Abstract
Objective
We aimed to design and test an ex-vivo human umbilical cord (HUC) perfusion model simulating a fetal inflammatory response (FIR) during intra-amniotic infection.
Study Design
A 2-chamber model was designed to accommodate 2 pieces of umbilical cord. Cord perfusion was performed with placental blood. Intra-amniotic exposure to infectious organisms was simulated by adding lipopolysaccharide to the artificial amniotic fluid (AAF) compartment. As a measure of inflammatory response, we used interleukin 8 (IL-8) concentration in AAF and plasma by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for statistical analysis.
Results
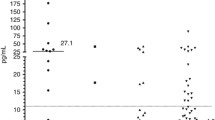
We established a stable physiological setup. Results revealed significantly elevated plasma IL-8 concentrations (n = 6, P < .05) in the blood compartment of umbilical cords exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Concentrations within AAF were not significantly elevated (n = 6, P = .3095).
Conclusion
Simulation of a FIR in an ex-vivo model of HUC perfusion under physiological conditions is possible. Further work is necessary to establish histological funisitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dammann O, O’Shea T. Cytokines and perinatal brain damage. Clin Perinatol. 2008;35(4):643–663, v.
Malaeb S, Dammann O. Fetal inflammatory response and brain injury in the preterm newborn. J Child Neurol. 2009;24(9): 1119–1126.
Romero R, Gomez R, Ghezzi F, et al. A fetal systemic inflammatory response is followed by the spontaneous onset of preterm parturition. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179(1):186–193.
Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(20): 1500–1507.
Gravett M, Witkin S, Haluska G, Edwards J, Cook M, Novy M. An experimental model for intraamniotic infection and preterm labor in rhesus monkeys. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171(6):1660–1667.
Gomez R, Romero R, Ghezzi F, Yoon BH, Mazor M, Berry SM. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179(1):194–202.
Dammann O, Leviton A. Role of the fetus in perinatal infection and neonatal brain damage. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2000;12(2): 99–104.
Kim CJ, Yoon BH, Romero R, et al. Umbilical arteritis and phlebitis mark different stages of the fetal inflammatory response. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185(2):496–500.
Liu Y, Shaw SK, Ma S, Yang L, Luscinskas FW, Parkos CA. Regulation of leukocyte transmigration: cell surface interactions and signaling events. J Immunol. 2004;172(1):7–13.
Koskinen K, Vainio PJ, Smith DJ, et al. Granulocyte transmigration through the endothelium is regulated by the oxidase activity of vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1). Blood. 2004;103(9):3388–3395.
De Dooy J, Colpaert C, Schuerwegh A, et al. Relationship between histologic chorioamnionitis and early inflammatory variables in blood, tracheal aspirates, and endotracheal colonization in preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 2003;54(1): 113–119.
Romero R, Chaiworapongsa T, Espinoza J. Micronutrients and intrauterine infection, preterm birth and the fetal inflammatory response syndrome. J Nutr. 2003;133(5 suppl 2): 1668S–1673S.
Dammann O, Leviton A. Inflammatory brain damage in preterm newborns—dry numbers, wet lab, and causal inferences. Early Hum Dev. 2004;79(1):1–15.
Lewalle JM, Castronovo V, Goffinet G, Foidart JM. Malignant cell attachment to endothelium of ex vivo perfused human umbilical vein. Modulation by platelets, plasma and fibronectin. Thromb Res. 1991;62(4):287–298.
Kolpakov V, D’Adamo MC, Salvatore L, et al. Neutrophil derived cathepsin G induces potentially thrombogenic changes in human endothelial cells: a scanning electron microscopy study in static and dynamic conditions. Thromb Haemost. 1994;72(1):140–145.
Gan L, Sjogren LS, Doroudi R, Jern S. A new computerized biomechanical perfusion model for ex vivo study of fluid mechanical forces in intact conduit vessels. J Vasc Res. 1999; 36(1):68–78.
Castronovo V, Parent B, Foidart JM, et al. Perfusion of human umbilical veins. A new approach to study the interactions of circulating malignant cells with vascular wall and their modulations. Invasion Metastasis. 1988;8(6):332–350.
Grosse J. Induktion von Proteinen der extrazellulären Matrix durch VEGF in der perfundierten Arterie der humanen Nabelschnur. Doctoral Thesis. Charité Berlin, Campus Benjamin Franklin. 2007.
Locatelli A, Andreani M, Ghidini A, et al. Amnioinfusion in preterm PROM: effects on amnion and cord histology. J Perinatol. 2008;28(2):97–101.
Kim CJ, Yoon BH, Kim M, Park JO, Cho SY, Chi JG. Histotopographic distribution of acute inflammation of the human umbilical cord. Pathol Int. 2001;51(11):861–865.
Ball M, Jobe A, Polglase G, et al. High and low body temperature during the initiation of ventilation for near-term lambs. Resuscitation. 2009;80(1):133–137.
Piper H, Alexander J, Shukla A, et al. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in pediatric patients during and after cardiac surgery. Pediatrics. 2006;118(3):1176–1184.
Yektaei-Karin E, Moshfegh A, Lundahl J, Berggren V, Hansson L, Marchini G. The stress of birth enhances in vitro spontaneous and IL-8-induced neutrophil chemotaxis in the human newborn. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007;18(8):643–651.
Cornblath M, Hawdon J, Williams A, et al. Controversies regarding definition of neonatal hypoglycemia: suggested operational thresholds. Pediatrics. 2000;105(5):1141–1145.
Ranjbaran H, Wang Y, Manes TD, et al. Heparin displaces interferon-gamma-inducible chemokines (IP-10, I-TAC, and Mig) sequestered in the vasculature and inhibits the transendothelial migration and arterial recruitment of T cells. Circulation. 2006;114(12):1293–1300.
Haraldsen G, Kvale D, Lien B, Farstad IN, Brandtzaeg P. Cytokine-regulated expression of E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in human microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1996;156(7):2558–2565.
D’Alquen D, Kramer BW, Seidenspinner S, et al. Activation of umbilical cord endothelial cells and fetal inflammatory response in preterm infants with chorioamnionitis and funisitis. Pediatr Res. 2005;57(2):263–269.
Byrne MF, Corcoran PA, Atherton JC, et al. Stimulation of adhesion molecule expression by Helicobacter pylori and increased neutrophil adhesion to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2002;532(3):411–414.
Lee TH, Avraham H, Lee SH, Avraham S. Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates neutrophil transendothelial migration via up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(12): 10445–10451.
Craven CM, Ward K. Fetal endothelial cells express vascular cell adhesion molecule in the setting of chorioamnionitis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2000;43(5):259–263.
Hsu C, Meaddough E, Aversa K, Copel J. The role of amniotic fluid L-selectin, GRO-alpha, and interleukin-8 in the pathogenesis of intraamniotic infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;178(3):428–432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S., Bueter, W., Acevedo, C. et al. Simulation of Intra-Amniotic Infection and the Fetal Inflammatory Response in a Novel Ex-vivo Human Umbilical Cord Perfusion Model. Reprod. Sci. 17, 426–433 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110361386
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110361386