Abstract
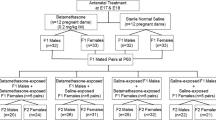
This study examined whether renin expression and secretion and plasma angiotensin II (Ang II) levels were altered in adult sheep exposed to antenatal betamethasone. Pregnant sheep received injections of 0.17 mg/kg betamethasone or vehicle, at 80 and 81 days of gestation, and offspring were studied at 6 and 18 months of age. At 6 months, plasma prorenin concentrations were significantly lower in betamethasone animals (4.63 ± 0.64 vs 7.09 ± 0.83 ng angiotensin I/mL/h, P < .01). The percentage of plasma active renin was significantly higher in the betamethasone group (31.93 ± 4.09% vs 18.57 ± 2.79%, P < .01). Plasma and renocortical renin levels were similar in both groups at 18 months, but plasma renin activity was lower than at 6 months. Ang II levels were suppressed by betamethasone. The data indicate that prenatal exposure to betamethasone alters processing and secretion of renin in offspring at 6 months, but that this difference is not apparent at 18 months.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liggins GC The role of cortisol in preparing the fetus for birth. Reprod Fertil Dev. 1994;6:141–150.
NIH Consensus Statement Online. The effect of antenatal steroids for fetal maturation on perinatal outcomes. 1994 Feb 28-Mar 2;12(2):1–24.
NIH Consensus Development Conference 1995. Effects of corticosteroid for fetal maturation on perinatal outcomes. JAMA. 1995;273:413–418.
Moritz KM, Boon WM, Wintour EM Glucocorticoid programming of adult disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2005;322:81–88.
Fowden A., Forhead AJ Endocrine mechanisms of intrauterine programming. Reproduction. 2004;127:515–526.
Jobe AH, Soll RF Choice and dose of corticosteroid for antenatal treatments. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;190:878–881.
Roberts D., Dalziel S. Antenatal corticosteroids for accelerating fetal lung maturation for women at risk of preterm birth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(3):CD004454.
Doyle L., Ford G., Davis N., Callanan C. Antenatal corticosteroid therapy and blood pressure at 14 years of age in preterm children. Clin Sci. 2000;98:137–142.
Miller S., Chai M., Loose J., et al. The effects of maternal betamethasone administration on the intrauterine growth-restricted fetus. Endocrinology. 2007;148:1288–1295.
Figueroa JP, Rose JC, Massmann GA, Zhang J., Acuna G. Alterations in fetal kidney development and elevations in arterial blood pressure in young adult sheep after clinical doses of antenatal glucocorticoids. Pediatr Res. 2005;58:510–515.
Dodic M., Abouantoun T., O’Connor A., Wintour EM, Moritz KM Programming effects of short prenatal exposure to dexamethasone in sheep. Hypertension. 2002;40:729–734.
Celsi G., Kistner A., Aizman R., et al. Prenatal dexamethasone causes oligonephronia, sodium retention, and higher blood pressure in the offspring. Pediatr Res. 1998;44:317–322.
Langley-Evans SC, Welham SJ, Jackson AA Fetal exposure to a maternal low protein diet impairs nephrogenesis and promotes hypertension in the rat. Life Sci. 1999;64:965–974.
Nwagwu MO, Cook A., Langley-Evans SC Evidence of progressive deterioration of renal function in rats exposed to a maternal low-protein diet in utero. Br J Nutr. 2000;83:79–85.
Gimonet V., Bussieres L., Medjebeur AA, Gasser B., Lelongt B., Laborde K. Nephrogenesis and angiotensin II receptor subtypes gene expression in the fetal lamb. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:F1062–F1069.
Dickinson H., Walker DW, Wintour EM, Moritz K. Maternal dexamethasone treatment at midgestation reduces nephron number and alters renal gene expression in the fetal spiny mouse. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292: R453–R461.
Wintour EM, Moritz KM, Johnson K., Ricardo S., Samuel CS, Dodic M. Reduced nephron number in adult sheep, hypertensive as a result of prenatal glucocorticoid treatment. J Physiol. 2003;549:929–935.
Wintour EM, Alcorn D., Butkus A., et al. Ontogeny of hormonal and excretory function of the meso- and metanephros in the ovine fetus. Kidney Int. 1996;50:1624–1633.
Woods LL, Ingelfinger JR, Nyengaard JR, Rasch R. Maternal protein restriction suppresses the newborn renin-angiotensin system and programs adult hypertension in rats. Pediatr Res. 2001;49:460–467.
Dodic M., May CN, Wintour EM, Coghlan JP An early prenatal exposure to excess glucocorticoid leads to hypertensive offspring in sheep. Clin Sci. 1998;94:149–155.
Figueroa JP, Acuna G., Rose JC, Massmann GA Maternal antenatal steroid administration at 0.55 gestation increases arterial blood pressure in young adult sheep offspring. J Soc Gynecol Invest. 2004;11:358A.
Vehaskari VM, Woods LL Prenatal programming of hypertension: lessons from experimental models. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:2545–2556.
Moritz KM, Johnson K., Douglas-Denton R., Wintour EM, Dodic M. Maternal glucocorticoid treatment programs alterations in the renin-angiotensin system of the ovine fetal kidney. Endocrinology. 2002;143:4455–4463.
Woods LL, Weeks DA Prenatal programming of adult blood pressure: role of maternal corticosteroids. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289:R955–R962.
Woods LL, Rasch R. Perinatal ANG II programs adult blood pressure, glomerular number, and renal function in rats. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:R1593–R1599.
Woods LL, Ingelfinger JR, Rasch R. Modest maternal protein restriction fails to program adult hypertension in female rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289: R1131–R1136.
Chen K., Carey LC, Valego NK, Liu J., Rose JC Thyroid hormone modulates renin and ANG II receptor expression in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289: R1006–R1014.
Rosnes JS, Valego N., Wang J., Zehnder T., Rose JC Active renin, prorenin, and renin gene expression after reduced renal perfusion pressure in term ovine fetuses. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:R141–R147.
Toffelmire EB, Slater K., Corvol P., Menard J., Schambelan, M. Response of plasma prorenin and active renin to chronic and acute alterations of renin secretion in normal humans. J Clin Invest. 1989;83:679–687.
Carbone GM, Sheikh AU, Rogers S., Brewer G., Rose JC Developmental changes in renin gene expression in ovine kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1993;264:R591–R596.
Velaphi SC The renin-angiotensin system in conscious newborn sheep: metabolic clearance rate and activity. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:681–686.
Fogo A., Yoshida Y., Yared A., Ichikawa I. Importance of angiogenic action of angiotensin II in the glomerular growth of maturing kidneys. Kidney Int. 1990;38:1068–1074.
Tufro-McReddie A., Johns DW, Geary KM, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor: role in renal growth and gene expression during normal development. Am J Physiol. 1994;266(6 Pt 2): F911–F918.
Gomez RA Role of angiotensin in renal vascular development. Kidney Int. 1998;67(Suppl):S12–S16.
Davidson D. Circulating vasoactive substances and hemodynamic adjustments at birth in lambs. J Appl Physiol. 1987;63: 676–684.
Assali NS Some aspects of fetal life in utero and the changes at birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967;97:324–331.
Wilson TA, Kaiser DL, Wright EM Jr, Peach MJ, Carey RM Ontogeny of blood pressure and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Sequential studies in the newborn lamb. Circ Res. 1981;49:416–423.
Robillard JE, Nakamura KT Neurohormonal regulation of renal function during development. Am J Physiol. 1988;254: F771–F779.
Hackenthal E., Paul M., Ganten D., Taugner R. Morphology physiology, and molecular biology of renin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1990;70:1067–1116.
Ganong WF Review of Medical Physiology. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Medical; 2005.
Kim SM, Chen L., Mizel D., Huang YG, Briggs JP, Schnermann J. Low plasma renin and reduced renin secretory responses to acute stimuli in conscious COX-2-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292: F415–F422.
Schnermann J. Juxtaglomerular cell complex in the regulation of renal salt excretion. Am J Physiol. 1998;274(2 Pt 2): R263–R279.
Peti-Peterdi J., Komlosi P., Fuson AL, et al. Luminal NaCl delivery regulates basolateral PGE2 release from macula densa cells. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:76–82.
Harris RC, Cheng HF The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: a paracrine system for the local control of renal function separate from the systemic axis. Exp Nephrol. 1996;4:2–7.
Ichihara A., Kobori H., Nishiyama A., Navar LG Renal renin-angiotensin system. Contrib Nephrol. 2004;143:117–130.
Nguyen G., Delarue F., Burckle C., Bouzhir L., Giller T., Sraer JD Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:1417–1427.
Catanzaro DF Physiological relevance of renin/prorenin binding and uptake. Hypertens Res. 2005;28:97–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by NIH grants HD17644 and HD47584.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kantorowicz, L., Valego, N.K., Tang, L. et al. Plasma and Renal Renin Concentrations in Adult Sheep After Prenatal Betamethasone Exposure. Reprod. Sci. 15, 831–838 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108318599
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108318599