Abstract
Objective
To determine the effect of endothelin-B (ETB)-selective receptor antagonism on pregnancy outcome in normal rats.
Methods
ETB receptor antagonist (A-192621; 5.0, 10.0, and 15.0 mg/kg per day) or vehicle was infused subcutaneously for 7 days by osmotic pump. Infusion was begun on day 14 of a 22-day gestation. Nonpregnant animals were treated similarly, and blood pressure (BP) responses and plasma antagonist levels were compared to those in pregnant animals. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) was measured on days 1, 4, and 7 of the infusion. Plasma ETB antagonist levels were measured on day 7 of infusion. On gestational day 21, fetal and placental weights and viability were evaluated at hysterotomy. Data were analyzed by analysis of variance and are presented at mean ± standard error of the mean.
Results
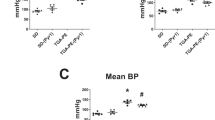
Fetal and placental weights were significantly lower at doses of 10 and 15 mg/kg per day of the ETB antagonist compared with vehicle-treated controls (P < .001); these effects were less severe at 15 than at 10 mg/kg per day despite a fourfold higher plasma level of antagonist. Mean arterial pressure was significantly higher at 10 and 15 mg/kg per day compared with controls, but only on infusion day 1 (P < .05). In contrast, MAPs for nonpregnant rats were elevated throughout the infusion at all doses of the ETB antagonist (P < .05).
Conclusions
ETB receptor antagonism inhibited fetal growth and increased maternal MAP in a dose-dependent manner, although the effect on BP was not sustained in pregnant animals. ETB receptor antagonism is detrimental to pregnancy outcome in the rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 1988;332:411–5.
Sokolovsky M, Ambar I, Galron R. A novel subtype of endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem 1992;267:20551–4.
Douglas SA, Beck GR Jr, Elliott JD, Ohlstein EH. Pharmacologic evidence for the presence of three functional endothelin receptor subtypes in rabbit saphenous vein. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1995;26(Suppl 3):S163–S8.
Fukuroda T, Fujikawa T, Ozaki S, Ishikawa K, Yano M, Nishikibe M. Clearance of circulating endothelin-1 by ETB receptors in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;199:1461–5.
Bremnes T, Paasche JD, Mehlum A, Sandberg C, Bremnes B, Attramadal H. Regulation and intracellular trafficking pathways of the endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem 2000;275:17596–604.
Wight E, Küng CF, Moreau P, Takase H, Lüscher TF. Chronic blockade of nitric oxide-synthase and endothelin receptors during pregnancy in the rat: Effect on pregnancy outcome. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1998;5:132–9.
Thaete LG, Neerhof MG, Silver RK. Differential effects of endothelin A and B receptor antagonism on fetal growth in normal and nitric oxide-deficient rats. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2001;8:18–23.
Thaete LG, Neerhof MG, Caplan MS. Endothelin receptor A antagonism prevents hypoxia-induced intrauterine growth restriction in the rat. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:73–6.
Thaete LG, Neerhof MG. Endothelin and blood pressure regulation in the female rat: Studies in normal pregnancy and with nitric oxide synthase inhibition-induced hypertension. Hypertens Pregnancy 2000;19:233–47.
Opgenorth TJ, Adler AL, Calzadilla SV, et al. Pharmacological characterization of A-127722: An orally active and highly potent ETA-selective receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996; 276:473–81.
von Geldern TW, Tasker AS, Sorensen BK, et al. Pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acids as endothelin antagonists. 4. Side chain conformational restriction leads to ETB selectivity. J Med Chem 1999;42:3668–78.
Adler AL, Wessale JL, Calzadilla SV, Dixon DB, Dayton BD, Opgenorth TJ. Characterization of hypertension induced by chronic ET-B receptor blockade in conscious rats. FASEB J 1999;13(Suppl):A782.
Gratton JP, Cournoyer G, Löffler BM, Sirois P, D’Orléans-Juste P. ETB receptor and nitric oxide synthase blockade induce BQ-123-sensitive pressor effects in the rabbit. Hypertension 1997;30: 1204–9.
Reinhart GA, Preusser LC, Burke SE, et al. Hypertension induced by chronic ET-B receptor blockade in conscious primates: Role of ET-A receptors. FASEB J 1999;13(Suppl):A782.
Lubarsky SL, Sibai BM, Ahokas RA. Evidence of a nonendothelial source of nitric oxide in the isolated perfused hindlimb vasculature of the pregnant rat. Hypertens Pregnancy 1999;18:11–21.
Danielson LA, Conrad KP. Prostaglandins maintain renal vasodilation and hyperfiltration during chronic nitric oxide synthase blockade in conscious pregnant rats. Circ Res 1996;79:1161–6.
Magness RR, Rosenfeld CR, Hassan A, Shaul PW. Endothelial vasodilator production by uterine and systemic arteries. I. Effects of ANG II on PGI2 and NO in pregnancy. Am J Physiol 1996;270(Heart Circ Physiol 39):H1914–H23.
Edwards DL, Arora CP, Bui DT, Castro LC. Long-term nitric oxide blockade in the pregnant rat: Effects on blood pressure and plasma levels of endothelin-1. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175: 484–8.
Neerhof MG, Thaete LG. Chronic NOS-inhibition-induced IUGR is associated with increased circulating endothelin-1 levels in the rat. Hypertens Pregnancy 1997;16:319.
Buhimschi I, Yallampalli C, Chwalisz K, Garfield RE. Preeclampsia-like conditions produced by nitric oxide inhibition: Effects of L-arginine, D-arginine and steroid hormones. Hum Reprod 1995; 10:2723–30.
Kimura A, Ohmichi M, Takeda T, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is involved in endothelin-1-induced rat puerperal uterine contraction. Endocrinol 1999;140:722–31.
Shigematsu K, Nakatani A, Kawai K, et al. Two subtypes of endothelin receptors and endothelin peptides are expressed in differential cell types of the rat placenta: In vitro receptor autoradiographic and in situ hybridization studies. Endocrinology 1996;137:738–48.
Wight E, Küng CF, Moreau P, Takase H, Lüscher TF. Chronic blockade of nitric oxide synthase and endothelin receptors during pregnancy in the rat: Effect on reactivity of the uterine artery in vitro. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1998;5:288–95.
Greenberg SG, Paul RJ, Yang DS, Clark KE. Vascular refractoriness to endothelin in pregnant ewes is not observed in vitro. J Soc Gynecol Investig 1995;2:190.
McElvy SS, Hirth JA, Mershon JL, Clark KE. Effects of pregnancy on the expression of big preproendothelin (BPP), endothelin converting enzyme 1 (ECE1), and endothelin A receptors (ETA) in uterine arteries of sheep. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2000; 7:251A.
Moreland S, McMullen DM, Delaney CL, Lee VG, Hunt JT. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;184:100–6.
McMurdo L, Corder R, Thiemermann C, Vane JR. Incomplete inhibition of the pressor effects of endothelin-1 and related peptides in the anaesthetized rat with BQ–123 provides evidence for more than one vasoconstrictor receptor. Br J Pharmacol 1993;108:557–61.
Sand AE, Östlund E, Andersson E, Fried G. Endothelin-induced contractions in placental arteries is mediated by both ETA- and ETB-receptors. Acta Physiol Scand 1998;163:227–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by NIH grant HD34777 and by March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation grant 6-FY99-0649. The ETB receptor antagonist was generously provided by Abbott Laboratories (Abbott Park, IL).
Plasma samples were assayed for A-192621 by Ms. Bach Nguyen and Dr. Kennan Marsh, Dept. 4EK, Pharmaceutical Products Division, Abbott Laboratories. We are grateful to Ms. Xiaopei Gao at Evanston Northwestern Healthcare for her technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, K.M., Neerhof, M.G., Wessale, J.L. et al. Influence of ETB Receptor Antagonism on Pregnancy Outcome in Rats. Reprod. Sci. 8, 239–244 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1177/107155760100800409
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/107155760100800409