Abstract
Kisspeptin, a placental polypeptide secreted throughout pregnancy, is suggested to play a role at parturition. Here we evaluated whether its placental mRNA expression and maternal/fetal plasma levels change at term and preterm delivery, and its effect on oxytocin secretion from placental explants.
Samples were collected from 40 women with singleton pregnancies who underwent elective cesarean section at term (TNL), term vaginal delivery (TD), and preterm vaginal delivery (PTD). Plasma Kisspeptin and oxytocin levels were assessed by ELISA; placental mRNA expression by Real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis.
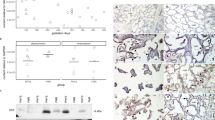
Placental expression was significantly (P < 0.0001) higher in PTD than TNL and TD and significantly (P < 0.001) higher in TD than TNL. Maternal/fetal plasma concentrations did not differ among the groups, and maternal were significantly higher than fetal levels (P < 0.05). In placental explants increasing doses of kisspeptin did not modify oxytocin secretion.
In conclusion, labor is associated with increased placental KiSS-1 expression without changes in maternal/fetal circulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Challis JRG, Matthews SG, Gibb W., Lye SJ Endocrine and paracrine regulation of birth at term and preterm. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:514–550.
Petraglia F., Florio P., Nappi C., Genazzani AR Peptide signaling in human placenta and membranes: autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine mechanisms. Endoc. Rev. 1996;17:156–186.
Lee JH, Miele ME, Hicks DJ, et al. KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:1731–1737.
Kotani M., Detheux M., Vandenbogaerde A., et al. The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:34631–34636.
Stafford LJ, Xia C., Ma W., Cai Y., Liu M. Identification and characterization of mouse metastasis-suppressor KiSS1 and its G-protein-coupled receptor. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5399–5404.
Harms JF, Welch DR, Miele ME KISS1 metastasis suppression and emergent pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20: 11–18.
Bilban M., Ghaffari-Tabrizi N., Hintermann E., et al. Kisspeptin-10, a KiSS-1/metastin-derived decapeptide, is a physiological invasion inhibitor of primary human trophoblasts. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1319–1328.
McMaster MT, Bass KE, Fisher SJ Human trophoblast invasion. Autocrine control and paracrine modulation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1994;734:122–131.
Murray MJ, Lessey BA Embryo implantation and tumor metastasis: common pathways of invasion and angiogenesis. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1999;17:275–290.
Horikoshi Y., Matsumoto H., Takatsu Y., et al. Dramatic elevation of plasma metastin concentrations in human pregnancy: metastin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:914–919.
Blanc WA Pathology of the placenta and cord in ascending and in haematogenous infection. Ciba Found Symp. 1979;77: 17–38.
Becker JA, Mirjolet JF, Bernard J., et al. Activation of GPR54 promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human tumor cells through a specific transcriptional program not shared by other Gq-coupled receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326:677–686.
Smith SC, Baker PN, Symonds EM Placental apoptosis in normal human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177:57–65.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408.
Hung T.-H, Skepper JN, Charnock-Jones DS, Burton GJ Hypoxia-reoxygenation: a potent inducer of apoptotic changes in the human placenta and possible etiological factor in preeclampsia. Circ Res. 2002;90:1274–1281.
Ashton SV, Whitley GS, Dash PR, et al. Uterine spiral artery remodeling involves endothelial apoptosis induced by extravillous trophoblasts through Fas/FasL interactions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:102–108.
Cindrova-Davies T., Yung HW, Johns J., et al. Oxidative stress, gene expression, and protein changes induced in the human placenta during labor. Am J Pathol. 2007;171:1168–1179.
Cindrova-Davies T., Spasic-Boskovic O., Jauniaux E., et al. NF-κB, p38 and stress activated protein kinase mitogenactivated protein kinase signaling pathways regulate proinflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in human placental explants in response to oxidative stress. Am J Pathol. 2007;170:1511–1520.
Ohtaki T., Shintani Y., Honda S., et al. Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2001;411:613–617.
Muir AI, Chamberlain L., Elshourbagy NA, et al. AXOR12, a novel human G protein-coupled receptor, activated by the peptide KiSS-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28969–28975.
Doualla-Bell F., Koromilas AE Induction of PG G/H synthase-2 in bovine myometrial cells by interferon-tau requires the activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. Endocrinology. 2001;142:5107–5115.
Karteris E., Hillhouse EW, Grammatopoulos D. Urocortin II is expressed in human pregnant myometrial cells and regulates myosin light chain phosphorylation: potential role of the type-2 corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor in the control of myometrial contractility. Endocrinology. 2004;145: 890–900.
Harms JF, Welch DR, Miele ME KISS1 metastasis suppression and emergent pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20: 11–18.
Roa J., Vigo E., Castellano JM, et al. Hypothalamic expression of KiSS-1 system and gonadotropin-releasing effects of kisspeptin in different reproductive states of the female Rat. Endocrinology. 2006;147:2864–2878.
Bischof P., Meisser A., Campana A. Paracrine and autocrine regulators of trophoblast invasion-a review. Placenta. 2000;21:S55–S60.
Xu P., Alfaidy N., Challis JR Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in human placenta and fetal membranes in relation to preterm and term labor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1353–1361.
Takino T., Koshikawa N., Miyamori H., et al. Cleavage of metastasis suppressor gene product KiSS-1 protein/metastin by matrix metalloproteinases. Oncogene. 2003;24;(22):4617–4626.
Weiss G. Endocrinology of parturition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:4421–4425.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torricelli, M., Galleri, L., Voltolini, C. et al. Changes of Placental Kiss-1 mRNA Expression and Maternal/Cord Kisspeptin Levels at Preterm Delivery. Reprod. Sci. 15, 779–784 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108322442
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108322442