Abstract
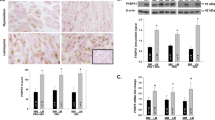
Progesterone plays a pivotal role in controlling uterine leiomyoma growth. The authors review studies they conducted to evaluate the comparative effects of asoprisnil on proliferation, apoptosis, and growth factor expression in cultured leiomyoma and normal myometrial cells. Treatment with asoprisnil decreased the proliferating cell nuclear antigen—positive rate and the number of viable cells and increased the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated 2′-deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphate nick end labeling— positive rate in cultured leiomyoma cells in a dose-dependent manner (P <.05). Similarly, asoprisnil decreased Bcl-2 expression and increased cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved poly(adenosine 5′-diphosphate-ribose) polymerase in leiomyoma cells but not in normal myometrial cells. Similarly, asoprisnil decreased epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor—I (IGF-I), and transforming growth factor (TGF) β mRNA and protein expression, as well as EGF receptor, IGF-IRα, and TGF RII protein expression in leiomyoma cells but not in cultured normal myometrial cells. These results suggest that asoprisnil selectively inhibits proliferation by downregulating the growth factors and their receptor expression and induces apoptosis in leiomyoma cells without affecting proliferation and apoptosis in normal myometrial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsuo H, Maruo, T, Samoto T. Increased expression of Bcl-2 protein in human uterine leiomyoma and its up-regulation by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:293–299.
Shimomura Y, Matsuo H, Samoto T, Maruo T. Up-regulation by progesterone of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and epidermal growth factor expression in human uterine leiomyoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:2192–2198.
Kurachi O, Matsuo H, Samoto T, Maruo T. Tumor necrosis factor-α expression in human uterine leiomyoma and its down-regulation by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:2275–2280.
Maruo T, Ohara N, Wang J, Matsuo H. Sex steroidal regulation of uterine leiomyoma growth and apoptosis. Hum Reprod Update. 2004;10:207–220.
Leonhardt SA, Edwards DP Mechanism of action of progesterone antagonists. Exp Biol Med. 2002;227:969–980.
Kastner P, Krust A, Turcotte B, et al.Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B. EMBO J. 1990;9:1603–1614.
Vegeto E, Shahbaz MM, Wen DX, Goldman ME, O’Malley BW, McDonnell DP. Human progesterone receptor A form is a cell- and promoter-specific repressor of human progesterone receptor B function. Mol Endocrinol. 1993;7:1244–1255.
Wen DX, Xu Y-F, Mais DE, Goldman ME, McDonnell DP The A and B isoforms of the human progesterone receptor operate through distinct signaling pathways within target cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:8356–8364.
Brandon DD, Bethea CL, Strawn EY, et al. Progesterone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein are overexpressed in human uterine leiomyomas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:78–85.
Viville B, Charnock-Jones DS, Sharkey AM, Wetzka B, Smith SK Distribution of the A and B forms of the progesterone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein in uterine leiomyomata and adjacent myometrium. Hum Reprod. 1997; 12:815–822.
Nisolle M, Gillerot S, Casanas-Roux F, Squifflet J, Berliere M, Donnez J. Immunohistochemical study of the proliferation index, oestrogen receptors and progesterone receptors A and B in leiomyomata and normal myometrium during the menstrual cycle and under gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:2844–2850.
Gao Z, Matsuo H, Wang Y, Nakago S, Maruo T. Up-regulation by IGF-I of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Bcl-2 protein expression in human uterine leiomyoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5593–5599.
Arici A, Sozen I. Expression, menstrual cycle-dependent activation, and bimodal mitogenic effect of transforming growth factor-β1 in human myometrium and leiomyoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:76–83.
Harrison-Woolrych ML, Charnock-Jones DS, Smith S. Quantification of messenger ribonucleic acid for epidermal growth factor in human myometrium and leiomyomata using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;78:1179–1184.
Van der Ven LTM, Roholl PJM, Gloudemans T, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), their receptors and IGF binding protein-3 in normal, benign and malignant smooth muscle tissues. Br J Cancer. 1997;75:1631–1640.
Boehm KD, Daimon M, Gorodeski IG, Sheean LA, Utian WH, ILan J. Expression of the insulin-like and platelet-derived growth factor genes in human uterine tissues. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990;27:93–101.
Giudice LC, Irwin JC, Dsupin BA, et al. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF), IGF binding protein (IGFBP), and IGF receptor gene expression and IGFBP synthesis in human uterine leiomyomata. Hum Reprod. 1993;8:1796–1806.
Englund K, Lindblom B, Carlström K, Gustavsson I, Sjöblom P, Blanck A. Gene expression and tissue concentrations of IGF-I in human myometrium and fibroids under different hormonal conditions. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:915–920.
Chandrasekhar Y, Hainer J, Osuamkpe C, Nagamani M. Insulin-like growth factor I and II binding in human myometrium and leiomyomas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:64–69.
Dixon D, He H, Haseman JK Immunohistological localization of growth factors and their receptors in uterine leiomyomas and matched myometrium. Environ Health Perspect. 2000; 108(suppl 5):795–802.
Dou Q, Zhao Y, Tarnuzzer RW, et al. Suppression of transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) and TGFβ receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein expression in leiomyomata in women receiving gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3222–3230.
Lee BS, Nowak RA Human leiomyoma smooth muscle cells show increased expression of transforming growth factor-β3 (TGFβ3) and altered responses to the antiproliferative effects of TGFβ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:913–920.
Chwalisz K, Perez MC, DeManno D, Winkel C, Schubert G, Elger W. Selective progesterone receptor modulator development and use in the treatment of leiomyomata and endometriosis [published correction appears in Endocr Rev. 2005;26:703]. Endocr Rev. 2005; 26:423–438.
DeManno D, Elger W, Garg R, et al. Asoprisnil (J867): a selective progesterone receptor modulator for gynecological therapy. Steroids. 2003;68:1019–1032.
Schubert G, Elger W, Kaufmann G, Schneider B, Reddersen G, Chwalisz K. Discovery, chemistry, and reproductive pharmacology of asoprisnil and related 11β-benzaldoxime substituted selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRMs). Semin Reprod Med. 2005;23:58–73.
Chwalisz K, Larsen L, Mattia-Goldberg C, Edmonds A, Elger W, Winkel CA A randomized, controlled trial of asoprisnil, a novel selective progesterone receptor modulator, in women with uterine leiomyomata. Fertil Steril. 2007;87: 1399–1412.
Chen W, Ohara N, Wang J, et al. A novel selective progesterone receptor modulator asoprisnil (J867) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in cultured human uterine leiomyoma cells in the absence of comparable effects on myometrial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1296–1304.
Wang J, Ohara N, Wang Z, et al. A novel selective progesterone receptor modulator asoprisnil (J867) down-regulates the expression of EGF, IGF-I,TGFβ3 and their receptors in cultured uterine leiomyoma cells. Hum Reprod. 2006;21:1869–1877.
Arici A, Sozen I. Transforming growth factor beta 3 is expressed at high levels in leiomyoma where it stimulates fibronectin expression and cell proliferation. Fertil Steril. 2000; 73:1006–1001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Submitted to the Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on the ECM of the Female Reproductive Tract (Maui, Hawaii, November 11–13, 2006)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohara, N., Morikawa, A., Chen, W. et al. Comparative Effects of SPRM Asoprisnil (J867) on Proliferation, Apoptosis, and the Expression of Growth Factors in Cultured Uterine Leiomyoma Cells and Normal Myometrial Cells. Reprod. Sci. 14 (Suppl 8), 20–27 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719107311464
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719107311464