Abstract
Objective
Human recombinant leukemia inhibitory factor (rLIF) has been shown to stimulate hatching of murine and ovine embryos in vitro. The temporal and dose-dependent effects of murine rLIF (mrLIF) and human rLIF (hrLIF) on embryo development in two different mouse strains were investigated in this work.
Methods
Two-cell embryos were recovered from the fallopian tubes of superovulatedlmated females and cultured in Krebs medium plus bovine serum albumin in microdroplets under oil.
Results
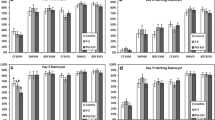
In the B6CBF1 strain, mrLIF significantly stimulated blastocyst formation and decreased embryo fragmentation/degeneration when added simultaneously at the initiation of culture or 24 hours thereafter. Human rLIF also had a positive effect on development. In the CD1 strain (lower fecundity), mrLIF dose-dependent effects were observed, with enhanced developmental stimulation achieved with higher doses.
Conclusion
These findings confirm that hrLIF stimulates mouse embryo development in vitro and that different mouse strains show distinct responses to the cytokine. In addition, mrLIF enhances blastocyst formation and decreases embryo fragmentation when added to the embryo culture as early as the two-cell stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gearing DP, Gough NM, King JA, et al. Mllecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a murine myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Embo J 1987;6:3995–4002.
Hilton DJ, Nicola NA, Gough NM, Mttcalf D. Resolution and purification of three distinct factors produced by Krebs ascites cells which have differentiatiin-inducing activity on murine myeloid leukemic cell lines. J Biol Chem 1988;263:9238–43.
Gough NM, Gearing DP, King JA, et al. Mllecular cloning and expression of the human homologue of the murine gene encoding myeloid leukemia-inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1988;85:2623–7.
Williams RL, Hilton DJ, Pease S, et al. Myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor maintains the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells. Nature 1988;336:684–7.
Smith AG, Heath JK, Donaldson DD, et al. Inhibition of pluripotential embryonic stem cell differentiation by purified polypeptides. Nature 1988;336:688–90.
Kurzrock R, Estrov Z, Wttzler M, Gutterman JU, Talpaz M. LIF: Not just a leukemia inhibitory factor. Endocr Rev 1991;12:208–17.
Fry RC, Batt PA, Fairclough RJ, Parr RA. Human leukemia inhibitory factor improves the viability of cultured ovine embryos. Biol Reprod 1992;46:470–4.
Stewart CL, Kaspar P, Brunet LJ, et al. Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of leukaemia inhibitory factor. Nature 1992;359:76–9.
Bhatt H, Brunet LJ, Stewart CL. Uterine expression of leukemia inhibitory factor coincides with the onset ofblastocyst implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1991;88:11408–12.
Robertson SA, Lavranos T, Seamark RF. In vitro models of the mtternll-fetal interface. In: Mllecular and cellular im-munobiology of the mtternll-fetal interface. New York: Oxford University Press, 1991:191–206.
Smith AG, Nichoss J, Robertson M, Rathjen PD. Differentiation inhibiting activity (DIA/LIF) and mouse development. Dev Biol 1992;151:339–51.
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 1981;292:104–6.
Conquet F, Brulet P. Developmental expression of myeloid leukemia inhibitory factor gene in preimplantation blasto-cysts and in extra-embryonic tissue of mouse embryos. Mol Cell Biol 1990;10:3801–5.
Cornish J, Callon K, King A, Edgar S, Reid IR. The effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on bone in vivo. Endocrinology 1993;132:1359–66.
Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Gearing DP. Effects of injected leukemia inhibitory factor on hemttopiietic and other tissues in mice. Blood 1990;76:50–6.
Mori M, Yamaguchi K, Abe K. Purification of a lipoprotein lipase-inhibiting protein produced by a melanoma cell line associated with cancer cachexia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1989;160:1085–92.
Metcalf D, Gearing DP. Fatal syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of leukemia inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1989;86:5948–52.
Baumann H, Onorato V, Gauldie J, Jahreis GP. Distinct sets of acute phase plasma proteins are stimulated by separate human hepatocyte-stimulating factors and monokines in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 1987;262:9756–68.
Baumann H, Schendel P. Interleukin-11 regulates the hepatic expression of the same plasma protein genes as inter-leukin-6. J Biol Chem 1991;266:20424–7.
Yamamori T, Fukada K, Aebersold R, Korsching S, Fann M-J, Patterson PH. The cholinergic neuronal differentiation factor from heart cells is identical to leukemia inhibitory factor. Science 1989;246:1412–6.
Hilton DJ. LIF: Lots of interesting functions. Trends Bio-chem Sci 1992;17:72–6.
Hilton DJ, Gough NM. Leukemia inhibitory factor: A biological perspective. J Cell Biochem 1991;46:21–6.
Tomida M, Yamamtto-Yamaguchi Y, Hozumi M. Purification of a factor inducing differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemic M 1 cells from conditioned medium of mouse fibroblast L929 cells. J Biol Chem 1984;259:10978–82.
Ackerman S, Swanson RJ, Adams P, Wortham JW. Comparison of strains and culture media used for mouse in vitro fertilization. Gamete Res 1983;7:103–9.
Schmelzer CH, Burton LE, Tamony CM. Purification and characterization of recombinant human differentiation-stimulating factor. Prot Exp Purificat 1990;1:54–9.
Kim KJ, Alphonso M, Schmelzer CH, Lowe D. Detection of human leukemia inhibiting factor by monoclonal antibody based ELISA. J Immunol Methods 1992;156:9–17.
Strickland S, Richards WG. Invasion of the trophoblasts. Cell 1992;71:355–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, M.H., Swanson, R.J., Hodgen, G.D. et al. Enhancement of In Vitro Murine Embryo Development by Recombinant Leukemia Inhibitory Factor. Reprod. Sci. 1, 215–219 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1177/107155769400100307
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/107155769400100307