Abstract
Objective
Asphyxia is one of the main causes of perinatal brain damage that can result in psychomotor, deficits during later development, Recently lubeluzole, a new glutamate antagonist, was shown to improve clinical outcome considerably without any safety concerns in adults who had acute ischemic stroke. However, our preliminary experiments showed transient alterations in heart as well as arterial hypertension after intravenous application of this compound of in fetal sheep. The aim of the present study was to examine in detail whether lubeluzole affects circulatory responses to acute asphyxia in fetal sheep near term.
Methods
Eleven fetal sheep were chronically instrumented at a mean gestational age of 133 ± 2 days (term is at 147 days). The fetuses in the study group (n = 6) received three bolus injections of lubeluzole at 30-minute intervals (3 × 0.11 mg/kg estimated body weight), and five controls received solvent. Organ blood flows and physiololgic variables were measured before, during, and after arrest of uterine blood flow for 2 minutes (ie, at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 30 minutes).
Results
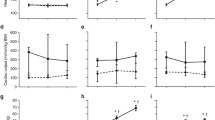
Before asphxia, distribution of combined ventricular output and physiologic variables in fetuses from the control group were in the normal ragne for chronically prepared fetal sheep near term. During acute asphyxia there was a redistribution of cardiac output toward the central organs accompanied by pronounced bradycardia and progressive increase in arterial blood pressure. There were nearly no differences between groups in the time course of physioloigic and cardiovascular variables measured before, during, and after acute intrauterine asphyxia.
Conclusion
Lubeluzole did not affect circulatory responses to acute asphyxia in fetal sheep near term.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volpe JJ. Neurology of the newborn. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1995.
Berger R, Garnier Y. Pathophysiology of perinatal brain damage. Brain Res Rev 1999;32:107–34.
De Ryck M, Keersmaekers R, Duytschaever H, et al. Lubeluzole protects sensorimotor function and reduces infarct size in a photochemical stroke model in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996;279:748–58.
Haseldonckx M, Van Rempts J, Van de Ven M, Wouters L, Borgers M. Protection with lubeluzole against delayed ischemic brain damage in rats. A quantitative histopathologic study. Stroke 1997;28:428–32.
Culmsee C, Junker V, Wolz P, Semkova I, Krieglstein J. Lubeluzole protects hippocampal neurons from excitatoxicity in vitro and reduces brain damage caused by ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 1998;342:193–202.
Wiedemann M, Hanke W. Lubeluzole shows neuroprotective effects in an "in-vitro"-model for neuronal lesions in the chicken retina. Brain Res 1998;842:243–8.
DeRyck M, Verhoye M, Van der Linden AM. Diffusion-weighted MRI of infarct growth in a rat photochemical stroke model: Effect of lubeluzole. Neuropharmacology 2000;4:691–702.
Grotta J. Lubeluzole treatment of acute ischemic stroke. The US and Canadian Lubeluzole Ischemic Stroke Study Group. Stroke 1997;28:2338–46.
Maiese K, Vincent AM. Membrane asymmetry and DNA deg- radation: Functionally distinct determinants of neuronal programmed cell death. J Neurosci Res 2000;59:568–80.
Maiese K, Vincent AM. Critical temporal modulation of neuronal programmed cell injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2000;20:383–400.
Marrannes R, De Prins E, Clincke G. Influence of lubeluzole on voltage-sensitive Ca++ channels in isolated rat neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998;286:201–14.
Hacke W, Lees KR, Timmerhuis T, et al. Cardiovascular safety of lubeluzole (Prosynap®) in patients with ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 1998;8:247–54.
Le Grand B, Dordain-Maffre M, John GW. Lubeluzole-induced prolongation of cardiac action potential in rabbit Purkinje fibres. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2000;14:159–62.
Herron J, Lee P, Pesco-Koplowitz L, Gajjar D, Soo YW, Woestenborghs R. Determination of the dose proportionally of single intravenous doses (5, 10, and 15 mg) of lubeluzole in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther 1998;20:682–90.
Jensen A, Hohmann M, Künzel W. Dynamic changes in organ blood flow and oxygen consumption during acute asphyxia in fetal sheep. J Dev Physiol 1987;9:543–59.
Jensen A, Lang U. Foetal circulatory responses to arrest of uterine blood flow in sheep: Effects of chemical sympathectomy. J Dev Physiol 1992;17:75–86.
Jensen A, Hanson MA. Circulatory responses to acute asphyxia in intact and chermodenervated fetal sheep near term. Reprod Fertil Dev 1995;7:1351–9.
Rudolph AM, Heymann MA. Circulation of the fetus in utero: Methods for studying distribution of blood flow, cardiac output and organ blood flow. Circ Res 1967;21:163–84.
Heymann MA, Payne BD, Hoffman JIE, Rudolph AM. Blood flow measurements with radionuclide-labeled particles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1977;20:55–79.
Jensen A, Roman C, Rudolph AM. Effects of reducing uterine blood flow on fetal blood flow distribution and oxygen delivery. J Dev Physiol 1991;15:309–23.
Jensen A, Berger R. Fetal circulatory responses to oxygen lack. J Dev Physiol 1991;16:181–207.
Cohn HE, Sacks EJ, Heymann MA, Rudolph AM. Cardiovascular responses to hypoxemia and acidemia in fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1974;120:817–24.
Itskovitz J, LaGamma EF, Rudolph AM. Effects of cord compression on fetal blood flow distribution and 02 delivery. Am J Physiol 1987;252:H100–9.
De Keyser J, van de Velde V, Schellens RLLA, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of the neuroprotective drug lubeluzole in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Ther 1997;19:1340–51.
Grotta J. Lubeluzole treatment of acute ischemic stroke. The US and Canadian Lubeluzole Ischemic Stroke Study Group. Stroke 1997;28:2338–46.
Diener HC. Multinational randomised controlled trial of lubeluzole in acute ischaemic stroke. European and Australian Lubeluzole Ischaemic Stroke Study Group. Cerebrovasc Dis 1998: 172–81.
Kroppenstedt SN, Stroop R, Kern M, Thomale UW, Schneider GH, Unterberg AW. Lubeluzole following traumatic brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 16:629–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The excellent technical assistance of Otmar Adam, Dorothea Ehler and Monika Nickel is gratefully acknowledged.
This work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and by Janssen Pharmaceutica (Beerse, Belgium).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, R., Garnier, Y., Löbbert, T. et al. Circulatory Responses to Acute Asphyxia Are Not Affected by the Glutamate Antagonist Lubeluzole in Fetal Sheep Near Term. Reprod. Sci. 8, 143–148 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1177/107155760100800304
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/107155760100800304