PS. Basic and translational advances in cancer metastasis: Nm23. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003;35(1):73–79.
Crawford RM, Treharne KJ, Best OG, Muimo R, Riemen CE, Mehta A. A novel physical and functional association between nucleoside diphosphate kinase A and AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 in liver and lung. Biochem J. 2005;392(pt 1):201–209.
Wang PH, Chang H, Ko JL, Lin LY. Nm23-H1 immunohistochemical expression in multisteps of cervical carcinogenesis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003;13(3):325–330.
Ravazoula P, Aletra C, Kourounis G, Ladopoulos I, Tzigounis V. Immunohistochemical analysis of nm23-H1 expression in human cervical lesions. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2000;21(5):51–52.
Branca M, Giorgi C, Ciotti M, et al. Down-regulated nucleoside diphosphate kinase nm23-H1 expression is unrelated to high-risk human papillomavirus but associated with progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and unfavourable prognosis in cervical cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59(10):1044–1051.
Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengelov H, Borregaard N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(14):10425–10432.
Bratt T. Lipocalins and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482(1–2):318–326.
Goetz DH, Willie ST, Armen RS, Bratt T, Borregaard N, Strong RK. Ligand preference inferred from the structure of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin. Biochemistry. 2000;39(8):1935–1941.
Wojnar P, Lechner M, Redl B. Antisense down-regulation of lipocalin-interacting membrane receptor expression inhibits cellular internalization of lipocalin-1 in human NT2 cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(18):16209–16215.
Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengeløv H, Borregaard N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. Biol Chem. 1993;268(14):10425–10432.
Xu S, Venge P. Lipocalins as biochemical markers of disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482(1–2):298–307.
Stoesz SP, Friedl A, Haag JD, Lindstrom MJ, Clark GM, Gould MN. Heterogeneous expression of the lipocalin NGAL in primary breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 1998;79(6):565–572.
Cho H, Kim JH. Lipocalin2 expressions correlate significantly with tumor differentiation in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009;57(5):513–521.
Syrjänen S, Naud P, Sarian L, et al. Up-regulation of lipocalin 2 is associated with high-risk human papillomavirus and grade of cervical lesion at baseline but does not predict outcomes of infections or incident cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134(1):50–59.
Choudhuri T, Murakami M, Kaul R, et al. Nm23-H1 can induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in B cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;9(12):1065–1078.
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, et al. DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(10):983–991.
Al-Haddad S, Zhang Z, Leygue E, et al. Psoriasin (S100A7) expression and invasive breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(6):2057–2066.
Handra-Luca A, Bilal H, Bertrand JC, Fouret P. Extra-cellular signal regulated ERK-1/ERK-2 pathway activation in human salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma: Association to aggressive tumor behavior and tumor cell proliferation. Am J Pathol. 2003;163(3):957–967.
Hsu CG, Lin LY, Ko JL, et al. High expression of human nonmetastatic clone 23 type 1 in cancer of uterine cervix and its association with poor cell differentiation and worse overall survival. J Surg Oncol. 2008;98(6):448–456.
Jung H, Seong HA, Ha H. Nm23-H1 tumor suprressor and its interacting partner STRAP activated p53 function. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(48):35293–35307.
Jung H, Seong HA, Ha H. Direct interaction between NM23-H1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is critical for alleviation of MIF-mediated suppression of p53 activity. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(47):32669–32679.
Bedelbaeva K, Snyder A, Gourevitch D, et al. Lack of p21 expression links cell cycle control and appendage regeneration in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(13):5845–5850.
Iannetti A, Pacifico F, Acquaviva R, et al. The neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), a NF-kappaB-regulated gene, is a survival factor for thyroid neoplastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):14058–14063.
Bolignano D, Donato V, Lacquaniti A, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human neoplasias: a new protein enters the scene. Cancer Lett. 2010;288(1):10–16.
Ak P, Levine AJ. p53 and NF-{kappa}B: different strategies for responding to stress lead to a functional antagonism. FASEB J. 2010;24(10):3643–3652.
Ogawara Y, Kishishita S, Obata T, et al. Akt enhances Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(24):21843–21850.
Bai D, Ueno L, Vogt PK. Akt-mediated regulation of NFkappaB and the essentialness of NFkappaB for the oncogenicity of PI3K and Akt. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(12):2863–2870.
Berger T, Cheung CC, Elia AJ, Mak TW. Disruption of the Lcn2 gene in mice suppresses primary mammary tumor formation but does not decrease lung metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(7):2995–3000.
Yang J, Bielenberg DR, Rodig SJ, et al. Lipocalin 2 promotes breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(10):3913–3918.
Kubben FJ, Sier CF, Hawinkels LJ, et al. Clinical evidence for a protective role of lipocalin-2 against MMP-9 autodegradation and the impact for gastric cancer. European J Cancer. 2007;43(12):1869–1876.
Moniaux N, Chakraborty S, Yalniz M, et al. Early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of pancreatic intraepithelial Neoplasia. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(9):1540–1547.
Niitsu N, Okamoto M, Honma Y, et al. Serum levels of the nm23-H1 protein and their clinical implication in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2003;17(5):987–990.
Niitsu N, Honma Y, Iijima K, et al. Clinical significance of nm23-H1 proteins expressed on cell surface in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia. 2003;17(1):196–202.
Okabe-Kado J, Kasukabe T, Honma Y, Kobayashi H, Maseki N, Kaneko Y. Extracellular NM23 protein promotes the growth and survival of primary cultured human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(10):1885–1894.
Rumjahn SM, Javed MA, Wong N, Law WE, Buxton IL. Purinergic regulation of angiogenesis by human breast carcinoma-secreted nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Br J Cancer. 2007;97(10):1372–1380.
Provatopoulou X, Gounaris A, Kalogeraj E, et al. Circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and their complex MMP-9/NGAL in breast cancer disease. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:390–396.
Lim R, Ahmed N, Borregaard N, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) an early-screening biomarker for ovarian cancer: NGAL is associated with epidermal growth factor-induced epithelio-mesenchymal transition. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(11):2426–2434.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, PH., Yang, SF., Tseng, CJ. et al. The Role of Lipocalin 2 and its Concernment With Human Nonmetastatic Clone 23 Type 1 and p53 in Carcinogenesis of Uterine Cervix. Reprod. Sci. 18, 447–455 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110395407
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110395407